Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile 29-05-2023 - Arhive
Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Petrochemicals – Ny6 – CPL – Ny66

Credit : Polyestertime
Crude Oil Prices Trend
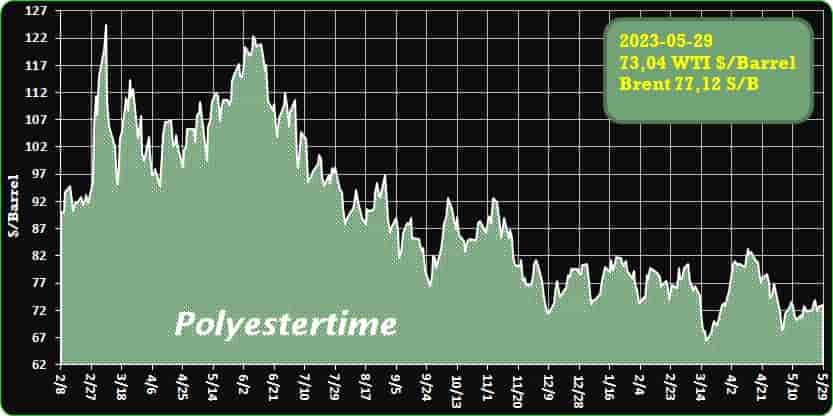
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
-Dow and New Energy Blue have joined forces to collaborate on the development of renewable plastic materials derived from corn residue
This groundbreaking partnership, the first of its kind in North America, aims to produce bio-based ethylene for Dow’s assets on the U.S. Gulf Coast. By harnessing the potential of renewable agricultural residues, New Energy Blue will create bio-based ethylene, which Dow plans to purchase and utilize in the production of recyclable applications across various fast-growing markets such as transportation, footwear, and packaging.
This agreement marks Dow’s first foray into utilizing agriculture residues for plastic production in North America. In this partnership with New Energy Blue, which comprises experts experienced in bio-conversion ventures, Dow seeks to unlock the value of agricultural residues. Karen S. Carter, Dow’s President of Packaging & Specialty Products, emphasizes that by committing to purchase bio-based ethylene, Dow supports waste recycling innovation, meets the demand for bio-based plastics from customers, and strengthens the ecosystem for diverse and renewable solutions.
Under the agreement, Dow is providing support for the design of a new facility called New Energy Freedom, located in Mason City, Iowa. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
This facility is expected to process 275KT (kilotonnes) of corn stover annually and produce commercial quantities of second-generation ethanol and clean lignin. Around half of the ethanol will be converted into bio-based ethylene feedstock for Dow’s products. Additionally, Dow has secured similar commercial supply options for New Energy Blue’s four future projects, enabling scalability and supporting farmers by creating a reliable market for agricultural residues. Together, these five projects are anticipated to displace over one million tons of greenhouse gas emissions annually, contributing to a reduction in Dow’s reliance on fossil fuels and subsequent emissions.
This collaboration aligns with Dow’s strategy to develop material ecosystems that prioritize waste transformation into circular products. By partnering with leading experts and employing cutting-edge technologies for waste collection, reuse, and recycling, Dow aims to facilitate the scaling of global material ecosystems. Manav Lahoti, Dow’s Global Sustainability Director for Olefins, Aromatics & Alternatives, expresses enthusiasm for the potential of agriculture-based plastics to help the company achieve its waste transformation and net-zero CO2 goals, as well as increase the use of renewable resources. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Thomas Corle, CEO of New Energy Blue, highlights the significance of this collaboration in redefining raw material sourcing for products, not only in Iowa but throughout the United States and globally. The partnership aims to reduce carbon emissions from farming, support rural communities, and enable the production of sustainable, low-carbon plastics made from a variety of biomass sources. By utilizing renewable yet recyclable resources, Dow aims to transform them into everyday consumer products. Furthermore, the agreement will help reduce carbon emissions from agriculture by repurposing carbon that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere during the decomposition of corn stover.
Dow intends to ensure the certification of its bio-based feedstocks from New Energy Blue through ISCC Plus, an international sustainability certification program that emphasizes traceability within the supply chain. This certification would enable Dow’s customers to account for bio-based materials in their own supply chains. By opening a dependable new market, Dow’s supply agreement with New Energy Blue would also create additional economic value for farmers. New Energy Blue’s upcoming processing facility in Iowa will directly source corn stover from local farmers each year, providing them with an additional income stream while employing farming practices that enhance carbon retention in the soil. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession

-MTMA Urges Collaboration between Malaysian and Chinese Textile Manufacturers
In a recent statement, the chairman of the Malaysian Textile Manufacturers Association (MTMA), Datuk Seri Tan Thian Poh, has called upon textile manufacturers in Malaysia to join forces with their Chinese counterparts to embrace digitalization and automation in their production processes. The aim is to enhance productivity and increase revenue within the industry.
Poh emphasized the need for Malaysia to adopt a system where manufacturers compensate employees based on their productivity, taking inspiration from the Chinese model. He highlighted the importance of addressing productivity levels alongside calls to raise the minimum wage, as low productivity can adversely affect competitiveness.
Poh acknowledged that the domestic textile industry has historically been viewed as labor-intensive and stagnant. However, he highlighted that significant progress has been made towards automation in recent times. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
One of the key challenges faced by Malaysia is the availability of labor, rather than the cost of labor. Poh noted that relying on the government’s continuous supply of foreign workers is not a sustainable long-term solution for local players. Therefore, he urged the industry to focus on branding and retailing, particularly in the online retail sector, to maintain competitiveness.
Speaking at the China Textile City Overseas Mini Fair, Poh emphasized the potential benefits of collaboration between Malaysian and Chinese textile manufacturers. By embracing digitalization and automation and adopting a productivity-focused approach, the industry can unlock new opportunities for growth and success.

-Headline: Germany Enters Recession as Berlin’s GDP Shrinks
Germany is facing a technical recession as new data from the Federal Statistical Office (Destatis) reveals a decline in the country’s GDP during the first quarter of 2023. Berlin, in particular, experienced a 0.3% drop in GDP from January to March compared to the previous quarter, which had already recorded a -0.5% decrease in GDP from October to December 2022. The overall growth lost since the beginning of summer 2022 to the present can be attributed to factors such as high inflation, elevated energy prices, disruptions in global supply chains, the Russo-Ukrainian war, and a slowdown in international trade, all of which have had significant macroeconomic effects.
Germany, as an economy focused on industrial transformation and trade, has been particularly affected. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Producers faced uncertainties due to high energy prices and inflation, while the domestic market was strongly influenced by the challenges faced by Olaf Scholz’s government coalition in managing ongoing bills. The decline in domestic consumption has had a severe impact on the German economy, with a decrease of 1.2% compared to the previous quarter. Citizens, intimidated by the high cost of living and 7.2% inflation, exhibited a limited propensity to spend. The country’s export sector, which is typically a driving force, only experienced a modest increase of 0.4%. The Financial Times reports that the construction industry has shown a positive rebound, with a 3.9% increase in value compared to the previous quarter, primarily attributed to a mild winter starting in January. However, industrial production remains 0.5% lower than pre-war levels in Ukraine, although it grew by 2% over the quarter. Furthermore, Germany’s GDP has fallen below pre-Covid levels, while most of Europe is recovering.
While some economists believe that a decrease in inflation and an acceleration in wage growth, combined with a robust labor market, could lead to tepid growth for the remainder of the year, the risk of a recession caused by stagnant demand persists. This situation could potentially create a contagion effect throughout the rest of Europe. A decrease in Germany’s production would result in reduced imports of semi-finished products from other European countries. As a result, there is a growing temptation for Germany to revert to austerity measures. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Christian Lindner, a prominent figure in finance known for his conservative stance, predicts a decline of 30 billion euros in tax revenues over the next decade due to the consequences of the Russo-Ukrainian war, including its impact on energy prices and domestic investments. The cost of servicing the debt, incurred as a result of pandemic-related spending, has risen from 4 to 34 billion euros since before the Covid crisis. Berlin is now faced with the temptation to implement severe public spending cuts, reminiscent of the austerity measures seen in 2014 under Angela Merkel’s leadership. The liberal Free Democratic Party, led by Lindner, advocates for reduced government spending to counter the fiscal shock. Meanwhile, the Green Party, represented by Deputy Prime Minister Robert Habeck, focuses on cutting spending related to fossil fuels to expedite the transition to renewable energy. The Social Democratic Party (SPD) remains committed to maintaining existing public welfare programs and is opposed to significant spending cuts. The budget dispute is expected to be challenging, and even Habeck, who is not known for advocating austerity, has proposed cutting at least 22 billion euros in public spending this year.
Criticism has also been directed at Scholz for his use of special and extra-budget funds for emergency programs, similar to the public loan guarantees implemented during the Covid crisis. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
These “shadow budgets,” including a controversial 200 billion euro fund to lower gas and energy prices for citizens and companies

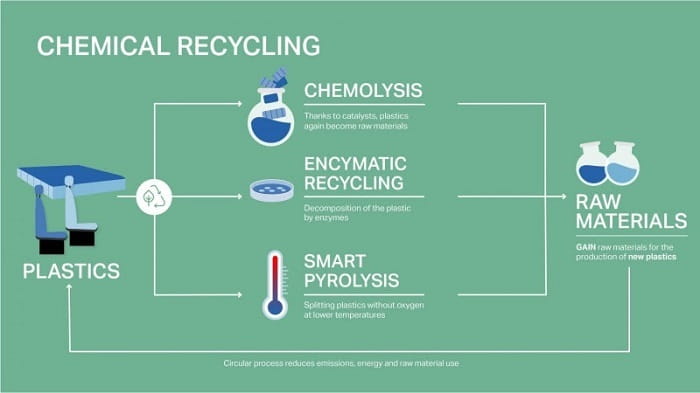
-Innovative Approaches to Address Plastic Waste through Recycling
Ahead of the upcoming UN conference dedicated to tackling plastic pollution, Covestro is emphasizing the importance of advancing innovative recycling technologies to increase the currently low rates of plastic recycling. Covestro has already achieved significant success through the development of its groundbreaking chemical recycling method. Moreover, the company is planning to collaborate with six other chemical groups to establish a global research center for processing plastic waste.
From May 29 to June 2, an international negotiation round, known as ‘INC-2,’ will take place in Paris, with the aim of drafting a comprehensive global agreement to combat plastic waste pollution. The agreement is expected to be finalized by the end of 2024. The international community initiated this process during the United Nations Environment Assembly in spring 2022. According to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), approximately 22 million tons of plastic waste, including microplastics, enter the oceans and the environment annually.
Without effective countermeasures, this annual amount could double by 2060.
Dr. Markus Steilemann, CEO of Covestro, emphasizes the urgent need to address the rising consumption of resources and the growing waste crisis, which have adverse consequences for the environment and climate. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Dr. Steilemann states that it is imperative to implement countermeasures, change consumption habits, and transform production patterns. He further emphasizes the importance of transitioning to a circular economy and highlights the critical role of recycling, along with the production of durable and resource-efficient products. Covestro is committed to playing a central role in achieving these goals.
Establishment of a Collaborative Research Center for Plastic Waste Processing
At present, the global recycling rate for plastic waste stands at a mere nine percent. However, a study suggests that with increased industrial-scale recycling, nearly 60 percent of plastic production could be met through recycled materials by 2050, resulting in a 30 percent reduction in petroleum consumption. To accelerate the development of low carbon emitting technologies for chemical production, including plastic waste processing, the World Economic Forum has initiated the Low Carbon Emitting Technologies initiative, promoting global collaboration. As part of this initiative, seven international chemical companies, including Covestro, have signed a collaborative agreement to establish a research and development center in partnership with the Dutch research institute TNO. The initial focus of their work will be on sorting, cleaning, and preparing plastic waste for subsequent recycling technologies.
Addressing the Challenge of Non-Recyclable Plastics
One significant challenge in plastic recycling is the presence of plastics that cannot be effectively recycled or have limited recycling options. Covestro is actively pushing for the development of chemical recycling as an additional solution. This process involves breaking down used plastics into their chemical components, enabling the production of new materials from these molecules. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Breakthrough in Recycling Mattress Foam
Covestro has achieved a technological breakthrough in the chemical recycling of soft foam used in mattresses. Currently, around 40 million mattresses in the European Union alone end up in waste incineration plants or landfills each year. Through the new ‘Evocycle CQ-Mattress’ process, the two central foam components can now be effectively recycled. Covestro is further developing this process at its Leverkusen site in Germany through a pilot plant, with the aim of eventual industrial implementation.
Circular Foam Research Project
Covestro is coordinating a Europe-wide research project called CIRCULAR FOAM, initiated in 2021, which focuses on the chemical recycling of rigid foam used for building insulation and refrigeration appliances. This collaborative effort involves 22 partners from nine countries. If the material cycle can be closed successfully, it is estimated that around one million metric tons of waste and three million metric tons of CO2 emissions per year could be saved in the European Union by 2040. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Enhancing Recycling of Food Packaging
In May 2023, Covestro introduced a new development to improve the recycling of food packaging made of paper and cardboard. The company has developed a special coating material that can be recycled alongside the packaging, unlike conventional coatings. The coating material itself is produced in line with the principles of circularity, utilizing raw materials that are partially derived from plants.
Through these innovative recycling initiatives, Covestro aims to contribute significantly to combating plastic waste and promoting a more sustainable approach to resource consumption and production.
-Asia gets most of Russian dark fuels after EU embargo
Asian countries remain the lead destinations for Russian vacuum gasoil (VGO) and fuel oil exports after the European Union’s embargo, traders said and Refinitiv data showed, said Hydrocarbonprocessing. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
“Pretty stable flows for refining and bunkering”, one trader said. According to Refinitiv data, China and India, which became main importers of embargoed Russian oil, were respectively accounting for about 2.6 million tons and 2.1 million tons of exports of dirty oil products from Russian ports since the start of the year, buying fuel oil and VGO for further processing at their refineries.
Singapore and Malaysia also hit the top five destinations for fuel oil and VGO of Russian origin with almost 3.5 million tons in total, while Turkey and Saudi Arabia received about 1.6 million tons each, Refinitiv data showed. Fujairah, key transit and blending hub for oil products in the United Arab Emirates, accepted almost 1.4 million tons of fuel oil and VGO since the start of this year.
In February 2023, the EU introduced a full ban on supplies of Russian oil products, but Russian fuel oil and VGO had already been diverted elsewhere as restrictions were applied partially in August 2022. Asia and the Middle East and also ship-to-ship (STS) loadings became the most popular ways to bypass sanctions since then.
STS loadings near the Greek port of Kalamata have attracted from Russia the biggest dirty oil products volumes, which surged to 8 million tons in 2022 and totaled almost 2.7 million tons from the beginning of 2023. Traders said those cargoes mostly end up in Asia. “(The main destinations were) China, Singapore and some cargoes went to India,” one trader added. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Russia also exports small amounts of dirty oil products to Africa, mostly to Senegal, which has bought about 114,000 tons of Russian fuel oil this month, according to Refinitiv.
We remind, Czech Republic can cover its oil needs through shipments via the Transalpine Pipeline (TAL) pipeline from 2025, Prime Minister Petr Fiala said on Tuesday after the country signed a deal to boost capacity along the link.
The Czech government is looking to eliminate all dependence on Russian oil in the coming years, and thus end its exemptions from a European Union ban on imports from Moscow last year. Czech refineries are owned by Polish state-controlled refiner PKN Orlen, which said in April it terminated a contract for Russian oil supplies for its Polish refineries.

-What is Recycling Equipment?
Recycling has become indispensable to our efforts to protect the environment and preserve natural resources. However, recycling involves more than simply tossing materials in bins – special equipment is essential in ensuring efficient recycling processes for various materials. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Waste management equipment consists of machinery and tools designed to transform waste into valuable resources, from sorting to shredding. Recycling machines ensure maximum resource recovery while mitigating environmental impact by automating and streamlining this process.
Recycling plays an integral role in sustainable waste management. Together we will explore this field, its various forms, and functions while emphasizing its role in creating an eco-friendlier future.
Types of Waste Management Equipment
- Sorting Equipment
Sorting equipment is crucial to accurately sorting materials according to composition and properties, using sophisticated technologies such as optical sorters and magnetic separators to efficiently recycle plastics, metals, glass, paper, and more.
- Shredding Equipment
Shredders are machines designed to reduce the size and volume of various materials. They can reduce bulky objects like cardboard boxes, plastic bottles, or aluminum cans into more manageable chunks for transportation and storage or allow further processing into new products. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
- Compacting Equipment
Compressors and balers make recycling materials easier to handle and transport by compacting their volume for storage or transportation purposes.
- Crushing Equipment
Crushing equipment reduces large objects or materials into smaller pieces for recycling, simplifying disposal while increasing separation, sorting, and recycling operations. Crushers specialize in material separation, including concrete, asphalt, demolition debris, and any other waste material that needs sorting or separation procedures.
Recycling Equipment Benefits
- Recycling Enhances Efficiency
Waste management equipment streamlines various recycling processes to increase their efficiencies and performance, improving performance. These machines can sort, shred, compact, crush and wash materials for increased outputs and better resource recovery rates while decreasing manual labor and time. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
- Cost Savings
Businesses investing in recycling can enjoy long-term cost savings through automated processes that replace manual labor with automatic methods, thus cutting labor costs. Furthermore, effective recycling maximizes resource utilization while minimizing waste disposal fees – recovered materials may then be sold or reused to generate extra revenues for an organization.
- Environmental Conservation
Recycling plays an integral part in environmental sustainability. Recycling machinery helps alleviate landfill strain and improve aesthetics by converting waste from landfills into valuable commodities.
- Improved Product Quality
Eco-friendly processing equipment such as washing machines can significantly increase the product quality of recycled materials by removing impurities such as dirt, labels, and adhesives to meet the required standards for reused material production – leading to high-quality recycled products suitable for various applications and opening up market opportunities. Renewable plastic – Chinese Textile Germany GDP Recession
Overall, recycling machinery is integral in optimizing the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling processes. Businesses investing in such machinery can expect improved productivity, cost savings, and environmental sustainability benefits, as well as conserve natural resources by reducing landfill waste volumes while mitigating pollution risks.
General Kinematics offers an expansive selection of recycling equipment with detailed descriptions of functions and benefits – an invaluable tool in creating a more sustainable future by increasing resource recovery rates and developing circular economies.

