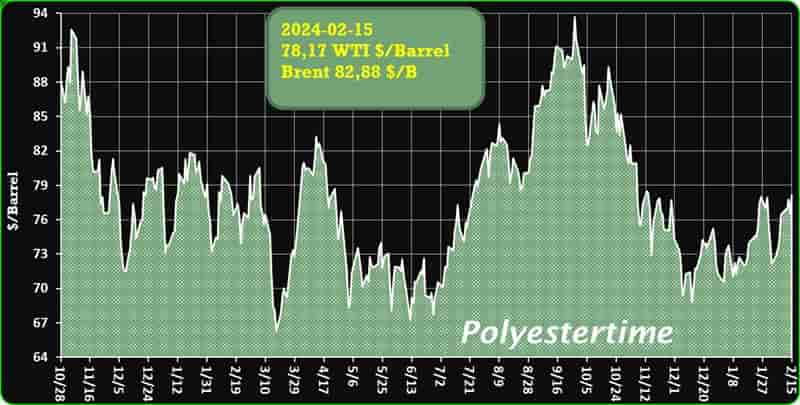
Closed-loop recycling – Researchers develop eco-friendly ‘magnet’ to battle microplastics 15-02-2024 - Arhive
Hydrogen emerges as a potential savior amidst the looming climate crisis, albeit with lingering uncertainties
A recent expedition in north-eastern France, initially in pursuit of methane, unveiled a colossal reservoir of natural hydrogen. While this discovery holds promise, skepticism persists.
In France, researchers from the University of Lorraine unearthed a staggering 250 million-ton cache of natural hydrogen, sufficient to satiate global demand for two years. The find, nestled 1000 meters below ground, underscores hydrogen’s prospective role in combating climate change and securing our future. Closed-loop recycling
Naturally occurring within the Earth’s crust, hydrogen is perpetually generated through chemical reactions, primarily tied to ferrous mineral oxidation. This perpetual genesis designates it as a sustainable energy font, resonating with the assertions of Isabelle Moretti, a researcher at the University of Pau and Pays de l’Adour.
Hydrogen’s allure lies in its versatility. It serves as an exemplary fuel, poised to mitigate the intermittent nature of renewables like solar and wind. Moreover, it doubles as an energy reservoir, buffering surpluses for subsequent release, thereby ensuring uninterrupted power supply. Closed-loop recycling
Beyond its utility, hydrogen boasts several advantages. Its adaptability in gas and liquid fuel production, coupled with existing infrastructure compatibility, renders it an appealing prospect. Notably, its emission-free combustion and sole byproduct of water amplify its eco-credentials.
Despite its promise, apprehensions persist. Hydrogen’s combustible nature underscores safety concerns, necessitating stringent storage protocols. Moreover, its production often hinges on non-renewable energy sources, challenging its environmental merit.
Nevertheless, ongoing research endeavors strive to surmount these hurdles, striving for a future where hydrogen stands not only as a climate ally but as a safe and efficient energy paradigm. Closed-loop recycling

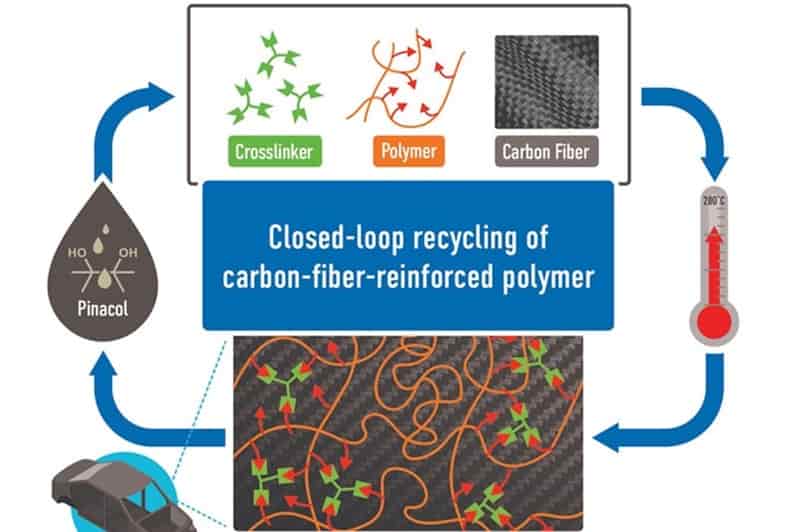
ORNL develops dynamically crosslinked CFRP, enabling closed-loop recycling
At laboratory scale, functionalized CFRP thermosets can be “released” via heat or chemicals to reincarnate them back into their starting materials.
Inventors at the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Oak Ridge National Laboratory (Oak Ridge, Tenn., U.S.) have designed a closed-loop path for synthesizing an exceptionally tough carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) and later recovering all of its starting materials. The findings, published in Cell Reports Physical Science, are said to accelerate addressing the challenge of recycling conventional CFRPs, which have typically been single-use materials. Closed-loop recycling
“We incorporated dynamic crosslinking into a commodity polymer to functionalize it. Then, we added a crosslinker to make it like thermoset materials,” explains ORNL chemist and inventor Md Anisur Rahman. “Dynamic crosslinking allows us to break chemical bonds and reprocess or recycle the carbon fiber composite materials.”
A conventional thermoset material is permanently crosslinked. Once synthesized, cured, molded and set into a shape, it cannot be reprocessed. ORNL’s system, on the other hand, adds dynamic chemical groups to the polymer matrix and its embedded carbon fibers. The polymer matrix and carbon fibers can undergo multiple reprocessing cycles without loss of mechanical properties, such as strength and toughness.
Rahman led the study with ORNL chemist Tomonori Saito. Rahman and ORNL postdoctoral fellow Menisha Karunarathna Koralalage conducted most of the experiments. The trio has applied for a patent for the innovation. Closed-loop recycling
Alpek Polyester Adjusts March PET Prices in US, Citing Increased Logistics Costs
Alpek Polyester has revealed its intention to implement a price increase for polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in the United States, set at 5 cents per pound (equivalent to USD 110.23 per tonne), effective from March 1, 2024. The decision to raise PET prices is attributed to the sustained challenges in logistics, particularly arising from ongoing disruptions in the Red Sea, which have reverberated across the market.
Recent developments have seen disruptions in logistics impacting US PET imports, with challenges manifesting in key transit routes such as the Red Sea, Panama Canal, and Suez Canal. These disruptions have exerted upward pressure on import prices, contributing to the decision by Alpek Polyester to adjust its pricing strategy. Closed-loop recycling
Additionally, the market is currently gearing up for the anticipated peak demand season for bottled PET. Traditionally, this peak season commences in the second quarter, signalling the onset of the summer season. Historically, rising temperatures during this period have led to increased consumer purchases of bottled beverages, subsequently driving up the demand for PET in bottling applications.
Alpek Polyester’s decision to raise PET prices reflects the intricate interplay of factors influencing the industry, with logistics disruptions serving as a prominent catalyst. The ongoing challenges in the Red Sea and other key transit routes have underscored the vulnerability of global supply chains, impacting various industries, including the PET sector.
Furthermore, the anticipation of a peak demand season for bottled PET introduces another layer of complexity to market dynamics. Closed-loop recycling
The historical trend of increased demand for bottled beverages during the warmer months’ places additional pressure on PET manufacturers to meet heightened consumer needs. This surge in demand adds to the considerations that PET producers like Alpek Polyester must weigh when implementing pricing adjustments.

A new online platform named Cyclops has been introduced in Germany to promote the use of recycled plastics in supply chains
Developed collaboratively by GreenDelta, Cirplus, Wuppertal Institute, and Centro Plastica SKZ, Cyclops (Circular Optimization for Plastics) is an open-source and free digital tool designed to facilitate the exchange of recycled materials among producers, recyclers, and manufacturers interested in transforming them into new products.
Cyclops offers a range of features tailored to different user types—waste owners, recyclers, and transformers. It provides valuable information on potential applications of recycled materials, pricing dynamics, and environmental benefits, aiding decision-making in the circular economy. Closed-loop recycling
The platform includes analysis tools for economic and environmental assessments, AI-driven quality specifications, waste management recommendations, and guidance on product design for recyclability.
Max Meister, co-founder of Cirplus, describes Cyclops as an accessible tool for comparing recycled materials quickly and effectively. Jan Werner, Group Manager for Sustainable and Circular Products at SKZ, highlights Cyclops’ potential to overcome existing barriers in the recycling market and promote coordinated recycling flows towards a circular economy.
Despite encountering some issues, such as AI prediction inaccuracies during initial testing, Cyclops aims to play a pivotal role in advancing recycling practices and fostering sustainability in future projects. Closed-loop recycling

Researchers develop eco-friendly ‘magnet’ to battle microplastics
Dynamic Cycle is a sustainable initiative in support of plastic circularity ti-films.com
Plastic pollution is a pressing environmental issue, and University of Kentucky Martin-Gatton College of Agriculture, Food and Environment researchers are leading the charge with an innovative solution.
The college’s Department of Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering (BAE) partnered with the U.K. Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering to tackle the tiny, often unseen, particles of plastic now found in the world’s oceans.
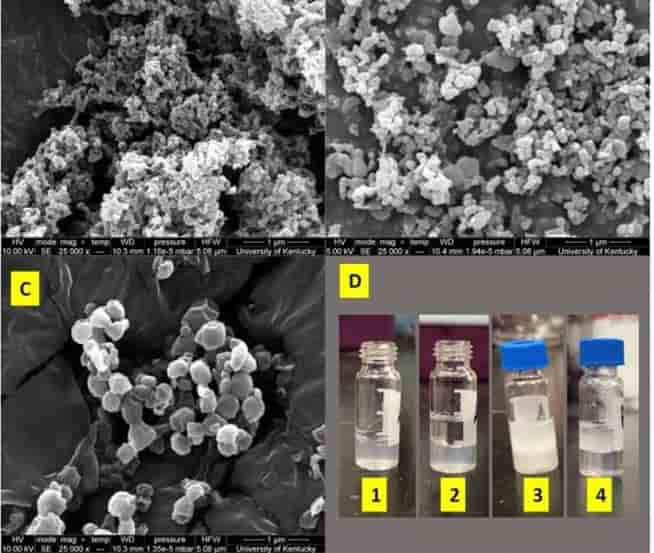
Their research, published in Scientific Reports, centers on an intriguing solution: using natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) to capture and remove these miniature particles from water. Closed-loop recycling
“The challenge of micro- and nano-plastics in our environment has been gaining intense attention recently,” said BAE associate professor Jian Shi. “These minute particles, often invisible to the naked eye, are the remnants of larger plastic pieces broken down by sunlight and physical stress. Their size makes them notoriously difficult to remove using conventional methods like centrifugation or filtration, which are either inefficient or too costly.”
Plastic is a durable, cheap material, making it a staple in daily life. However, its strength is also its environmental downfall.
Plastics don’t break down easily, leading to massive piles of waste. Over time, these plastics break into smaller fragments. The smallest, nano-plastics, are so tiny they can’t be seen without a microscope. Their size makes them a significant hazard, as they can be ingested by marine life and enter the human food chain. Closed-loop recycling

Raw material crisis imperils Indonesia polyester units: Reports
INSIGHTS
- The Association of Indonesian Spun and Filament Yarn Producers reportedly warned many Indonesian polyester factories may halt production due to challenges in sourcing raw materials.
- Farhan Aqil of APSyFI reportedly claimed the restrictions are linked to Trade Ministerial Regulation No. 36/2023.
- Polyester is crucial for textiles, automotive, and packaging.
According to the Association of Indonesian Spun and Filament Yarn Producers (APSyFI), numerous polyester factories in the country are facing imminent threat of halting production, faced with substantial challenges encountered by them in procuring essential raw materials. Closed-loop recycling
The primary hindrance reportedly stems from the government’s stringent import restrictions, exacerbating the scarcity of vital supplies for the production process.
Reports added the supplying countries of mono-ethylene glycol (MEG) to Indonesia have paused shipments awaiting government permit clarification.
As firms grapple with these constraints, the continuity of operations within the polyester industry hangs in the balance.

Closed-loop recycling