Hydrogen Cars – The Ampack machine fills preformed plastic bottles with liquids in aseptic conditions 01-03-2024 - Arhive
Hydrogen Cars
Crude Oil Prices Trend
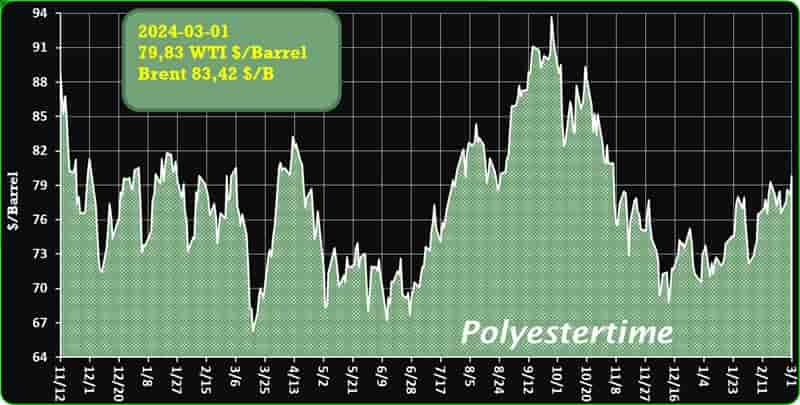
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
Hydrogen Cars vs. Electric Cars: A Sustainable Showdown
In the ongoing discourse about the future of energy, two contenders have captured the spotlight: hydrogen cars and electric cars. While both promise a cleaner, more sustainable tomorrow, they diverge significantly in operation, charging infrastructure, and costs. Let’s delve into the key differences between these burgeoning technologies and determine which might be the optimal choice for consumers.
- Electric Cars:
- Propelled by lithium-ion batteries, electric cars power one or more electric motors.
- Recharging options include domestic electrical outlets and public charging stations.
- Environmentally friendly, electric cars emit no direct pollutants during operation. Hydrogen Cars
- Hydrogen Cars:
- Employ fuel cells that convert hydrogen gas and oxygen into water, generating electricity.
- Like electric cars, hydrogen cars produce only water as a by-product.
- However, hydrogen refueling stations remain scarce compared to electric charging infrastructure.
- Challenges:
- Electric cars face evolving charging infrastructure issues.
- Hydrogen cars grapple with limited refueling stations, but efforts are underway to expand availability.
- Cost Considerations:
- Electric cars have a lower initial cost due to expensive fuel cells and hydrogen infrastructure.
- Hydrogen cars may offer lower long-term operating costs with faster charging times and comparable range.
In summary, both electric and hydrogen cars contribute significantly to sustainability. The choice depends on factors such as charging infrastructure, upfront expenses, and individual preferences Hydrogen Cars

Eunomia finds bioplastic shortcomings
Consulting firm’s report lists lack of recycling infrastructure as one problematic aspect of polylactic acid bioresin.
While products made from bioresins may carry recyclability or compostability labels, Eunomia says such infrastructure is lacking.
Olivier Le Moal | stock.adobe.com
A life cycle analysis of the bioplastic polylactic acid (PLA) undertaken by Eunomia Research & Consulting has identified a disappointing recycling track record as one of several environmental and social impacts that are challenging prevailing perceptions of the material’s sustainability. Hydrogen Cars
Eunomia collaborated with the Washington-based Plastic Pollution Coalition (PPC) to create the 18-page report on PLA. The report, “Bioplastics Are Trash: The Unforeseen Environmental Consequences of PLA from Production to Disposal,” was prepared by the New York office of United Kingdom-based Eunomia.
PLA and other bioplastics have been met with a critical eye by material recovery facility (MRF) operators and plastics reprocessors because they are not considered compatible with most established mechanical recycling processes.
Thus, recyclers of the most commonly recycled postconsumer plastics, such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP), treat PLA in the mixed container stream as a contaminant.
“If PLA is not sorted and removed from conventional plastic recycling streams, it acts as a contaminant and will have a detrimental impact on the final product in terms of strength and color,” Eunomia says. Hydrogen Cars
Proponents of the bioplastic have recommended composting discarded PLA, but the Eunomia report identifies shortcomings in that process, too.
“PLA does not biodegrade at the same speed as other organic materials in composting facilities, which can lead to contamination of the final compost product” at most existing composting locations,” Eunomia says.

The Ampack machine fills preformed plastic bottles with liquids in aseptic conditions
Ampack, from Syntegon, offers a solution for aseptic filling of liquids in preformed plastic bottles. Their versatile FBL filling machine, equipped with neck-handling capabilities, delicately fills HDPE, PP, and PET bottles with products like baby food, milk- and plant-based beverages, dairy items, and soups.
Capable of handling bottles ranging from 50ml to 1.5L, this multifunctional machine boasts a neck-handling system facilitating swift bottle format changes. It accommodates various bottle types, including collapsible formats like those used for enteral nutrition.
The machine’s maintenance is simplified with movable dosing stations, streamlining inspection and component upkeep, ultimately enhancing productivity and saving operational time. Hydrogen Cars
Oguz Karcier, Ampack’s product manager, highlights the machine’s adaptability to different bottle formats, ensuring efficient production and transportation.
Additionally, the dosing stations are redesigned to incorporate multiple fillers, catering to highly sensitive products and facilitating gentle product filling. Special dosing processes have been developed to minimize foaming, particularly in liquids like clinical nutrition.
Ampack claims a high output rate of up to 36,000 bottles per hour, depending on volume, with the SmartFill dosing concept ensuring ease of use and precise filling.
Designed in compliance with 3-A requirements, the machine prioritizes product safety and hygiene. It features separate chambers for production and mechanics, reducing the risk of food contamination. Hydrogen Cars
Moreover, the machine’s compatibility with other systems allows for seamless integration, further enhancing its versatility and utility in various production setups.
Ampack aims to showcase this solution at Angua FoodTec in Cologne, demonstrating its commitment to innovation and excellence in aseptic filling technology. Syntegon’s broader offerings, including the LFS filling solution and the GKF Capsylon 6005 capsule filling machine, reinforce the company’s leadership in the industry.

Kelheim Fibres, the Bavarian manufacturer specializing in viscose fibers, will implement price increases effective April 1, 2024
The company anticipates raising prices for its viscose fibers by approximately 12% to 15%. Hydrogen Cars
This decision comes in response to the significant surge in demand for viscose, particularly in Asia, driven by the recent upswing in cotton fiber prices.
Explaining the rationale behind the price adjustment, Kelheim highlights the substantial rise in various operational costs, including interest rates, wages, chemicals, and environmental expenses. Coupled with a prolonged period of subdued fiber prices, the company asserts that this move is essential to restore margins to sustainable levels.
Kelheim Fibres specializes in producing fibers for a diverse array of applications, spanning fashion, hygiene, medical products, nonwovens, and specialty papers. All of its fibers are crafted from 100% wood pulp sourced from PEFC or FSC certified origins, ensuring sustainability. Moreover, these fibers are fully biodegradable, offering an eco-friendly alternative to petroleum-based materials across a wide range of end products, while also maintaining or enhancing functional performance. Hydrogen Cars
The manufacturing process is exclusively conducted in Germany, adhering strictly to the nation’s stringent environmental regulations.

Syensqo is set to unveil a unique iteration of its MTM 49-3 epoxy prepreg at the upcoming JEC World in Paris, showcasing advancements in sustainable materials
Among the highlights of the event will be Syensqo’s innovative MTM 49-3 epoxy prepreg, enriched with 30% monomers sourced from biological origins. Tailored specifically for structural applications within the automotive industry, such as body panels, chassis components, and spoilers, this prepreg offers a sustainable alternative without compromising on performance. Hydrogen Cars
The integration of biobased resins significantly reduces the reliance on fossil raw materials, thereby diminishing the material’s carbon footprint. Despite its environmentally friendly composition, the prepreg maintains the same high standards of quality, workability, and mechanical performance as its conventional counterpart.
With a dry glass transition temperature (Tg) standing firm at 190°C, the material is compatible with both autoclave and press manufacturing processes. Polymerization can be achieved within 60 minutes at 135°C, ensuring efficiency in production. Moreover, the manufacturer emphasizes that the resin is devoid of any carcinogenic, mutagenic, or reproductive toxic agents, prioritizing safety alongside sustainability.
This groundbreaking development heralds a promising future for eco-conscious materials in the automotive sector, aligning technological innovation with environmental responsibility. Hydrogen Cars

Vietnam aims to produce 100,000-500,000 tons of hydrogen a year by 2030
Vietnam has set ambitious targets in its energy transition roadmap, aiming to produce between 100,000 and 500,000 metric tons of hydrogen annually by 2030, as outlined in its recently adopted hydrogen development strategy, reported by Hydrocarbonprocessing.
According to a government document reviewed by Reuters, this production volume is expected to escalate significantly to 10-20 million tons by 2050, encompassing green hydrogen.
The strategic focus on hydrogen production, distribution, and utilization is pivotal in achieving the nation’s objectives concerning climate change mitigation, fostering green growth, and attaining a net-zero status by 2050. Hydrogen Cars
Hydrogen, particularly when sourced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy, earns the ‘green’ label and holds promise in decarbonizing various industries, albeit currently characterized by high costs and early-stage technological development.
By 2030, hydrogen output is projected to supplant a portion of natural gas and coal in power generation, with envisaged applications spanning transport, fertilizer, steel, and cement production. By 2050, hydrogen is slated to contribute 10% of the country’s electricity generation.
Vietnam intends to pool resources from public and private sectors for hydrogen production, leveraging mechanisms like green bond issuance and participation in the Just Energy Transition Partnership (JETP), which involves equity investments, grants, and concessional loans from G7 members, multilateral banks, and private financiers. Hydrogen Cars
Moreover, Ecolab, Inc. recently inaugurated a state-of-the-art manufacturing plant near Ho Chi Minh City, underscoring its dedication to customer support, innovation, and sustainability in Vietnam and Southeast Asia.

NGO-business coalition calls on the decision-makers to consider a real compromise by voting for a “polymer-only” allocation method to account for recycled content in the implementing decision of the Single-Use Plastic Directive (SUPD)
The undersigned organisations – civil society organisations and companies operating along the value chain in relevant sectors – are writing to you to express their concerns and to highlight the importance of prioritising robust and transparent chain of custody models for calculating recycled content in the European Commission‘s implementing decision that establishes rules for the application of Directive (EU) 2019/904. Hydrogen Cars
We believe it is important to consider amending the proposal’s allocation rules where it pertains to the ‘fuel-use excluded’ for mass balance accounting. Just like in 2019 with the SUPD, our current decisions will shape future legislation such as the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation, the Ecodesign for Sustainable Product Regulation (ESPR) and the End-of-life Vehicles Regulation. The rules adopted will play a significant role in either facilitating genuine circularity or retaining the status quo of relying on virgin feedstock.
The decisions made regarding the EU methodology in this implementing act will have implications beyond its immediate scope. Failing to establish a suitable chain of custody now will hinder Europe’s ambitions for carbon neutrality by 2050 and slow down progress towards a circular economy.
It is thus crucial to maintain ambitious goals and oppose opaque and distorting rules which run against environmental objectives. Hydrogen Cars

Hydrogen Cars
