Textiles sector petrochemical – Is the Internet of Things the solution? 29-07-2023 - Arhive
Textiles sector petrochemical
Versalis, the chemical company of the ENI group, faced another challenging quarter in the petrochemical industry as demand weakness and increased imports continued to impact their sales and operating margins
The second quarter proved to be equally difficult as the first, painting a bleak financial picture for the company.
During the second quarter, Versalis reported an adjusted operating loss of 70 million euros, a stark contrast to the 125 million euros profit achieved in the same period last year. The cumulative loss for the first six months of the year reached a staggering 179 million euros, in stark contrast to the operating margin of 10 million euros recorded in the first half of 2022. These disappointing results reflect the considerable decline in demand across all sectors and the uncertainties that plague the market, which have significantly slowed down purchasing decisions made by retailers. Moreover, the company faced continuous competitive pressure from imported products.
One of the significant indicators of this downturn is the decline in sales volume. Between April and June, Versalis sold only 820,000 tonnes of petrochemical products, down by 24% compared to the 1.07 million tonnes sold during the same period in 2022. This substantial drop in sales volume is indicative of the challenges the company encountered in this quarter. In addition to that, the plant utilization rate plummeted from 69% to 55%, signaling the severity of the situation. Textiles sector petrochemical
The cracker margin, a crucial metric for the company’s profitability, also witnessed a decline in the second quarter compared to the previous year. Margins on polyethylene and styrenics also took a hit, primarily due to the decrease in commodity prices. These margin contractions further exacerbated Versalis’ financial struggles.
The petrochemical industry as a whole experienced a complex and challenging landscape during this period, grappling with various issues related to demand, supply, and competitive pressures. Versalis’ financial woes are emblematic of the broader challenges faced by companies in this sector.
Looking ahead, Versalis will need to adopt a strategic approach to navigate through these turbulent times successfully. The company must analyze the ever-changing market dynamics and identify opportunities to optimize its operations and reduce costs. Moreover, investing in research and development to create innovative and high-value products could help them differentiate themselves in the market and gain a competitive edge.
Collaboration with key stakeholders, such as suppliers and customers, will be crucial to adapting to shifting market demands effectively. This partnership can help in streamlining the supply chain and ensuring a steady flow of products to the market when demand starts to recover. Textiles sector petrochemical
Furthermore, Versalis should explore avenues to enhance their product portfolio and focus on developing sustainable and eco-friendly solutions. With growing environmental awareness and regulations, there is an increasing demand for greener products in the petrochemical sector. By aligning their offerings with these emerging trends, the company can open new markets and strengthen their position in the industry.
In conclusion, Versalis faced another challenging quarter with significant losses, primarily driven by weakened demand and competitive pressure from imports. The uncertainties in the market and subdued purchasing decisions by retailers further compounded their financial woes. To overcome these challenges, Versalis must proactively adapt its strategies, foster collaborations, and invest in innovation to steer the company towards a more resilient and profitable future.

Smart Carpets: Revolutionizing the World of Knotted Textile Floor Coverings with IoT and Technology
The realm of interior design is undergoing a revolutionary transformation with the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced technology. Among the innovations gaining traction are smart carpets – knotted textile floor coverings embedded with sensors and connected to the internet, offering functionalities that go beyond aesthetics and comfort.
Smart carpets epitomize how IoT and technology are driving innovation in interior design. By interacting with the environment and the people within it, they provide valuable data that can enhance safety, health, and overall living experience.
At the core of smart carpets lies sensor technology. Textiles sector petrochemical
These sensors detect pressure, temperature, and moisture, providing real-time data with a myriad of applications. For instance, pressure sensors can monitor foot traffic, helping businesses optimize their spaces and homeowners understand their living habits better.
Safety is a paramount concern, and smart carpets address this by detecting unusual movements and acting as early warning systems for falls. This feature proves especially beneficial for the elderly and those with mobility issues. In the event of a fall, the carpet can send alerts to designated contacts or emergency services, ensuring timely assistance.
Health and wellness are also areas where smart carpets can make a significant impact. Some models can monitor vital signs, such as heart rate and breathing patterns, providing valuable data for individuals with chronic conditions and informing medical interventions.
Moreover, smart carpets contribute to energy efficiency by detecting the presence or absence of people in a room. They can communicate with other smart devices to adjust lighting, heating, or cooling systems accordingly, reducing unnecessary energy consumption. Textiles sector petrochemical
Though the concept of smart carpets may seem futuristic, several companies have already made strides in this field. Sensing Tex, a Spanish tech company, has developed a smart carpet that can detect falls and monitor foot traffic. Similarly, the German company Future-Shape has created a smart floor covering that recognizes gestures and movements, enabling interaction with other smart devices.
However, like any emerging technology, smart carpets face challenges. Privacy concerns loom large due to the potential collection of personal data by these devices. Additionally, the current high cost of smart carpets makes them inaccessible to many, hindering their widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, the potential of smart carpets is undeniable. As IoT and technology continue to evolve, we can expect more innovative applications of these knotted textile floor coverings. They represent a significant step towards creating smarter, safer, and more efficient living spaces, redefining the future of interior design.
In conclusion, smart carpets are a fascinating example of how IoT and technology are transforming the world of knotted textile floor coverings. They offer a glimpse into a future where our homes and workplaces are intelligent environments that adapt to our needs, enhancing our quality of life. With further development and accessibility, smart carpets are poised to revolutionize the way we perceive and interact with our living spaces, making them not just visually appealing but also technologically advanced hubs of safety, health, and efficiency. Textiles sector petrochemical

Braskem, the Brazilian petrochemical producer, reported a significant decline in resin sales volume during the second quarter in Brazil
According to Reuters, the company experienced a 10% year-on-year drop, primarily attributed to lower demand in the market.
During this quarter, Braskem’s ethylene plants in Brazil faced challenges, with their average utilization rate reaching 72%. This was two percentage points lower than the previous year and five percentage points below the utilization rate recorded in the first quarter.
On the other hand, the company witnessed a positive trend in its polyethylene sales in Mexico, which saw a remarkable 13% increase compared to the previous year. This surge was accompanied by a significant rise in the utilization rate for polyethylene plants in Mexico, reaching 86%.
The increase in polyethylene sales and utilization rate in Mexico can be credited to a larger supply of ethane provided by the Mexican state oil company, Pemex. Braskem stated that Pemex supplied an average of 36,000 barrels of ethane per day, surpassing the contractual volume. Textiles sector petrochemical
Braskem’s performance in the first quarter was not much better, as it also experienced challenges in its main chemicals sales in Brazil. The company reported a 15% year-on-year decrease in sales volume for main chemicals during Q1. However, resin sales remained stable during this period.
Under the umbrella of main chemicals, Braskem includes several products such as ethylene, propylene, butadiene, cumene, gasoline, benzene, toluene, and paraxylene. The sales volume for these main chemicals in Q1 2022 decreased significantly due to lower demand, which had a direct impact on the utilization rate of petrochemical crackers.
Looking at both quarters together, Braskem faced headwinds in its Brazilian operations due to weakened demand in the market. This, in turn, affected the utilization rates of their ethylene plants and petrochemical crackers.
In contrast, the positive growth in polyethylene sales in Mexico can be seen as a bright spot for the company during this challenging period. The increase was fueled by the surplus supply of ethane from Pemex, enabling Braskem to meet the rising demand in the Mexican market.
As the company continues to navigate through market fluctuations and challenges, it will be essential for Braskem to remain vigilant and adaptable. By monitoring demand trends and optimizing production capabilities, Braskem can position itself for recovery and growth in the petrochemical industry. Textiles sector petrochemical

SK Capital Partners, a private equity firm, has taken over the majority stake in Ecopol, a leading Tuscan company specializing in the production of water-soluble and biodegradable polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-based films
These films are widely used in packaging single-dose detergents, agricultural chemicals, and water treatment applications across Europe.
As a result of this acquisition, the ownership structure of Ecopol will undergo significant changes. However, Mauro Carbone, the current CEO and previous controlling shareholder of the company, will retain a substantial stake and continue to hold the position of CEO. This move ensures continuity and stability in the leadership of the company. Additionally, Tikehau Capital, an existing investor, will maintain its presence in Ecopol as a minority stakeholder, having previously held 38% of the company.
The completion of this acquisition is subject to the fulfillment of standard regulatory requirements and approvals, ensuring a smooth transition of ownership and operations. Both Ecopol and SK Capital are committed to finalizing the deal promptly.
Ecopol has been on a growth trajectory since 2019, investing over 70 million euros in expanding its production capacity and product range. A new production line in Chiesina Uzzanese, Pistoia, was established to manufacture polyvinyl alcohol cast films (PVOH) for detergency applications. Textiles sector petrochemical
Simultaneously, a new manufacturing facility was set up in Griffin, Georgia, USA, to cater to the North American market.
Mauro Carbone expressed enthusiasm about the partnership with SK Capital, describing them as the perfect fit due to their expertise in the sector, extensive experience in the North American market, and successful track record of collaborating with entrepreneur-led companies. The shared vision of creating a more sustainable future and adherence to the values that have contributed to Ecopol’s success so far make this collaboration a strategic move for both parties.
Daniele Ferrari, Senior Director of SK Capital, sees immense potential for Ecopol to expand its presence within existing target markets and capitalize on its expertise in biodegradable films to explore new applications. As sustainability becomes an increasingly significant focus for brands and consumers alike, Ecopol’s environmentally friendly solutions are expected to gain even more traction.
Founded in 2009 and headquartered in Chiesina Uzzanese, Ecopol operates through three manufacturing facilities, two in Italy and one in the United States.
The company employs over 130 people and generates an annual turnover of approximately 45 million euros. With SK Capital’s financial backing and strategic guidance, Ecopol is well-positioned to scale its operations and further solidify its position as a prominent player in the market. Textiles sector petrochemical
The partnership with SK Capital represents an exciting chapter for Ecopol, offering access to new opportunities and resources that will drive the company’s growth and innovation. Together, they aim to continue providing sustainable packaging solutions to various industries, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives.
As the deal awaits regulatory approvals, both parties are optimistic about a successful outcome. The combination of Ecopol’s industry leadership and SK Capital’s expertise and support is poised to pave the way for a prosperous and sustainable future for the company. By advancing their shared commitment to environmental responsibility, Ecopol and SK Capital are set to make a positive impact on the packaging and chemical industries while contributing to a greener and more sustainable world.

Zero Waste Europe: EU failed to rein in emissions in textiles sector
A recent paper highlights the emissions gap that apparel industry giants will face if no urgent action is taken to prevent overproduction by governments.
Published by Zero Waste Europe, the paper notes that despite being the top buyer of clothes globally, the EU has yet to set concrete measures on textile waste prevention, thereby cancelling any progress towards a sustainable fashion industry.
Theresa Mörsen, Waste & Resources Policy Officer at Zero Waste Europe, states: “Evidence shows that even with the foreseen interventions in the textile production chain, there is still a gap of almost 40% of necessary emissions reductions to meet the 1.5 degrees target. This suggests that the only way forward is to reduce overproduction”
Entitled “T(h)reading a path: Towards textiles waste prevention targets”, the paper emphasised that the most significant global warming impact of the textiles industry lies in the production phase, and urges a radical remodelling of the industry.
The EU’s Waste Hierarchy laid down by the Waste Framework Directive prioritises waste prevention over other methods like reuse, recycling, and recovery. While the Waste Framework Directive obligates countries to take measures against waste, the proposed revision of the Directive fails to include prevention targets for textiles, undermining the Waste Hierarchy’s core principle. Textiles sector petrochemical
Experience from the past decade has shown that voluntary measures such as awareness-raising campaigns always fall short of their aims and instead, Zero Waste Europe advocates for real textile waste reduction targets at EU level, a measure previously backed by the European Parliament and the European Environmental Agency.
Theresa Mörsen, Waste & Resources Policy Officer at Zero Waste Europe goes on to say, “Since member states’ waste prevention programmes have not delivered any tangible waste reduction over the past 10 years, we suggest setting concrete targets, starting with textile waste in the current revision of the Waste Framework Directive. We propose an overall reduction target for textile waste of at least one third by 2040 in comparison to 2020. It is essential to set policy on the right trajectory for substantial waste reduction as soon as possible.”
One feasible indicator for waste prevention would be to measure the weight of new textile products put on the market per capita per year.
According to the paper, the average European consumes a staggering 26 kg of textiles annually, while generating 11 kg of textile waste. The environmental consequences extend beyond the EU’s borders, as material extraction and production mostly take place outside the EU and exports of textile waste are commonplace, polluting soil and water in recipient countries in the Global South. Textiles sector petrochemical

Volvo Embraces Sustainability: Reducing the Environmental Impact of the EX30 SUV
Volvo, a renowned name in the automotive industry, has long been committed to sustainability and environmental consciousness. With the upcoming release of the all-electric EX30 small SUV, Volvo has taken significant strides to reduce its carbon footprint and minimize environmental impact. Through innovative engineering and a thoughtful selection of materials, the company has set an exemplary standard for eco-friendly automobile production. Textiles sector petrochemical
One of the most remarkable achievements in the development of the EX30 is the reduction of its total carbon footprint over a distance of 200,000 kilometers of driving. Comparatively, the EX30 boasts a footprint that is 25% lower than its counterparts, the fully electric C40 and XC40 models. This achievement is a testament to Volvo’s dedication to sustainable practices throughout the vehicle’s life cycle.
One aspect that has contributed to the EX30’s environmentally-friendly design is the use of an electric drivetrain. By opting for an all-electric powertrain, Volvo eliminates tailpipe emissions, which are a significant source of greenhouse gases. The decision to go fully electric aligns with Volvo’s ambitious goal of reducing overall CO2 emissions per car by 40% from 2018 levels by 2025.
However, the reduction in carbon footprint is not solely attributed to the electric drivetrain. The smaller size of the EX30 SUV requires less steel and aluminum in its construction. Additionally, Volvo has been conscious about incorporating recycled materials into the manufacturing process. Approximately 25% of the aluminum and 17% of the steel used in the chassis construction are derived from recycled sources, further lowering the vehicle’s environmental impact. Textiles sector petrochemical
The interior of the EX30 is a testament to Volvo’s commitment to sustainable materials. Upholstering the seats, dashboard, and doors with recycled and renewable materials has been a priority. Denim, flax, and a wool blend, which contains around 70% recycled polyester, are cleverly utilized to create a stylish and environmentally-conscious interior. Volvo has ingeniously utilized fibers that would have otherwise become waste products during the denim recycling process, giving new life to discarded materials.
Moreover, the company has integrated recycled plastics into 17% of the interior components, including the exterior bumpers. This thoughtful approach to material selection ensures that Volvo not only reduces its reliance on virgin materials but also diverts waste from landfills, thereby contributing to a circular economy.
The culmination of Volvo’s sustainable efforts results in the EX30 achieving a commendable cradle-to-gate CO2 impact of approximately 18 tons. Furthermore, the company’s commitment to recycling and sustainability extends beyond the vehicle’s initial life cycle. At the end of its service life, an impressive 95% of the EX30 can be recovered through efficient recycling of its materials, making it a truly eco-friendly choice for environmentally-conscious consumers.
Anders Kärrberg, Volvo’s head of global sustainability, emphasized the significance of the EX30 in realizing their sustainability ambitions. He stated, “Our new EX30 is a big step in the right direction for our sustainability ambitions. By 2025 we aim to reduce our overall CO2 emissions per car by 40% from 2018 levels through a 50% reduction in overall tailpipe emissions and a 25% reduction in emissions from our operations, raw material sourcing and supply chain – all on the way toward our ambition of being a climate-neutral company by 2040.” Textiles sector petrochemical
Volvo’s dedication to sustainability and environmental responsibility is a shining example of how automakers can contribute positively to the planet’s well-being. By adopting renewable and recycled materials, embracing electric drivetrains, and setting ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions, Volvo paves the way for a greener automotive industry. The EX30 small SUV stands as a symbol of Volvo’s commitment to shaping a more sustainable future for generations to come.

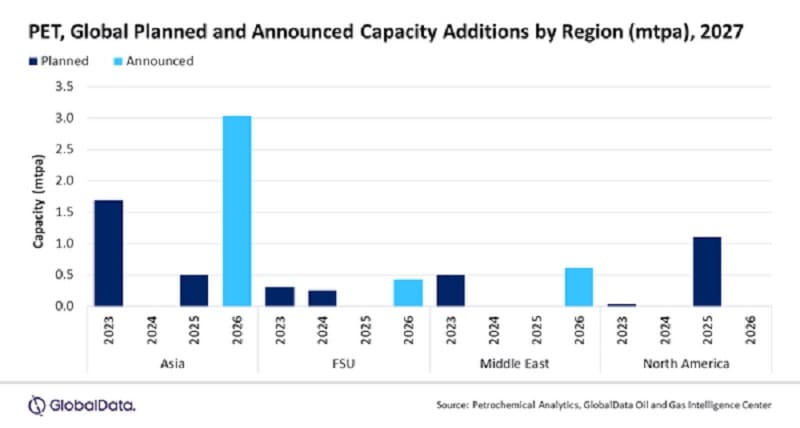
Asia to lead global polyethylene terephthalate capacity additions by 2027, says GlobalData
Asia is set to lead the global polyethylene terephthalate (PET) industry capacity additions with a share of 61.8% by 2027, by gaining capacities from new-build and expansion projects between 2023 and 2027, according to GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
GlobalData’s latest report, ‘Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Industry Installed Capacity and Capital Expenditure (CapEx) Forecasts by Region and Countries including details of All Active Plants, Planned and Announced Projects, 2023-2027’ reveals that the total PET capacity of new-build and expansion projects in Asia is expected to be 5.21 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) by 2027. Increased usage of plastic in end use industry segments such as food and beverages, FMCG and pharmaceuticals are the key factors for PET industry growth in Asia. Textiles sector petrochemical
Nivedita Roy, Oil and Gas Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “For the upcoming new build projects, the region is expected to add a capacity of 5.13 mtpa from six planned and announced projects, whereas, for the expansion of the existing PET projects, the region is expected to add a capacity of 0.08 mtpa from two announced and planned projects.”
China and India are the key countries in Asia in terms of PET capacity additions. The main capacity addition in China will be from an announced project, Zhejiang Petrochemical Daishan Polyethylene Terephthalate Plant 2, with a capacity of 2 mtpa. It is expected to commence production of PET in 2026.
Renewable Hydrogen Bottling – Repreve closes the PET bottles circuit 28-07-2023
