Green-hydrogen H2
RadiciGroup unveils its visionary Sustainability Plan, aptly named “From Earth to Earth,” signaling its unwavering commitment to a sustainable future
This comprehensive strategy encompasses Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) objectives, underscoring the company’s dedication to value creation for all stakeholders while prioritizing adherence to evolving sustainability regulations.
With a focus on transparency and responsibility across its entire value chain, RadiciGroup aims to address economic, social, and environmental concerns head-on. The plan reflects the organization’s evolution towards ESG governance, evident in its longstanding engagement with environmental and social issues, as exemplified by its forthcoming 20th annual Sustainability Report. Green-hydrogen H2
“From Earth to Earth” emerges as a pivotal component of RadiciGroup’s overarching sustainability strategy, capitalizing on past achievements while charting a course towards medium-term goals. Encompassing all “material” areas, the plan addresses ESG principles and their financial ramifications, aiming to ensure business continuity and foster growth for the company and its stakeholders alike.
Angelo Radici, President of RadiciGroup, emphasizes the plan’s significance, framing it as a testament to the company’s ethical commitment and foresight. With tangible, measurable goals established, the focus now shifts to collaborative action, as RadiciGroup strives to realize its objectives and uphold its credibility with stakeholders.
In essence, “From Earth to Earth” encapsulates RadiciGroup’s proactive stance towards sustainability, reflecting not only its resilience and competitiveness but also its enduring ethical values and dedication to responsible business practices. Green-hydrogen H2
Visit
Read the press release to find out more
Click here to view the RadiciGroup Sustainability Plan “From Earth to Earth”.

Mr. Maurizio Radici – RadiciGroup
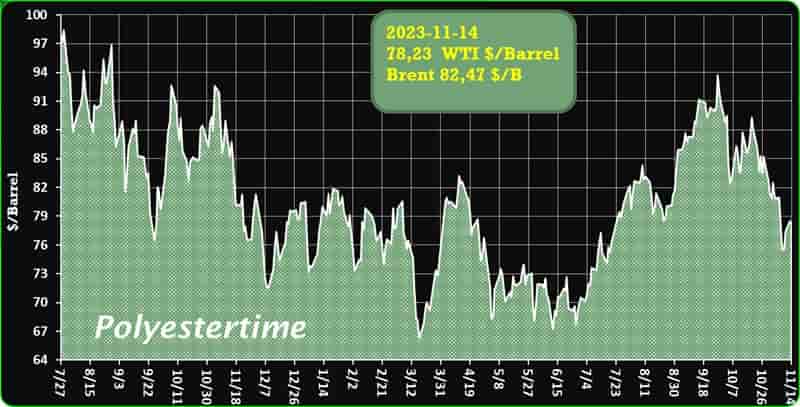
Crude Oil Prices Trend
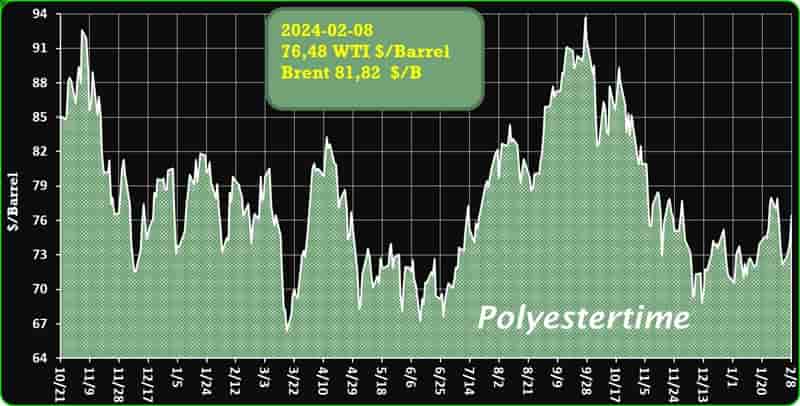
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
Taiwan Cement Corporation (TCC) has recently announced a significant collaboration with thyssenkrupp Polysius (tkPOL) aimed at developing innovative carbon capture technology
This partnership is pivotal in the context of Taiwan’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
The collaboration, formalized through a memorandum of understanding (MOU) signed on January 31st, focuses on implementing a Separate Oxyfuel Calciner technology at the Hoping Plant.
This cutting-edge technology involves the addition of pure oxygen to the calcination process, enhancing carbon dioxide capture to over 90% while simultaneously reducing energy consumption. Green-hydrogen H2
The project, slated for completion by 2026, aims to commercialize the technology by 2030, with an annual carbon dioxide capture target exceeding 100,000 tons. The captured carbon dioxide will find applications across various industries, aligning with government policies on storage, carbon credits, and value-added utilization.
Mr. Nelson Chang, Chairman of TCC, expressed the significance of this collaboration in addressing emissions from the cement industry and reaffirmed TCC’s commitment to supporting sustainable development. Mr. Pablo Hofelich, CEO of tkPOL, commended TCC’s dedication to innovation and sustainability, emphasizing the strategic importance of the partnership. Green-hydrogen H2
Building upon previous collaborations focused on carbon capture technologies, TCC and tkPOL will embark on a phased approach to implementing the Separate Oxyfuel Calciner technology. Leveraging tkPOL’s expertise and experience in similar projects, the collaboration is poised to make significant contributions to carbon reduction efforts, advancing towards a greener and more sustainable future.

Despite challenges, circularity is still the way to go, says Borealis CEO
After the record results reported by Borealis in 2022, the year 2023 was by comparison less than stellar. It was, in the words of Thomas Gangl, CEO at Borealis, ‘definitely a challenging year, not just for us but for the entire industry’. Nonetheless, while inflation, the economic slowdown and geopolitical developments have taken their toll, Borealis has continued to pursue its sustainability journey: implementing its Strategy 2030, the company’s transformation framework for the future. The goal: to become a global leader in advanced and sustainable chemicals and material solutions.
“We have taken some important steps forward, and I would love to say we have achieved more. But at the moment our customers are in the difficult situation that they cannot afford to pay more than what they need to pay. Right now, the regulatory framework is the driving force for the transformation towards circularity,” said Gangl, speaking during an online interview on 4 Feb. with Sustainable Plastics. Green-hydrogen H2
Looking at Borealis’ five main financial KPIs, however, the company would appear to have adeptly navigated the challenges of the past year.
Sales were down roughly €2 bn, noted Daniel Turnheim, although the actual volumes sold remained for the most part stable. “So, this reduction in revenue can, by and large, be attributed to the lower prices of polyolefins,” he explained. The operating profit, which plummeted from €703 in 2022 to €18m in 2023 – a drop of 94% – was a different story, he continued. This was due in the first place to inventory effects – ‘selling products purchased in a higher pricing environment’ – as well as to what he described as a ‘very difficult market environment, especially in Europe’: cheap imports, inflation and high energy costs. Green-hydrogen H2
The margins achieved on the commoditised part of the business suffered from the pressures of the market, but the specialities side of the business, representing around 45%, ‘held up quite nicely’, he said. “As a European-based producer, we do not have a feedstock advantage, so we have to focus on delivering a very good product. Our European asset base contributed strongly to the result.”
More…

Venator, a leading manufacturer of titanium dioxide (TiO2) and additives for plastic materials, is undergoing significant strategic changes in its European operations
Emerging from Chapter 11 in the USA, the company has embarked on a new transformation plan following a strategic review. This plan includes the rationalization of production activities in Europe, focusing on consolidating production capacities and optimizing operational efficiency.
In Germany, production will be concentrated in Uerdingen, with the closure of the TiO2 plant in Duisburg, which has a capacity of 50,000 tonnes per year. The shutdown is scheduled for the second quarter of this year, with the site shifting its focus to functional additives. Meanwhile, the 80,000 tonnes per year TiO2 plant in Scarlino, Italy, remains inactive due to regulatory factors and market conditions. Green-hydrogen H2
Venator’s transformation plan aims to strengthen its TiO2 portfolio through innovation and investments while improving margins through price and cost management. Additionally, the company seeks to identify opportunities for monetizing specific segments in additives.
With headquarters in the United Kingdom, Venator operates with approximately 2,700 employees and divides its businesses into two main segments: titanium dioxide and high-performance additives.
These strategic changes underscore Venator’s commitment to adapt to market dynamics and enhance its competitiveness in the industry. Green-hydrogen H2

PiovanGroup has solidified its global presence in the industrial process cooling segment through the amalgamation of Thermal Care and Aquatech, unveiling a new strategic division
Drawing on their shared 50-year legacy of delivering top-notch heat transfer solutions across 50 industries, the unified division emerges as a worldwide player, boasting manufacturing capabilities across North and Latin America, Europe, and Asia. With an expansive service structure, it ensures proximity to customers globally.
This integration promises synergies in research and development, enriching the portfolio of products, solutions, and services, and facilitating efficient support for diverse market sectors. Lee Sobocinski, the current president of Thermal Care Inc., will spearhead the division, operating under the Thermal Care brand and anticipating global consolidated sales of around 100 million euros. Green-hydrogen H2
Filippo Zuppichin, CEO at PiovanGroup, expresses excitement about establishing a benchmark in industrial refrigeration solutions. Lee Sobocinski shares the sentiment, envisioning the new division as a global leader, providing unparalleled assistance to customers worldwide. The creation of the Thermal Care brand, coupled with the exchange of institutional knowledge within PiovanGroup, signifies a bright future for the division, set to deliver unmatched solutions in industrial heat transfer. Together, they aspire to reach new heights and redefine industry standards.
Visit Piovan

LyondellBasell, a global petrochemical leader, has recently inked an agreement to acquire a 35% stake in National Petrochemical Industrial Co (Natpet), a Saudi Arabia-based firm, from Alujain Corp for approximately $500 million
Natpet currently boasts a polypropylene (PP) capacity of 400,000 tonnes per year. As part of this strategic move, LyondellBasell and Alujain are jointly exploring the possibility of constructing a propylene via propane dehydrogenation and PP facility at the Natpet site, pending a final investment decision. Green-hydrogen H2
The completion of this transaction is contingent upon regulatory approvals and other customary closing conditions.
In a separate development, Bora LyondellBasell Petrochemical, a collaboration between Liaoning Bora Enterprise and LyondellBasell, successfully resumed production of low-density polyethylene (HDPE), linear polyethylene (LDL), and polypropylene (PP) at its Panjin facility in China on January 5. This revival followed a scheduled shutdown for preventive maintenance that began on December 27 of the preceding year. The production facility, with an annual capacity of 350 thousand tons of HDPE, 450 thousand tons of LDL, and 200 thousand tons of PP, plays a crucial role in the regional petrochemical landscape. These strategic moves reinforce LyondellBasell’s commitment to expanding its presence and capabilities in the global petrochemical market. Green-hydrogen H2

JSW Neo Energy Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of JSW Energy Limited, has achieved a significant milestone by securing a capacity allocation of 6.5 KTPA for the establishment of a green hydrogen production facility
This accomplishment resulted from the company’s participation in the inaugural auction held by the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) under the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) scheme.
Following the successful bid, JSW Neo Energy received a Letter of Award (LoA) from SECI, committing to commission the production capacity within 36 months. The venture is projected to yield incentives totaling Rs. 67.6 crores over a three-year period post-commissioning. Green-hydrogen H2
This strategic move aligns seamlessly with JSW Neo Energy’s sustainability objectives and contributes significantly to India’s broader net-zero aspirations. The company’s success in this auction further solidifies its position as a trailblazer in the green hydrogen sector, capitalizing on its profound understanding of the Indian energy landscape, robust financial standing, and unwavering commitment to technological advancements.
JSW Neo Energy has set an ambitious target of achieving 20 GW in generation capacity and 40 GWh in energy storage capacity by 2030. Currently boasting a total capacity of 9.8 GW (including projects under construction), the company is well on track to meet its interim goal of 10 GW by 2025. Green-hydrogen H2
Moreover, JSW Energy has already secured 3.4 GWh of energy storage capacity through battery energy storage systems and hydro pumped storage projects. This puts the company on a trajectory towards its broader goal of a 50% reduction in carbon footprint by 2030, ultimately aiming for Carbon Neutrality by 2050.

Asda has recently taken a significant step towards sustainability by introducing recyclable plastic film packaging for its Just Essentials beef mince range, effectively replacing traditional plastic trays
This innovative move not only reduces plastic waste but also aligns with Asda’s commitment to achieving 100% recyclable packaging by 2025. The new packaging boasts a remarkable 60% reduction in plastic usage, a testament to Asda’s dedication to environmental responsibility.
By adopting this lighter and recyclable flexible plastic film alternative, Asda aims to eliminate a substantial 67.6 tonnes of plastic from its supply chain annually. The introduction of vacuum-packaging not only extends shelf life but also results in a smaller pack size, further reducing environmental impact. Green-hydrogen H2
Jon Wells, Sustainable Packaging Manager at Asda, emphasized the significance of this initiative, stating, “We’re always looking at new ways that we can make positive changes which will benefit both our customers and the planet and we believe that this is one of those changes.” He highlighted the dual benefits of improved shelf life and convenience for customers, along with the substantial reduction of non-recyclable plastic in the supply chain, ultimately contributing to a decrease in Asda’s carbon footprint.
Overall, Asda’s transition to recyclable packaging for its beef mince range signifies a proactive approach towards sustainability, setting a commendable example for the retail industry as a whole. Green-hydrogen H2

Green-hydrogen H2
CO2 into ethylene – Growth in China projected to slow to 4.6% in 2024, 3.5% in 2028: IMF 07-02-2024