Circular Economy Automotive Recovery – Christine Lagarde ECB: stop to a new rate hike in September? 25-08-2023 - Arhive
Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
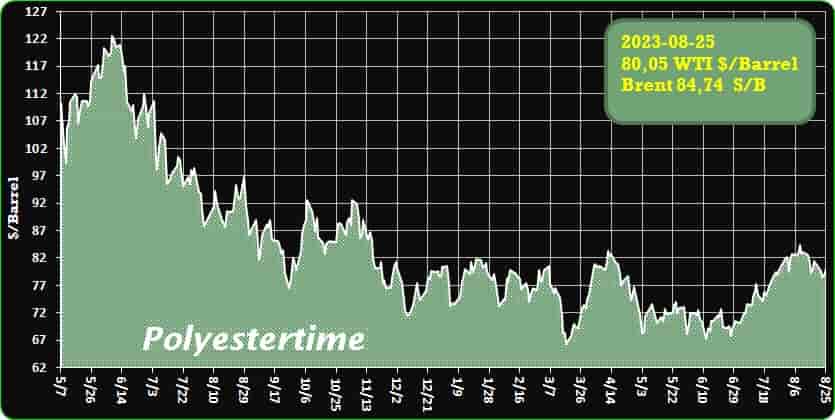
Crude Oil Prices Trend
The European BioICEP Project has achieved a significant breakthrough by transforming synthetic plastics into biodegradable bioplastics
Spearheaded by AIMPLAS, the Plastics Technology Centre, this project has harnessed innovative techniques based on microwaves and reactive extrusion. The outcome of this endeavor holds great promise for the packaging and pharmaceutical industries, offering sustainable solutions for plastic waste.
The central methodology behind this accomplishment involves the utilization of microwave-assisted thermochemical degradation. This pioneering approach is designed to convert fossil-based plastic waste into natural, biodegradable alternatives. Notably, it expedites the biodegradation process of conventional plastics, ensuring their complete decomposition in less than 28 days. AIMPLAS further elaborates that the depolymerisation of polyamides is another instrumental technology within this project. By reverting polymers back to their original monomers, these materials become susceptible to degradation by microorganisms, ultimately contributing to the creation of bioplastics and other valuable products.
Incorporated into AIMPLAS’ contributions to the Bio Innovation of a Circular Economy for Plastics (BioICEP) project, these advancements are made possible through a three-step sequential process. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
The first step involves chemical disintegration, employing a novel microwave-based technology to reduce the molecular weight of base polymers, thereby enhancing biodegradability. The second step, biocatalytic digestion, integrates improved enzymes through techniques like fluorescent sensor screening and directed evolution. Finally, the third step leverages microbial consortia derived from top-tier single microbial strains, strategically combined to effectively degrade mixed plastic waste streams.
The profound potential of these developments extends to the creation of end products that can be integrated into the production of new polymers and bioproducts. This aligns perfectly with the vision of establishing a circular economy for plastic waste, addressing the mounting environmental concerns posed by plastic pollution.
Crucially, AIMPLAS holds a pivotal role in the BioICEP project. It serves as the coordinator responsible for communication activities, as well as the dissemination and exploitation of project outcomes. By facilitating effective collaboration and knowledge-sharing among project stakeholders, AIMPLAS plays a vital role in driving the project’s success.
Beyond the BioICEP project, AIMPLAS is an active participant in the European BeonNAT project. Notably, this initiative has recently achieved the cultivation of biomass from organic materials such as poplar, elm, and birch wood. The primary aim is to produce bioplastics that find application in various sectors, including bioactive cosmetics, biochar, activated carbon, and pet litter infused with essential oils.
This multi-faceted approach demonstrates a holistic commitment to sustainable alternatives across diverse industries. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
In alignment with broader EU efforts, the Bio-Uptake project, led by Aitiip Centro Tecnológico, focuses on generating bio-based intermediates tailored for the manufacturing of eco-container lids. This strategic endeavor seeks to seamlessly integrate bioplastic composites into the fabric of the European manufacturing industry, contributing to both sustainability goals and the advancement of digitalization.
In conclusion, the European BioICEP Project, spearheaded by AIMPLAS, has harnessed innovative microwave and reactive extrusion technologies to transform synthetic plastics into biodegradable bioplastics. This breakthrough has far-reaching implications for industries reliant on plastics, such as packaging and pharmaceuticals, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic materials. Through a multi-step process, AIMPLAS and its collaborators aim to usher in a circular economy for plastic waste, addressing environmental concerns and propelling the paradigm shift towards a more sustainable future. This endeavor aligns with AIMPLAS’ broader participation in projects like BeonNAT and EU-funded Bio-Uptake, solidifying its role as a catalyst for innovation and sustainability within the plastics industry. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery

Indorama Ventures and AMB Spa Forge Partnership to Revolutionize Food Packaging with rPET
San Daniele del Friuli, Italy-based packaging producer, AMB Spa, has embarked on a groundbreaking collaboration with Bangkok’s Indorama Ventures Public Co. Ltd. The focal point of this partnership is the utilization of recycled polyethylene terephthalate (rPET) from discarded trays to manufacture film suitable for food packaging. This dynamic venture holds the potential to transform the landscape of sustainable packaging and environmental preservation.
The overarching objective of this innovative alliance is to divert an impressive volume of more than 150 million postconsumer PET trays away from detrimental fates in landfills or incineration sites, paving the way for a more eco-conscious future. Underpinning this endeavor is the cutting-edge technology developed by Indorama Ventures, which ingeniously transforms rPET flakes sourced from used trays into food-grade transparent film. This infusion of recycled content into AMB’s end products significantly bolsters the company’s commitment to sustainability. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
AMB’s Chief Procurement Officer, Paolo Cescutti, aptly underscores the pressing need for packaging solutions that resonate with contemporary consumer values. Cescutti states that today’s consumers place a premium on both sustainability and food safety. With the advent of this partnership, AMB can offer an unequivocal assurance that its food trays are not only recyclable but also uphold rigorous standards of food safety. This transformative step epitomizes AMB’s pioneering spirit, exemplified by its collaboration with Indorama Ventures.
The culmination of over six years of intensive research and development, Indorama Ventures has achieved a significant milestone in the commercial production of rPET flakes derived from postconsumer trays. This breakthrough process has the dual impact of preventing countless PET trays from succumbing to the confines of landfills or being incinerated. By adopting this recycling technology, Indorama Ventures demonstrates its unwavering commitment to sustainability, resource efficiency, and waste reduction.
D.K. Agarwal, Deputy Group CEO and Executive President of the combined PET business segment at Indorama Ventures, accentuates the transformative potential of partnerships with sustainability pioneers like AMB. Agarwal aptly characterizes these partnerships as catalysts that propel the journey towards a circular economy for PET trays. By extending the lifecycle of PET products through innovative recycling processes, this collaboration signifies a significant stride towards resource conservation and waste reduction.
Agarwal’s sentiments echo the heart of Indorama Ventures’ philosophy: a fervent endorsement of a circular economy that mitigates landfill burdens and minimizes incineration. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
The groundwork for this impactful partnership was laid with AMB’s launch of AMB TrayRevive in 2022. Designed as a brand dedicated to tray-to-tray recycling, TrayRevive embodies AMB’s holistic approach to sustainability. This initiative dovetails seamlessly with the European Union’s ambitious target of rendering all packaging recyclable and capable of conversion into recycled raw materials by 2035.
Aligned with a global commitment to elevate PET recycling rates, Indorama Ventures envisions an annual input of 750,000 tons of postconsumer PET bales by 2025. This grand vision epitomizes the company’s dedication to resource efficiency and sustainable practices, making the circular economy a reality on a global scale.
In essence, the partnership between Indorama Ventures and AMB Spa transcends traditional business collaborations. It exemplifies a shared mission to reimagine packaging, align it with modern sensibilities, and create a more sustainable future. This strategic alliance not only diverts plastic waste from its grim fate but also champions the vision of a circular economy that nurtures the planet and its resources.
Through innovation, commitment, and a shared resolve, Indorama Ventures and AMB Spa set an inspiring precedent for industries worldwide to follow suit in crafting a greener tomorrow. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery

The Eurozone was jolted by an unexpected chill as the latest PMI indices from Germany delivered a sobering reality check
The economic landscape, gauged through the lens of company purchasing managers, revealed a mixed bag of results that could potentially set off a cascade of repercussions across the continent. This unanticipated twist has sent shockwaves through the markets and raised concerns of a possible domino effect that could cast a shadow over Europe’s economic prospects.
The German manufacturing sector index, a crucial indicator of economic health, displayed a surprising uptick in August. Climbing to 43.7, it surpassed expectations set at 42.6 points, a glimmer of hope amidst a largely uncertain economic atmosphere. This ascent follows a previous mark of 42.7 in July, indicating some measure of resilience within the manufacturing domain. However, the services sector did not fare as well. In a rather bleak turn of events, the European composite PMI of services recorded a disheartening 47 points, falling short of the average analyst estimate of 48.5. This worrisome figure was further accentuated by the services sector’s purchasing managers index, which hit 48.3 against an anticipated 50.5. The symbolic threshold of 50, signifying neutrality, now feels like a distant ambition. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
Against the backdrop of these revelations, the broader implications are impossible to ignore. The immediate aftermath saw ripples across the stock market and a weakening of the Euro against the dollar. As investors grappled with the newfound uncertainty, government bonds in the Eurozone strengthened their position. Notably, the yield on 10-year bonds experienced a notable drop. These swift reactions underscore the profound interplay between economic data and market sentiment.
Perhaps the most concerning aspect of this development is the latent potential for a domino effect that could reverberate throughout Europe. The German economy, often considered the stalwart of the Eurozone, has historically held considerable sway over the economic trajectory of its neighbors. The ramifications of this latest data could be felt most acutely by countries with deep interdependencies on Germany’s economic engine. Foremost among them is Italy, a nation intricately linked to Berlin’s economic fortunes.
Cyrus de la Rubia, chief economist of HCOB, captured the sentiment aptly, stating, “Any hope that the service sector could save Germany’s economy has evaporated.” The disheartening reality is that the service sector, once seen as a potential buoy in tumultuous economic waters, now appears poised to join the manufacturing sector in a recessionary descent. The warning signs, perhaps present for some time, have crystallized into a stark narrative of economic contraction.
Collaborating in the release of this data with S&P Global, de la Rubia’s insights hint at a more ominous prospect on the horizon. The forecasting model for Germany’s GDP, which assimilates flash PMI estimates, now paints a bleaker picture than previously imagined. The projected economic fall has deepened by at least 1%, a somber revision that underscores the magnitude of the challenge ahead. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
As Europe navigates these uncharted waters, the intricate web of economic connections becomes all the more evident. The German economy, long regarded as the lynchpin of the Eurozone, holds the potential to set off a series of interconnected events that ripple across borders and economies. The recent data release serves as a stark reminder that economic health is not an isolated affair; rather, it is an intricate dance between sectors, countries, and policies.
In conclusion, the recent revelation of PMI indices from Germany has cast a chilling spell on the Eurozone. The divergence between a modest manufacturing sector uptick and a disappointing services sector performance paints a complex picture of economic dynamics. Swift market reactions and the potential for a domino effect across Europe underscore the interconnected nature of the continent’s economies. As Germany’s economic ripples spread, nations like Italy stand at the precipice of uncertainty, bracing for the impact of a potential economic downturn with far-reaching implications. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery

Economic Slowdown and Inflation Concerns Prompt ECB Caution
The European Central Bank (ECB) finds itself at a crossroads as winds of crisis sweep through the continent, accompanied by falling inflation rates. The once unequivocal trajectory toward tightening monetary policy is now subject to doubt and caution. ECB President, Christine Lagarde, has altered her tone, introducing uncertainty about a potential rate increase in September. Previously, the Governing Council’s hawks had advocated for consistent monetary tightening. However, with a noticeable cooling of inflation and a growing recognition of economic deceleration across major European economies, a more careful approach has become imperative.
Lagarde emphasized a data-driven approach, reflecting a pivotal shift in the ECB’s stance. While “core” inflation, excluding energy, remained higher than desired, recent data trends indicated a shift away from the previously aggressive stance. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
A significant contributing factor to this revised stance is the state of Germany’s economy, the largest in Europe.
The most recent data portray a struggling German industry, with both orders and production experiencing continual decline. An additional blow came from the services sector, which plunged to its lowest level in over three years. Economists like Andrew Kenningham from Capital Economics speculate that this downturn in services could signify a waning rebound in tourism, potentially leading to a Eurozone recession in the latter half of the year. Germany, bearing the brunt, is predicted to be among the most affected nations.
While the ECB’s primary mandate revolves around inflation, it cannot disregard the broader economic picture. Germany’s producer prices, a precursor to consumer prices, recorded a 6% decline in July—the first drop since 2020. This development signals potential deflationary pressures, especially in a nation where 40% of the manufacturing sector experiences lower prices than the challenging year of 2022.
The convergence of a contracting economy and descending prices in Germany underscores the need for cautious decision-making. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
Carsten Brzeski, ING’s Chief Economist, points out that the significant drop in the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) is a wake-up call for even the most resolute rate hawks. However, taking a pause in September could signal the end of the current series of rate hikes.
Global economic institutions like the IMF and OECD forecast that Germany will be the slowest-growing among major economies in the latter half of the year. Additionally, China’s economic slowdown poses a substantial risk, given its status as Germany’s primary trading partner. The country grapples with concerns of a potential exodus of industries, particularly those with high energy consumption.
Apart from elevated energy prices, burdensome bureaucracy, limited digitalization in the public sector, high taxes, and a scarcity of skilled labor hinder Germany’s economic growth. The appeal of the United States, buoyed by the Inflation Reduction Act—a comprehensive plan for green economy subsidies introduced by President Joe Biden—has led some companies to consider relocating their operations from Germany.
With a recent contraction in the services sector challenging ECB optimism regarding GDP growth, experts speculate on the central bank’s next move. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
Deutsche Bank’s Chief Economist, Mark Wall, anticipates a pause in September. However, uncertainty remains about whether inflation has reached levels deemed satisfactory by the ECB. A pause, Wall asserts, should not be misconstrued as a peak in interest rates. Notably, interest rates are already at their highest since the euro’s inception.
The mood of major central bankers could potentially offer insights into future actions. The annual Jackson Hole symposium brings together key figures like Fed Chairman Jerome Powell and ECB President Christine Lagarde. Analysts anticipate a cautious approach, with Powell likely to avoid discussing the possibility of another rate hike in the upcoming September meeting.
In conclusion, the ECB faces a complex confluence of factors: a faltering European economy, dwindling inflation, and the growing specter of recession. As the institution navigates these challenges, it must find a delicate balance between its inflation-focused mandate and the broader economic realities unfolding across the Eurozone.

Autoneum’s Impressive Sales Growth Marks Automotive Recovery and Supply Chain Relief in Europe and North America
In a promising turn of events, Autoneum, a global leader in automotive components, has reported a remarkable 24.1% surge in consolidated revenue during the initial half of 2023. The figures have surged from CHF 888.7 million to an impressive CHF 1,102.6 million. This notable upswing is attributed to multiple factors, including a noteworthy recovery within the European and North American automotive markets and the strategic acquisition of Borgers, a prominent German entity. Moreover, as supply chain bottlenecks gradually abate, coupled with an uptick in production volumes across the vehicle sector, especially in regions that were hitherto grappling with supply chain constraints, Autoneum’s outlook appears increasingly optimistic. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
Global vehicle production has also witnessed a substantial 11.8% escalation compared to the corresponding period in 2022. However, it is important to note that despite this resurgence, consumer demand remains somewhat muted due to the prevailing high vehicle prices prevalent in certain markets. The assimilation of Borgers into Autoneum’s operations has proven to be a substantial boon, contributing positively to the overall company performance from the very outset. This strategic acquisition has significantly expanded Autoneum’s operational footprint, bolstering its presence with 67 production facilities worldwide and a workforce of approximately 16,600 individuals spanning 24 countries.
An encouraging aspect is the enhanced profitability witnessed across all Autoneum business units, collectively manifesting in a CHF 33 million surge in EBIT, ultimately settling at CHF 45 million. The positive trajectory of Autoneum’s performance is reinforced by prevailing market projections. According to S&P’s current forecasts, the global automotive production landscape is anticipated to scale up by 5.7% in 2023 compared to the preceding year. While customer negotiations continue to evolve, Autoneum’s prudent strategies are poised to offset the escalating costs associated with raw materials, energy, transportation, and staff. This strategic approach positions the company favorably, projecting a total revenue range of CHF 2.4-2.5 billion for the entirety of 2023, with exchange rates remaining stable. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
Unsurprisingly, the theme of vehicle electrification remains paramount across Autoneum’s operational domains. Notably, the company has proactively ventured into producing components tailored specifically for electric vehicles. These innovative components, designed to be lightweight, contribute to extended driving ranges due to their reduced mass while also impeccably meeting the latest acoustic standards. An exemplary illustration of Autoneum’s innovation prowess is the introduction of the Ultra-Silent Tune, a revolutionary technology catering to sustainable noise mitigation. This novel, eco-friendly technology, embedded within underbody shields, efficiently curbs tire noise through the incorporation of chamber resonators. The utilization of polyester as the core material renders this noise-absorbing technology not only effective in reducing noise pollution but also remarkably conducive to enhancing driving comfort within electric vehicles. Furthermore, the material’s recyclability aligns seamlessly with Autoneum’s commitment to sustainability.
As the automotive sector navigates these dynamic times, Autoneum emerges as a frontrunner, adeptly capitalizing on market resurgence and operational enhancements. The first half of 2023 signifies not only impressive financial growth but also underscores Autoneum’s unwavering dedication to innovation, sustainability, and optimal consumer experience within the evolving automotive landscape. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
For more detailed information and insights, please visit Autoneum’s official website at www.autoneum.com.

US fiber, plastic exports decrease
Exports of both recovered fiber and plastics fell during the first six months of 2023, newly released federal trade statistics show.
U.S. companies exported 16% less fiber during the first half of 2023 than they did during the corresponding period of the prior year. Scrap plastic shipments dropped by 7%.
The Census Bureau recently released data for June exports, allowing Resource Recycling to compare statistics from the first half of 2023 to those from the prior year.
Recovered fiber exports fall
U.S. companies exported 7.29 million short tons of fiber scrap in the January-June period, not including recycled pulp. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
Among the top 10 destinations, most reduced their purchases of U.S. bales, although there were some notable exceptions in East Asia. For example, shipments to Thailand surged, rising 44% year over year and making the Southeast Asian country the second largest downstream destination for U.S. fiber bales during that period.

Navigating Europe’s Energy Dependency: Decisions on Russian LNG
The conundrum surrounding Europe’s reliance on Russian liquefied natural gas (LNG) has positioned policymakers and industries in a challenging dilemma. As the energy crisis persists, Russia’s growing LNG exports continue to bolster its revenues, prompting calls for the reduction of this dependence. While the task of diminishing reliance on Russian LNG is undoubtedly complex, it’s imperative to explore alternatives for Europe’s energy security. In this discourse, we delve into the intricacies of this issue and examine potential pathways forward. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
Amidst the ongoing energy crisis, Europe’s vulnerability to the volatile LNG market has further compounded the issue. Faced with urgent energy demands, European importers have resorted to emergency measures, including increased LNG purchases from various sources, not solely Russian gas. Despite exorbitant prices, the shift to LNG has shown relative success, with LNG’s share surpassing Gazprom’s piped gas by the close of 2022. This shift was hastened by the Nord Stream pipeline explosion in September 2022, which led to a 45% decline in Russian piped gas supplies compared to the previous year. In this scenario, LNG imports reached historic highs, underscoring the extent of Europe’s dependence on this energy source.
Nevertheless, the LNG supply chain has encountered its share of challenges. Low production growth in exporting nations, inadequate LNG tanker capacity, and fierce international competition for floating storage and regasification units have all contributed to supply chain bottlenecks. Consequently, European states have been hesitant to impose restrictions on Russian LNG, even as concerns regarding energy security and geopolitical dependencies persist. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
A noteworthy distinction arises in how Europe views Russian gas imports from different sources. Gazprom, as Russia’s pipeline gas export monopoly, is often seen through the lens of state control due to its formal ties to the Russian government. In contrast, the Russian LNG operator, formally a private entity, is de facto tightly controlled by the Kremlin. This distinction has implications for Europe’s approach to regulating these imports, especially given the historical context of sanctions targeting individuals closely connected to Russian President Putin.
Despite the ongoing Ukraine crisis, Russian LNG exports to Europe surged by approximately 20% in 2022 compared to the previous year. Remarkably, up to a quarter of LNG arriving in the Iberian Peninsula, a significant hub for Europe’s LNG capacity, originated from Russia in the first quarter of 2023. This paradoxical situation unfolds as Europe endeavors to lessen its dependence on Russian piped gas while increasing its reliance on Russian liquefied gas.
In response to the growing prominence of Russian LNG in the European market, Estonia proposed implementing price caps in February 2023 to curb funds flowing to Novatek, Russia’s LNG producer. The primary objective is to restrict the company’s profits without compromising Europe’s physical supply. While this approach mirrors the G-7’s decision to set a price cap for Russian oil, its efficacy remains uncertain due to potential implementation challenges. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
The European Commission has since engaged in discussions on various strategies to limit Russian LNG imports. However, successful execution of price caps necessitates coordinated efforts from other major gas importers and the United States to create a conducive market environment. The feasibility and effectiveness of such restrictions also hinge on several factors:
- Diversification of Suppliers: Europe’s ability to secure long-term contracts with alternative suppliers is crucial in reducing dependence on Russian LNG.
- US LNG Exports: Continuous growth in US LNG exports to Europe, despite North America’s rising gas demand, can play a pivotal role.
- Asian Competition: Competition for available LNG supplies, particularly from Asia due to China’s growing gas demand, could influence global dynamics.
While factors like the increase in US LNG exports and competition with Asia depend on international market dynamics, the first factor largely relies on strategic commercial decisions made by European gas companies. Notably, the challenge lies in these companies’ commitments to purchase Russian piped gas, even if Gazprom reduces flows. This dual commitment to both Russian and non-Russian gas might elevate market risks and costs. Circular Economy Automotive Recovery
In conclusion, the path to minimizing Europe’s dependence on Russian LNG is a multifaceted endeavor. Balancing energy security, geopolitical considerations, market dynamics, and commercial interests will be pivotal in shaping Europe’s stance. As policymakers navigate these complexities, a nuanced and collaborative approach that takes into account the interplay of diverse factors will be necessary to shape a sustainable energy future for Europe.

Circular Economy Automotive Recovery