Hydrogen vehicles – Recycled plastic reduces carbon consumption by up to 87 per cent 27-11-2023
Petrochemicals Ny66 – Polymers : PET – r-PET – Filament grade semidull chips -Filament grade bright chips – Ny6 – Ny66 – PP

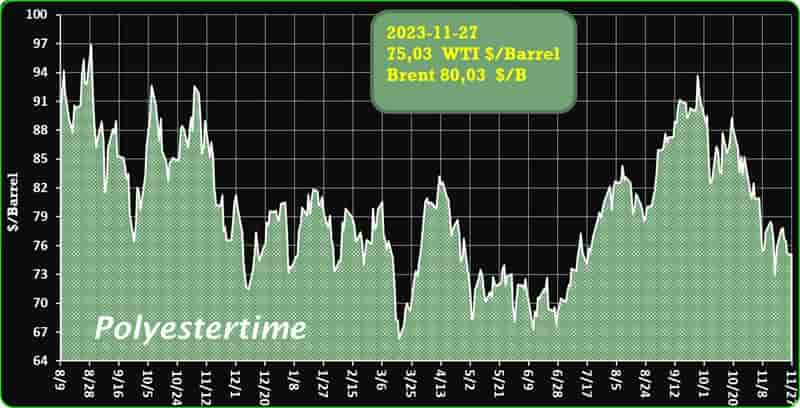
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
Recycled plastic reduces carbon consumption by up to 87 per cent
Recycling works: plastic packaging specialist ALPLA operates state-of-the-art plants worldwide under the brand ALPLArecycling for the production of rPET (recycled PET) and rHDPE (recycled HDPE). Calculation of the product carbon footprint by the independent consultancy c7-consult now provides new data for a total of four plants in Mexico and Germany. Carbon reductions of up to 87 per cent compared to virgin materials confirm the climate protection effect of recycled plastics and the ecological importance of regional bottle-to-bottle loops. Hydrogen vehicles
ALPLA processes used plastic packaging into recyclate. The recycled material produced in Mexico and Germany causes up to 87 percent less CO2 emissions than virgin material.
ALPLA is focusing on the circular economy: the global packaging specialist invests more than 50 million euros annually in recycling and uses state-of-the-art technologies to produce recycled material. With an installed and projected output capacity of 350,000 tonnes per year, the company is one of the world’s leading plastics recyclers. Analyses performed by the life cycle assessment specialist c7-consult now confirm efficient production at a total of four additional sites in Mexico and Germany. There, ALPLArecycling produces rPET and rHDPE, which produces up to 87 per cent fewer carbon emissions than virgin materials.
‘The figures confirm our path. We produce climate-friendly recycling solutions with a regional focus and convert the material into new packaging, thereby promoting the bottle-to-bottle loop. In this way, we ensure there are safe, affordable and sustainable packaging solutions all over the world,’ emphasises Georg Lässer, Director of Business Development, Procurement and Sales, Recycling, at ALPLA. Hydrogen vehicles
Circular economy pioneers in Mexico
ALPLArecycling produces 30,000 tonnes of rHDPE per year at its Toluca recycling plant in Mexico. Production in Toluca causes 0.69 kg of CO2e per kilogram. This is 70 per cent fewer emissions than with HDPE virgin material (2.32 kg of CO2e per kilogram[1]). ALPLA has been operating what was the first PET recycling plant in Latin America at the time in Toluca since 2005 within the joint venture IMER (Industria Mexicana de Reciclaje S.A. de C.V.) together with Coca-Cola FEMSA and The Coca-Cola Company. It has an annual production capacity of 16,000 tonnes of rPET. According to the analysis, production causes only 0.38 kg of CO2e per kilogram, which is 87 per cent less than virgin PET (2.90 kg of CO2e per kilogram[2]). Hydrogen vehicles
The rPET production capacity in Mexico will be increased to 51,000 tonnes next year. The PLANETA plant (Planta Nueva Ecología de Tabasco) in Cunduacán is currently being built in cooperation with Coca-Cola FEMSA. The joint venture partners are setting new collection priorities with the model of paying for the receipt of used PET bottles and with social cooperations. ‘Recycling is a key element in packaging solutions of the future. We want to convince people of the benefits and are drawing on substantiated data to do so. Exact analysis of our plants also enables us to improve our ecological footprint in a targeted manner,’ explains Carlos Torres Ballesteros, ALPLA Managing Director, Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean. Hydrogen vehicles

China in red, lithium in free fall. Here because
This financial turbulence unfolded against the backdrop of Beijing’s concerted efforts to rescue the beleaguered real estate sector, strained under the weight of mounting debt. Compounding the unease were anxieties surrounding China’s October PMI figures, slated for release the following week, following September readings that signaled a contraction in manufacturing and a deceleration in service activities.
Amidst these concerns, skepticism swirled regarding the efficacy of Beijing’s various real estate stimulus measures, including the decision to allow banks to extend unsecured short-term loans to sector companies. Hydrogen vehicles
Despite the day’s downturn, the Hang Seng index was on course for its second consecutive weekly gain, rising by approximately 1.0%.
This optimism stemmed from the hope that the Federal Reserve’s tightening trajectory might be nearing its conclusion, with the first rate cut anticipated in March 2024.
Meanwhile, Japan grappled with a surge in inflation, reaching 3.3% in October 2023, up from the previous month’s 3.0%.
This marked the highest level since July, with core inflation also climbing to 2.9%, just below the consensus of 3.0%. Hydrogen vehicles
Notably, the Bank of Japan’s 2% inflation target remained elusive for the 19th consecutive month.
In a starkly different economic arena, the price of Chinese lithium carbonate, denominated in yuan, continued its month-long descent, plummeting by 75% for the year.
An oversupply in the market exerted downward pressure on prices, prompting electric vehicle manufacturers to reevaluate their strategies.
Chinese lithium carbonate prices dipped by 2.3% on Thursday and a staggering 20% thus far in November, with the last recorded daily gain occurring on October 25th.
The spodumene, a lithium-bearing rock extracted in Australia, witnessed more than a 50% decrease in value in 2023. Hydrogen vehicles
Shifting the focus to geopolitics, Argentina’s newly elected president, Javier Milei, adopted a more tempered tone compared to his previous sharp rhetoric.
Following his victory, Milei extended well-wishes to the Chinese people, a notable departure from his earlier characterization of the Chinese government as an “assassin” during an August interview.
Milei’s gesture included responding to a congratulatory letter from Xi Jinping and hinting at the potential inclusion of former central bank president Luis Caputo in a significant economic role. Hydrogen vehicles

Hydrogen, often hailed as a beacon of eco-friendly transportation, particularly in the context of fuel cell technology
While electric cars dominate green conversations, fuel cell-powered vehicles, like the Toyota Mirai and Hyundai Nexo, are making their mark in the Italian automotive landscape. These models leverage hydrogen-oxygen reactions to generate electrical energy, offering the notable advantage of rapid refueling, with the Mirai boasting a mere five minutes for a substantial range exceeding 600 km. However, this green innovation comes at a price—both the Mirai and Nexo command high price tags of 66,000 and approximately 80,000 euros respectively. Hydrogen vehicles
Beyond these initial offerings, car manufacturers like Toyota and BMW are exploring hydrogen’s potential in different vehicle types. Toyota showcased the GR Yaris H2, integrating hydrogen as fuel while maintaining a modified turbocharged internal combustion engine. On the other hand, BMW, an early advocate for hydrogen engines since 2000, remains in the experimental phase, producing small series for testing purposes, as seen in the iX5 Hydrogen.
Despite promising strides in vehicle technology, a critical hurdle to widespread adoption is the lack of infrastructure. With only two operational hydrogen refueling stations—located in Bolzano and Mestre—accessing fuel remains a challenge for Italian motorists. Hydrogen, currently perceived as more suitable for heavy transport, is reflected in logistical decisions favoring areas like the Brenner road axis and the Trieste-to-Turin corridor. The Ministry of Transport’s 2023 ranking of 36 new projects earmarks public funding for expanding the hydrogen refueling network by 2026, encompassing regions from Valcamonica and Umbria to Puglia and Calabria. Hydrogen vehicles
Territorial imbalances compound the issue, as private mobility needs are not met uniformly across regions. Of the 36 proposed projects, only six are slated for implementation in southern regions, with Veneto leading the charge with nine refueling stations. Comparatively, Germany, a hydrogen pioneer, already boasts 92 supply points, revealing the substantial gap in Italy’s hydrogen infrastructure development. As European nations race toward hydrogen expansion goals, Italy aims for 70 stations by 2030, falling behind Germany, the United Kingdom, and France in this ambitious pursuit.
The journey toward making hydrogen a viable solution in Italy’s transportation landscape is underway, but substantial challenges must be surmounted for it to become a mainstream reality. Hydrogen vehicles
Hydrogen vehicles represent a promising yet underutilized facet of the automotive landscape, offering a unique alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars and electric vehicles
Although their popularity has been eclipsed by the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, understanding how hydrogen vehicle engines work sheds light on their potential and the challenges they face.
At the heart of hydrogen vehicles is the fuel cell, a device that enables the conversion of hydrogen into electricity through an electrochemical process. Unlike conventional internal combustion engines, hydrogen vehicles employ electric motors for propulsion. This distinction positions them as electric vehicles (EVs), despite the divergent energy source.
In a hydrogen vehicle, the journey from hydrogen gas to electrical power begins with the storage of hydrogen in a high-pressure tank. Hydrogen vehicles
This gaseous fuel is then directed to a fuel cell stack, a crucial component housing a catalyst, often platinum. As hydrogen molecules interact with the catalyst in a controlled electrochemical reaction, electrons are released, generating electrical energy.
This process is known as the proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell technology, one of the most common designs in hydrogen vehicles.
The produced electricity is subsequently harnessed to power the electric motor, propelling the vehicle forward. Remarkably, the sole byproduct of this energy conversion is water vapor, positioning hydrogen vehicles as exceptionally clean and environmentally friendly transportation options.
However, despite their potential ecological advantages, hydrogen vehicles face significant challenges hindering their widespread adoption. Hydrogen vehicles
The dearth of hydrogen refueling infrastructure poses a substantial hurdle, limiting the practicality of these vehicles for everyday consumers. Additionally, concerns regarding the flammability of hydrogen gas have contributed to apprehension surrounding its use as a fuel source.
As of now, the disparity in adoption rates between electric vehicles and hydrogen vehicles is stark. The United States, for instance, boasts over 2 million electric vehicles on its roads, dwarfing the approximately 15,000 hydrogen-powered vehicles in operation. Nevertheless, ongoing advancements in technology, coupled with efforts to expand hydrogen infrastructure, may yet breathe new life into the hydrogen vehicle revolution, offering a compelling alternative in the quest for sustainable transportation.

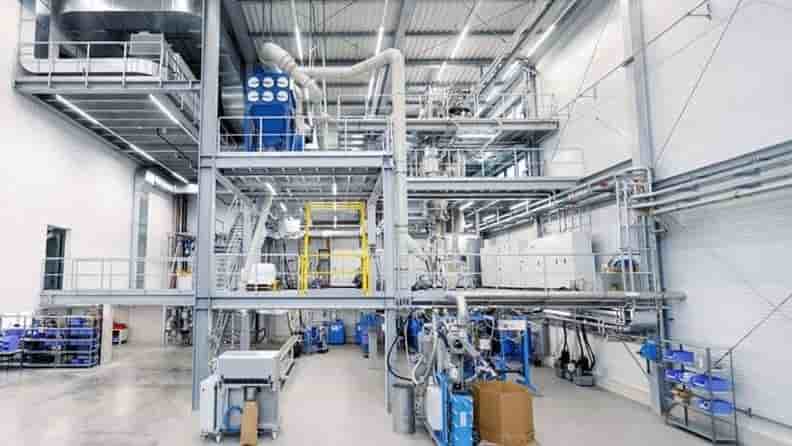
Coperion recycling innovation centre starts operations in Germany
The high-tech test centre for plastics recycling applications is located in Niederbiegen near Weingarten, Germany
Machinery producer Coperion has started operations at its plastics recycling innovation centre in Niederbiegen near Weingarten, southern Germany. Hydrogen vehicles
The Recycling Innovation Centre is situated in the immediate vicinity of Coperion’s existing test centre for Bulk Solids Handling, expanding the company’s test lab capacities in Germany alone up to 5,000 square meters.
The high-tech centre allows Coperion’s customers to test every recycling process step, from material handling and feeding to extrusion, compounding, pelletising, material postprocessing, and deodorisation. Extensively equipped recycling systems are available that can be modified in myriad ways, depending upon the specific requirements of the recyclate to be produced. Hydrogen vehicles
Machinery available include the Fluidlift ecodry for material flash drying during conveying; the Mix-a-Lot bulk solid mixer for creating pre-mixes including flakes or powders; and a ZS-B MEGAfeed side feeder, especially for extruding and compounding plastic recyclates with bulk densities starting as low as 20 kg/m³ at high throughputs.
“With this new Recycling Innovation Centre, we’re in a position where we can simulate the entire plastics recycling process,” said Massimo Serapioni, general manager of Coperion’s Recycling Business Unit. “Our customers can test the complete process, from mechanical pre-treatment of plastics in Herbold Meckesheim’s Test Centre up to compounding and pelletizing, prior to making the investment.
As a supplier of entire recycling systems, we are very proud to be able to offer our customers this enormous added value.” Hydrogen vehicles

Here is the extraordinary news: BYD, the Chinese giant, has started construction of the largest salt battery factory in the world, located in Xuzhou, between Beijing and Shanghai, with a monumental investment of 1.2 billion euros

BST India’s focus on consistent quality in flexible packaging
BST India at Food Packaging and Innovations India Summit 2023
BST India, a leading manufacturer of quality assurance systems for printing, flexible packaging, and the web-based processing industry, showcased its potential in changing the future of food packaging at the recently concluded Food Packaging and Innovations India Summit 2023 in Mumbai. BST India supported the summit as a gold partner for the event. Hydrogen vehicles
A presentation by Khushal Patel, director of sales and marketing, on ‘BST’s role in delivering consistent quality in flexible packaging’, delved into the company’s role in ensuring a standard of quality paramount in the flexible packaging industry.
The presentation explored how BST, integrated into the manufacturing process, can streamline operations, and enhance the overall quality of flexible packaging. It emphasized the importance of consistency in meeting industry standards, addressing challenges, and ultimately providing customers with products that surpass expectations.
“Our Gold Partnership and presentation at the Food Packaging & Innovations India Summit 2023 reflect our ongoing commitment to staying at the forefront of advancements in food packaging technology. By sharing our insights and experiences, we aim to contribute not only to our industry’s growth but also to the success of our valued partners and clients,” Patel said. Hydrogen vehicles
The two-day summit from 1 November in Mumbai saw the active participation of companies such as Emami, Wagh Bakari Tea, Marico, Britannia, and many more. Their presence added depth to the discussions, fostering an environment of collaboration and knowledge exchange.
The multi-channel B2B in print and digital 17-year-old platform matches the industry’s growth trajectory. The Indian, South Asian, Southeast Asian, and Middle East packaging industries are looking beyond the resilience of the past three years. They are resuming capacity expansion and diversification, with high technology and automation in new plants and projects. Hydrogen vehicles
As we present our 2024 publishing plan, India’s real GDP growth for the financial year ending 31 March 2024 will exceed 6%. The packaging industry growth will match the GDP growth in volume terms and surpass it by at least 3% in terms of nominal growth allowing for price inflation in energy, raw materials, consumables, and capital equipment.

Hydrogen vehicles
