Petrochemicals oil output – Will Saudi Arabia’s cut in oil production take oil above $100/barrel? 07-08-2023 - Arhive
Petrochemicals oil output
Petrochemicals r-PET adipic-acid – Can the car help the environment with the recycling of plastic?
Crude Oil Prices Trend
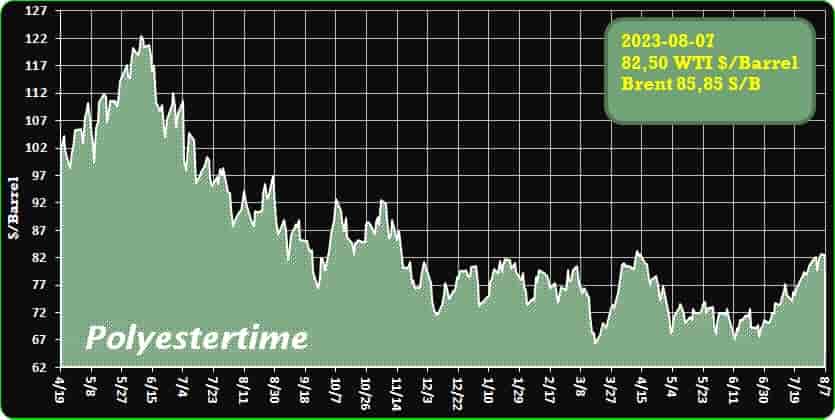
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
Oil prices experienced a significant surge in the current week due to the latest announcement from Saudi Arabia regarding yet another round of production cuts
The kingdom’s decision to reduce its oil production by one million barrels per day in September came after implementing similar cuts in both July and August. This move sent shockwaves through the oil market, leading to a 1.9% increase in U.S. crude prices, which reached a substantial $83.08 per barrel. The price of Brent crude, traded in London, also rose by 1.6% to $86.53 per barrel, marking its highest level since April.
Throughout the week, the U.S. crude benchmark experienced a notable 3% rise, while Brent crude saw an increase of almost 2%. This upward trend in oil prices brought optimism to some investors, but market analysts expressed caution, particularly regarding Russia’s pledge to cut exports by 300,000 barrels per day. Russia has a history of not fully adhering to its promised production cuts, and this skepticism influenced the outlook on oil prices. Petrochemicals oil output
Sunil Kumar Dixit, a technical chartist, shared his analysis, suggesting that the recent rally in oil prices could soon lose momentum. Dixit pointed to potential resistance levels at the 100-day simple moving average of $85.45 and the monthly middle Bollinger band of $86.90. Despite these potential hurdles, he still believed there was room for some short-term upside momentum.
As the market continued to monitor developments, some experts anticipated a correction in oil prices that might provide an opportunity for a renewed rally. Key indicators for such a correction included a drop below the 5-day exponential moving average of $81.45, signaling possible exhaustion in the upward trend.
The subsequent OPEC+ meeting, conducted via Zoom, was relatively uneventful, given that Saudi Arabia had already announced its production cut prior to the meeting. Nevertheless, the market remains closely tied to OPEC’s decisions and any potential future reductions in oil production. Petrochemicals oil output
Looking ahead, global oil prices are expected to remain volatile as they are subject to a myriad of factors, including geopolitical tensions, supply-demand dynamics, and the ongoing energy transition. Concerns over the stability of some oil-producing regions and the potential impact of unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or political crises, further contribute to the uncertainty surrounding oil prices.
Investors and industry players are keeping a close eye on OPEC’s actions, as the organization plays a significant role in influencing oil prices through its decisions on production levels. Any deviations from OPEC’s projected production targets could result in market fluctuations and price volatility.
Moreover, the global transition towards cleaner and renewable energy sources is an essential factor shaping the future of the oil market. As countries strive to reduce their carbon footprints and implement more sustainable practices, the demand for fossil fuels may gradually decrease, putting additional pressure on oil prices.
In conclusion, the recent surge in oil prices following Saudi Arabia’s production cut announcement has brought both hope and caution to the market. While some anticipate continued momentum in the short term, others remain skeptical due to potential resistance levels and concerns over Russia’s compliance with production cuts. The market’s performance in the coming weeks and months will largely depend on OPEC’s decisions and how various geopolitical and environmental factors unfold. Investors and stakeholders should brace themselves for continued volatility and closely monitor developments to make informed decisions in this ever-changing landscape of the global oil market. Petrochemicals oil output

ADBioplastics, a Spain-based additives and bioplastics manufacturer, has made significant strides in the development of sustainable packaging solutions
Among its innovations is a bioplastic called PLA-Premium, which boasts improved processability and is 100% compostable under industrial conditions, similar to regular PLA. This achievement has been recognized and certified by TÜV Austria, affirming that the single-use product will disintegrate within a mere three months.
The rising awareness of environmental concerns, coupled with the European Union’s plastics strategy demanding that all packaging be reusable or recyclable by 2030, has spurred manufacturers to explore bio-based and compostable alternatives to conventional oil-based plastics in the packaging industry. Petrochemicals oil output
Polylactic acid (PLA) has emerged as a popular bioplastic choice, typically derived from renewable sources such as corn, sugarcane, or beets. However, PLA requires a thermal trigger of at least 50°C to initiate degradation, making it practically non-biodegradable in landfill or marine environments.
To address this limitation, ADBioplastics has introduced its industrially compostable PLA-Premium. The company achieved this breakthrough by incorporating an impact modifier called ADBio PLA+ into virgin PLA, enhancing the material’s processing properties. In a collaboration with Capricho Andaluz, a subsidiary of Borges International Group and a renowned oils and dressings producer, ADBioplastics is now manufacturing single-serve packaging for extra virgin olive oil using their new bioplastic.
In their official statement, ADBioplastics confirmed that these single-use products will be initially marketed under the Capricho Andaluz and Borges brands, with plans to introduce new references to the market in the near future. With TÜV Austria’s certification for industrial compostability, PLA-Premium can be disposed of in organic waste bins and treated at industrial composting facilities where available, ensuring a sustainable end-of-life scenario. Petrochemicals oil output
ADBioplastics offers a variety of PLA-Premium grades, catering to different industrial applications of extrusion and injection. The material demonstrates up to a 70% improvement in elongation at break compared to virgin PLA, yielding a more elastic and less brittle end product. Moreover, PLA-Premium boasts cycle times and density comparable to polyethylene terephthalate (PET) while maintaining a similar level of transparency, making it suitable for various packaging applications in the food, beverage, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and other industries.
Crucially, PLA-Premium complies with the applicable European legislation, allowing its safe use in food contact applications. This significant advantage further reinforces its viability for a wide range of packaging uses, meeting both sustainability and regulatory requirements.
As ADBioplastics forges ahead with its commitment to environmentally friendly solutions, the introduction of PLA-Premium has the potential to revolutionize the single-use packaging landscape. By offering an industrially compostable alternative to conventional plastics, the company contributes to reducing the environmental impact of packaging waste and aligns with the EU’s sustainability goals. Petrochemicals oil output
In conclusion, ADBioplastics’ development of PLA-Premium, an industrially compostable single-use packaging material for olive oil and other applications, marks a significant step towards a more sustainable future. With TÜV Austria certification and compliance with European legislation for food contact, PLA-Premium presents a promising alternative to traditional plastics, contributing to the global efforts to mitigate plastic pollution and promote eco-friendly practices in the packaging industry.

Stellantis, the giant born from the merger of FCA and PSA, has envisioned a brilliant idea that could revolutionize the automotive industry – the transformation of hybrids into biofuels
In Brazil, this visionary concept has come to life through the introduction of the new Bio-Hybrid engines, featuring mild hybrid, full hybrid, and plug-in systems.
At the forefront of this groundbreaking technology is the Bio-Hybrid, a remarkable innovation that electrifies existing flex engines, which can run on petrol or ethanol, or a combination of both fuels. This cutting-edge engine technology was unveiled at the Betim automotive hub in the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais. The development of Bio-Hybrid technology originated in Brazil, fostered by the collaborative platform “Bio-Electro,” involving Stellantis’ Tech Center for South America, suppliers, researchers, and other partners. Petrochemicals oil output
Stellantis has introduced three distinct Bio platforms in Brazil, all supplemented by a fourth, fully electric architecture:
- Bio-Hybrid Technology: This platform features a multifunctional electrical device that replaces the alternator and starter motor, generating additional torque for the internal combustion engine and energy for a small 12-volt lithium-ion battery. These advancements lead to enhanced performance and reduced fuel consumption, with an impressive power output of up to 3 kW.
- Bio-Hybrid e-DCT: This platform integrates two electric motors – the first replaces the traditional alternator and starter motor, while the second, larger motor couples with the transmission. Together, they power a 48-volt battery, providing a higher level of electrification.
- Bio-Hybrid Plug-in: Equipped with an accumulator rechargeable via regenerative braking, the internal combustion engine, or an external source, this platform incorporates an electric motor that directly supplies energy to the car’s wheels.
The primary focus of Stellantis’ Bio-Hybrid concept is to address Brazil’s unique circumstances and work towards decarbonization in the country. Brazil stands out as a nation where ethanol is already used in 80% of the vehicle fleet, thanks to Flex Fuel technology. Stellantis recognizes that ethanol, when combined with electrification, can significantly contribute to reducing CO2 emissions. Moreover, this combination represents a competitive and cost-effective alternative for decarbonizing transportation, especially compared to full electric vehicles that can still be expensive in developing countries like Brazil and other South American states. Petrochemicals oil output
To validate the potential of this innovative technology, Stellantis conducted dynamic tests with a vehicle powered by four distinct energy sources. The results were striking, indicating that ethanol propulsion emits 18% less CO2 than a comparable electric vehicle powered by European energy sources, and it is also 60% cheaper than using petrol.
The introduction of the Bio-Hybrid engines in Brazil marks a significant milestone in Stellantis’ commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility. By leveraging the country’s existing ethanol infrastructure and integrating advanced electrification solutions, Stellantis is paving the way for a cleaner and more efficient future of transportation.
In conclusion, the emergence of Stellantis’ Bio-Hybrid technology in Brazil represents a game-changing step towards decarbonization and sustainable mobility. By harnessing the power of biofuels and advanced electrification, Stellantis is proving that innovation and collaboration can drive positive change in the automotive industry, benefitting both the environment and consumers alike. As this visionary concept gains traction, it has the potential to reshape the global automotive landscape and lead the way towards a greener and more sustainable future for all. Petrochemicals oil output

Driving Sustainability in India: Insights from Sulzer Chemtech Leadership at Pune Customer Engagement Evening
In an era marked by heightened environmental awareness and the urgent need to address carbon emissions and resource depletion, industries worldwide are facing increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. In India, a country with a plethora of heavy industries, the imperative to track carbon footprints and embrace sustainability has become even more critical. Recognizing this need, Sulzer Chemtech organized the Customer Engagement Evening in Pune on the 18th of July 2023, focusing on the theme of enabling a low-carbon society. The event brought together industry professionals, including Sulzer leadership and prominent figures, to discuss sustainable innovations and energy transitions within and beyond India. Petrochemicals oil output
Dr. Uwe Boltersdorf, the Division President of Sulzer Chemtech, emphasized the significance of political measures and regulations to drive holistic sustainability in India. He advocated for imposing appropriate regulations on heavy industries while incentivizing them, leading to a win-win situation for corporations, citizens, and the government. Drawing inspiration from Europe’s success, Dr. Uwe proposed that India could adopt similar measures to encourage the manufacturing of bio-based and biodegradable products, with Sulzer Chemtech’s support in implementing modern technologies.
During the event, Dr. Sander van Donk, the Global Head of Mass Transfer Components and Services at Sulzer Chemtech, shed light on how India can benefit from Sulzer’s CCUS (carbon capture, utilization, and storage) solutions. He explained the company’s equipment designed to absorb carbon dioxide from emissions, particularly in industries like cement manufacturing and power generation that contribute significantly to India’s carbon footprint. By capturing and storing carbon in a manner that facilitates the development of beneficial resources, Indian industries can reduce their reliance on precious natural resources and embrace sustainability.
Mr. Pramod Khade, Head of Sulzer India Pvt Ltd, celebrated India’s potential and talent. He proudly announced that Sulzer Chemtech India not only ranks among the largest exporters of chemicals but also boasts a wealth of talent. With the Indian workforce’s inherent eagerness to learn and their relentless dedication, training and nurturing Indian talent to become global industry leaders is a rewarding endeavor for the company.
Sulzer Chemtech’s Customer Engagement Evening served as a platform for disseminating awareness about the importance of sustainability and fostering collaborative efforts to address environmental challenges. As global corporations seek to align themselves with sustainable practices, Sulzer Chemtech’s commitment to driving positive change in India’s industrial landscape was evident throughout the event. Petrochemicals oil output
The discussions and insights presented during the evening underscored the urgent need for a collective commitment to reducing carbon footprints and implementing sustainable practices in India’s industries. The event’s emphasis on political measures and regulations echoes the sentiment that governments must play a pivotal role in steering industries towards a greener future.
The spotlight on Sulzer’s CCUS solutions demonstrated that innovation and technology can serve as powerful allies in the fight against climate change. By capturing and repurposing carbon emissions, Indian industries can make significant strides towards reducing their environmental impact.
Moreover, Mr. Pramod Khade’s acknowledgment of India’s abundant talent pool showcased the country’s potential to not only become a global player in industries but also to lead sustainable initiatives. The combination of talent and innovative solutions offered by Sulzer Chemtech holds the promise of transforming India’s industrial landscape into a beacon of sustainability.
The Sulzer Chemtech Customer Engagement Evening in Pune stands as a testament to the company’s commitment to promoting sustainable practices in India and beyond. By fostering dialogue and collaboration among industry leaders, the event has undoubtedly sparked a renewed sense of purpose in driving the nation towards a greener, more sustainable future. Petrochemicals oil output
As industries worldwide grapple with the challenge of balancing growth with environmental responsibility, events like these serve as crucial stepping stones towards a brighter and more sustainable tomorrow. The exchange of ideas, expertise, and experiences at the Customer Engagement Evening undoubtedly contributed to the collective effort to create a low-carbon society for the betterment of all. Sulzer Chemtech’s leadership in organizing and participating in such initiatives demonstrates its dedication to being a catalyst for positive change in the realm of sustainability and environmental stewardship.

The Future of Reusable and Refillable Packaging: Overcoming Challenges for Sustainable Growth
The push for sustainability has driven global brands to adopt strategies aimed at reducing their usage of virgin plastics. Reusable and refillable packaging is one such approach gaining attention, with companies like Nestle, PepsiCo, Mars, P&G, Coca-Cola, and Kraft Heinz leading the charge. Despite its promise, this innovative packaging concept faces challenges in meeting consumer expectations and achieving widespread adoption. Smithers, a US-based consultancy firm specializing in the packaging, paper, and print industries, sheds light on the five key strategies being deployed by these brands to achieve their plastic reduction goals and explores the future prospects of reusable and refillable packaging. Petrochemicals oil output
The Quest for Plastic Reduction
In response to mounting pressure to curb plastic waste, global brands have been exploring various strategies to achieve their plastic reduction goals. Smithers highlights five primary approaches:
- Switching to Fiber-Based or Biodegradable Packaging: Some companies have started transitioning from traditional plastics to more eco-friendly alternatives, such as fiber-based or biodegradable materials.
- Increasing Post-Consumer Recyclate (PCR) Content: Brands are incorporating higher amounts of post-consumer recycled materials into their packaging through product design and chemical recycling.
- Deploying Reusable and Refillable Packaging: One of the promising solutions is the implementation of reusable and refillable packaging systems, which can significantly reduce packaging waste.
Current Status and Projected Growth
The market for reusable and refillable packaging has been steadily growing, with global sales reaching $42 billion in 2022. This represents a modest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.0% since 2017. Smithers predicts a further acceleration in growth, with an annual CAGR of 4.9%, expected to reach $53.4 billion by 2027.
Business Models for Reusable and Refillable Packaging
Various business models are being explored to facilitate the adoption of reusable and refillable packaging. These models include refill at home, return from home, refill in-store, return in-store, and deposit return schemes. Such initiatives align with the European Commission’s proposal for revising EU legislation on packaging and packing waste, targeting a 15% reduction in packaging waste per Member State per capita by 2040 compared to 2018 levels. Petrochemicals oil output
Challenges Hindering Widespread Adoption
While the potential for reusable and refillable packaging is evident, it faces significant challenges:
- Consumer Convenience: Consumers have grown accustomed to the convenience of single-use packaging, making the transition to reusable and refillable systems less appealing.
- Supply Chain Adaptation: Implementing these new packaging systems requires substantial changes to existing supply chains, potentially increasing the carbon footprint through additional transportation.
- Cost: Despite performing at a similar level to virgin plastic, reusable and refillable packaging remains costlier. The cost parity with traditional packaging is not expected to be achieved by 2030.
- Limited Availability: The lack of commercial-scale availability is an obstacle to wider adoption, as companies may be hesitant to invest in unproven systems.
- Consumer Perception: Modest consumer perception of reusable and refillable packaging also presents a challenge, as awareness and education efforts are required to change attitudes.
Success Stories and Ongoing Efforts
Despite these challenges, some companies have taken steps towards adopting reusable and refillable packaging. Nestle, for instance, introduced a steel refillable container for their Nesquick powdered chocolate milk brand. However, trials have not met the company’s re-purchase and return rate goals, largely due to consumer expectations of high convenience at low costs. Petrochemicals oil output
Conclusion
The shift towards reusable and refillable packaging is a significant step in reducing plastic waste and achieving sustainable packaging solutions. While the industry faces challenges in consumer convenience, supply chain adaptation, cost, availability, and perception, the potential for positive change is evident. Moving forward, a systems-level approach that incorporates reverse logistics and reduced carbon transportation options is necessary. Additionally, a fundamental shift in consumer attitudes and behaviors is crucial to making reusable and refillable packaging a widely adopted and successful solution for a more sustainable future.

How the Auto Industry Is Embracing Plastic Recycling
The dual needs to reduce the consumption of new resources in creating plastic products and to reduce the eventual creation of plastic waste when products have been used drive the pursuit of recycled materials in the auto industry.
Plastics are pervasive in modern vehicles, creating the opportunity for significant reuse of plastic. We’ve seen this in the case of the Ford Bronco Sport, which employs recycled plastic from recovered fishing nets in its wiring harness clips. The aim is to expand use of the material into other applications such as engine covers. The ultimate potential is for as much as 700 lbs. of plastic per vehicle to be created from recycled materials, according to Ford technical expert Alper Kiziltas, with about 10 percent of that eligible to be made using the recycled fishing net material. Petrochemicals oil output
Reusing Wreckage
Some more visible applications of recycled plastics in new automotive parts are in the cars’ interiors, where consumers will see the materials during every drive. Audi has partnered with LyondellBasell, the world’s largest producer of polymer products, to produce plastic seat belt buckle covers for the Q8 e-tron EV using plastic recovered from parts of crashed Audis.
“As part of the PlasticLoop project, we are working with Audi to establish an innovative closed-loop process, recycling plastic automotive parts for use in new vehicles,” said Erik Licht, LyondellBasell Advanced Polymer Solutions New Business Development Director. “For the first time, we are using chemical recycling to recycle mixed automotive plastic waste into plastic granulate for automotive interior applications,” he said. “The plastic granulate is then used in the production of the seatbelt buckle covers for the Audi Q8 e-tron.”
“We want to use secondary material wherever it is technically possible, ecologically feasible, and of course, environmentally friendly,” said Philip Eder, project manager for circular economy procurement strategy at Audi.
“Recycling is not that easy, because as you can imagine, if something is mixed up, it is not that easy to separate it again.” Petrochemicals oil output
PET Water Bottles
The polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic used in plastic bottles is a more homogenous source of post-consumer plastic that Audi is also using. The company uses that PET in combination with residual textiles, and fabric selvages recovered from manufacturing plants to create Kaskade, a new fabric material that provides the soft surface and three-dimensional texture of natural fiber materials such as wool.
Kaskade cannot be made from entirely recycled materials, but the company strives to maximize the recycled portion of the material mix, reports Christine Maier of Audi Design. “We used only as much new polyester and as many new resources as was technically necessary,” she said. “The result is a fabric that is reminiscent of wool and natural fibers, and has a very pleasant feel.”
The recovered selvage fabric comes from a plant making automotive products, so the material is already automotive-grade. Audi separates these into black and white components, using them to create an anthracite-colored blend that requires no additional dye. “We leave out another chemical process, which is better for the environment,” noted Maier. Petrochemicals oil output
Audi said that the company strives to procure well-sorted PET waste that is of high purity and then they process to avoid any minor impurities in the filament process. This could result in fiber inhomogeneity and potentially make the fabric unattractive. An advantage of using recycled PET is that it is abundant, which is an important consideration for an industry still bedeviled by supply headaches.
Finding the Right Mix
The selvage material, PET, and new polyester combine to create new yarn that is used to make the Kaskade seat cover fabric. The final product contains 15 percent selvage material, 35 percent PET, and 50 percent new polyester. “We performed a lot of tests to see how high the portion of selvages can be while ensuring the fabric still looks flawless,” Maier explained.
Audi started making seat covers using recycled materials for the fourth-generation A3. Those seat covers contain as much as 89 percent recycled material, using plastic from 45 1.5-liter PET plastic bottles. Then there are the additional 62 PET bottles that are recycled for the car’s carpet.
The carpeting and floor mats in the Audi e-tron GT are made of Econyl – a material that consists of 100 percent recycled nylon fibers from production waste, fabric and carpet scraps, or old fishing nets. Petrochemicals oil output
Audi acknowledges that one of the hurdles en route to a circular economy is that the cost of these recycled materials is higher than for virgin materials. Energy consumption in the process is about the same as for virgin materials, so efficiency is not an obstacle, according to the company.
Faurecia’s Seat for the Planet
Auto industry supplier Faurecia aims to use recycled materials throughout the entire seat and to make those same materials easier to separate at the seat’s end-of-life for future reuse and recycling. The company’s “Seat for the Planet” is a project that has created a lightweight seat that is about 15 percent lighter than a conventional seat
It is made from ten modules each made entirely of a single material, made from bio-sourced or recycled materials, or from materials that are compatible for recycling, according to project manager Marthin Frétigné. Conventional seats are made using between 100 and 150 separate parts. The polyurethane used in seat cushions is especially challenging to replace with something earth-friendly. “This material performs well but is very difficult to recycle” said Frétigné. “So we had to replace it with a technical solution called Auraloop, incorporating high-performance PET combined with a new transformation process”. Petrochemicals oil output

Petrochemicals oil output
