PET Bottles EV Cars – Rethinking Polymer Waste Biodegradation: An Innovative Perspective 14-08-2023 - Arhive
PET Bottles EV Cars
Petrochemicals PET Bottles – Filament grade Bright chips domestic market

Crude Oil Prices Trend
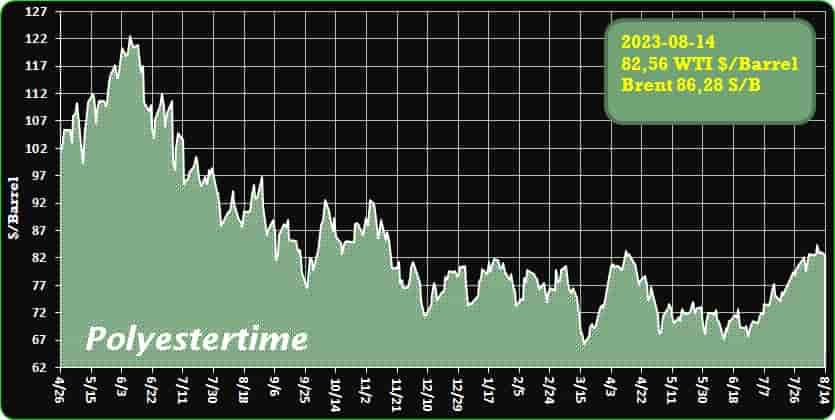
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
Volkswagen, a pioneering force in the automotive industry, is taking another electrifying step forward by incorporating Hyundai’s cutting-edge batteries into their upcoming line of electric cars
This innovative collaboration stems from the partnership between Volkswagen and Hyundai Mobis, the Korean manufacturer’s division at the forefront of battery technology. The focus of this alliance centers on Hyundai Mobis’ Battery System Assembly (BSA), a technological marvel that encapsulates a battery pack, a state-of-the-art battery management system (BMS), and various complementary components, seamlessly engineered to ensure the utmost safety and efficiency in electric vehicles (EVs). PET Bottles EV Cars
This strategic decision carries significant implications, as it diverges from the norm of keeping all aspects of production in-house. Instead, Volkswagen is tapping into Hyundai Mobis’ expertise to equip their next generation of electric cars with this advanced BSA technology, redefining the narrative of competition between these two industry giants. What makes this choice even more intriguing is the backdrop of Volkswagen’s recent partial acquisition of the Chinese company Xpeng, a move that grants them access to a treasure trove of Asian technological prowess.
The heart of this collaboration lies in the integration of Hyundai Mobis’ BSA into the core platform of Volkswagen’s upcoming vehicles. This integration is not merely conceptual; it embodies a tangible commitment as Hyundai Mobis is setting up a new production base in the vicinity of Volkswagen’s forthcoming gigafactory in Spain. While exact specifics are shrouded in anticipation, this development heralds a new era of cross-industry collaboration, merging the strengths of two global powerhouses to propel the electric car evolution.
Venturing beyond their existing production lines in Korea and the Czech Republic, Hyundai Mobis is venturing into new horizons with production centers earmarked for the United States and Indonesia. This move speaks volumes about the global vision of Hyundai Mobis, positioning itself as a key player in the surge toward greener transportation solutions. The company’s comprehensive battery systems, aptly coined as xEVs, encompass a spectrum of green vehicles, spanning from hybrids to pure battery electric cars. This holistic approach underscores their commitment to catering to the diverse needs of the modern eco-conscious consumer. PET Bottles EV Cars
As Hyundai Mobis anticipates an influx of orders for electric vehicle components across the global market, it is clear that this collaboration is not just an isolated event, but a stepping stone towards a broader transformation of the automotive landscape. This ambitious venture aligns with the broader industry trend of seeking external collaborations to drive innovation and efficiency. Amidst this backdrop, Volkswagen’s choice to source vital EV components externally signals a strategic shift, potentially influenced by both financial opportunities and evolving market dynamics.
In conclusion, the Volkswagen-Hyundai Mobis partnership represents a seismic shift in the automotive world. The melding of German engineering prowess with Korean technological excellence embodies a new era of cooperation that transcends traditional boundaries. As the automotive landscape evolves at an electrifying pace, collaborations like these will likely become the norm, driving the industry toward a sustainable and interconnected future. PET Bottles EV Cars

Rethinking Polymer Waste Biodegradation: An Innovative Perspective
In the global pursuit of resolving the plastic waste crisis, scientific attention has increasingly turned toward leveraging biological mechanisms for sustainable solutions. Two distinct methodologies have emerged from these efforts. The first involves the utilization of microorganisms, fungi, and related organisms, colloquially termed “bugs,” to consume plastic waste. The second approach, less conventional but remarkably promising, centers on the application of biochemical agents, specifically enzymes produced by these “bugs,” to catalyze the breakdown of plastics.
Enzymes, as protein-based catalysts, facilitate targeted chemical reactions without undergoing consumption within the process. PET Bottles EV Cars
Recent strides made by researchers at the University of Texas at Austin (UT-Austin) exemplify the potential of the latter approach. Employing the principles of synthetic biology, these scientists have engineered an enzyme with the capability to disintegrate polyester materials into their constituent components. This enzymatic process ingeniously dismantles the ester bonds inherent in polyester, thereby enabling the retrieval of original chemical constituents for subsequent reincorporation into new polyester products.
In sharp contrast, the first approach – involving microbial degradation – has demonstrated less precise control over the degradation process, often yielding severely compromised end-products unfit for meaningful reuse. A prime example of this outcome is observed in compostable plastics, which transform into compost incapable of reverting to plastic. Enzymatic degradation, however, offers a higher degree of specificity, targeting particular chemical reactions while leaving others unaffected.
The UT-Austin researchers have effectively demonstrated this enzymatic loop by not merely hypothesizing its viability but substantiating it through a sequential process involving degradation of samples into monomers, followed by the reformulation of polyester plastic. Nonetheless, while this innovative breakthrough is noteworthy, its economic feasibility remains uncertain. While details are scant, the patent application may already be in progress, reflecting the complexity of translating scientific achievements into commercially viable technologies. PET Bottles EV Cars
Initial skepticism may arise regarding the potential economic practicality of this enzymatic approach. At first glance, it seems to introduce an additional layer of complexity into the standard recycling loop – production, sale, use, retrieval, and reprocessing – by introducing degradation and repolymerization stages. In essence, this poses the question: what is the value added by these supplementary steps? After all, commencing with PET and concluding with PET essentially maintains the status quo, prompting contemplation on the problems addressed or the benefits accrued.
However, further contemplation unveils a more nuanced perspective. The recycling stream frequently harbors post-consumer waste laden with contaminants stemming from inadequate separation of recyclables, combined with impurities like dirt and food residues. Recycling operators are tasked with managing this heterogeneous input, necessitating considerable expertise and resources. Yet, the enzymatic approach might hold the promise of ameliorating this challenge in the future.
The specificity of enzymatic reactions implies a potential to selectively target and degrade polyester amidst a mixture of contaminated plastics. In this scenario, the liquid monomers coalesce, accumulating at the base of the mixture. In an even more visionary scenario, a mix of plastics could potentially be subjected to multiple enzymes, each tailored to disintegrate a specific plastic type. The resultant process would yield monomers while leaving behind materials that should not have been part of the recycling stream, rendering the remaining waste truly non-recyclable. PET Bottles EV Cars
Undoubtedly, this speculation requires caution, and it is contingent upon economic viability. The idea of addressing diverse plastics through tailored enzymatic breakdown holds potential for polyester, marking an encouraging beginning. Ultimately, the crux of the matter remains rooted in economic considerations, necessitating a patient wait-and-see approach. The prospects are alluring, yet the bridge between scientific innovation and scalable commercial implementation demands meticulous planning, research, and evaluation.
In the perpetual quest to manage polymer waste sustainably, the enzyme-driven depolymerization pathway brings to light a novel dimension. While skepticism regarding its economic viability is reasonable, the potential to revolutionize the treatment of contaminated plastic waste is undeniable. This enzyme-mediated disassembly aligns with the specificity required to address a heterogeneous plastic waste stream. Nevertheless, a comprehensive assessment encompassing economic, environmental, and technical aspects will ultimately determine whether this innovative approach realizes its promise and reshapes the landscape of polymer waste management.

The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) has provided insights into the expected expansion of Non-OPEC oil supply in the year 2023
In its Monthly Oil Market Report for August, OPEC reveals that Non-OPEC oil supply is anticipated to witness a growth of 1.5 million barrels per day (mb/d) during the upcoming year. This prediction marks a slight adjustment from the previously assessed figure of 1.4 mb/d. The report, recently obtained by the News Agency of Nigeria (NAN), sheds light on various aspects of the global oil landscape.
Non-OPEC oil producers encompass a range of countries that are engaged in crude oil production but are not part of the OPEC group, including notable entities like the United States, Canada, and China. These nations, alongside shale oil producers, contribute significantly to the global oil supply. Among these, the U.S. stands as the foremost oil producer, followed by Canada and China. The projected expansion of Non-OPEC oil supply in 2023 is attributed to several factors, with the primary contributors expected to be the United States, Brazil, Norway, Kazakhstan, Guyana, and China.
In contrast, the report predicts the most substantial decline in oil supply to come from Russia. PET Bottles EV Cars
Despite these forecasts, the report also acknowledges the presence of uncertainties. It points to potential fluctuations in U.S. shale oil output and unplanned maintenance activities in the year 2023. These factors could introduce variations in the actual oil supply growth as compared to the projections. Looking ahead to 2024, the report maintains a forecast of 1.4 mb/d for non-OPEC oil production growth, consistent with the previous assessment.
The drivers for oil supply growth in 2024 are expected to mirror those of 2023, with the United States, Canada, Guyana, Brazil, Norway, and Kazakhstan leading the way due to existing project ramp-ups. In contrast, Mexico and Azerbaijan are anticipated to experience the most significant declines in oil supply during that period. Additionally, the report highlights the growth trajectory of OPEC Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs) and non-conventional liquids, which are projected to reach an average of 5.4 mb/d in 2023 and 5.5 mb/d in 2024.
A retrospective glance at July reveals that OPEC-13 crude oil production underwent a decline of 836 tb/d on a month-on-month basis, averaging at 27.31 mb/d. These figures are drawn from available secondary sources. Moving on to global oil demand, the report underlines a projection of 2.4 mb/d growth in 2023, aligning with the assessment made in July. However, the report specifies that upward revisions to the first quarter of 2023, driven by actual data from the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) America and OECD Europe, were offset by downward revisions to the second quarter of 2023, primarily centered in Europe and Other Asia.
Delving into regional dynamics, the report highlights that within the OECD region, oil demand is poised to rise by 74 tb/d, reaching an average of 46.0 mb/d.
Simultaneously, in the non-OECD region, total oil demand is projected to grow by nearly 2.4 mb/d, averaging 56.0 mb/d. Looking ahead to 2024, the report maintains a positive outlook with a projected global oil demand growth of 2.2 mb/d, in line with previous forecasts. PET Bottles EV Cars
Geographically, the OECD region is expected to experience a growth of around 0.3 mb/d, with the largest contribution coming from OECD Americas. The non-OECD region is predicted to be the major driver of growth, expanding by approximately 2.0 mb/d. Within this context, China, the Middle East, and Other Asia are set to be significant contributors, with additional support from India, Latin America, and Africa.
In conclusion, the OPEC Monthly Oil Market Report for August presents a comprehensive overview of the projected developments in the Non-OPEC oil supply sector for 2023 and beyond. The report underscores the complexities of the oil market, as well as the influential factors that can shape supply and demand dynamics.
While certain uncertainties remain, these projections serve as a valuable guide for industry stakeholders and analysts navigating the intricate landscape of global oil production and consumption. PET Bottles EV Cars

Revolutionizing Car Recycling through Big Data: A Path to Sustainability
In an era dominated by the urgency of climate change, the imperative for sustainable practices across industries is undeniable. Within this context, the automobile sector has come under intense scrutiny for its ecological footprint. However, a ray of hope shines through as big data technology emerges as a transformative force in enhancing car recycling processes, ushering in a more sustainable future.
The concept of big data, denoting the vast and incessant flow of information, has triggered profound shifts across various domains, and the sphere of auto recycling is no exception. Its integration in this sector is fostering operational efficiency, waste reduction, and informed decision-making, thus orchestrating a paradigm shift in the recycling landscape.
The intricate process of car recycling encompasses several stages, spanning from initial disassembly to the ultimate disposal of residual materials. Each stage produces a trove of data, which, when subjected to thorough analysis, can unveil insights into process efficiency. PET Bottles EV Cars
Harnessing the might of big data empowers auto recyclers to identify operational bottlenecks, target areas for enhancement, and instigate changes that amplify efficiency while mitigating environmental repercussions.
Predominantly, big data’s prowess materializes through predictive analytics. By mining historical data, recyclers can prognosticate forthcoming trends and patterns. For instance, dissecting data pertaining to the types of vehicles entering the recycling stream enables forecasted demand for specific parts. This acumen informs purchasing decisions, thwarting overstocking and subsequently curbing waste accumulation.
Furthermore, big data serves as a catalyst for optimizing inventory management. Real-time tracking and analysis of available parts vis-à-vis their turnover rate empowers recyclers to ensure the right parts are accessible at the right junctures. This dual-benefit approach not only amplifies customer satisfaction but also economizes storage space, thereby augmenting overall efficiency. PET Bottles EV Cars
Waste management emerges as another domain revolutionized by big data’s influence. Scrutinizing data encompassing waste categories and volumes spawned during recycling operations unearths avenues for waste reduction and heightened environmental performance. Unveiling patterns, it may become evident that specific processes yield redundant waste, which can then be restructured or replaced with greener alternatives.
Embracing big data bolsters compliance with stringent environmental regulations. Thorough tracking and analysis of emissions and waste disposal data ensure alignment with legal mandates, sparing recyclers from exorbitant penalties while contributing to a cleaner ecosystem.
Beyond operational enhancements, big data’s insights ripple into marketing strategies. A deep understanding of customer preferences and behaviors empowers recyclers to tailor their offerings and communication tactics, effectively aligning with customer needs.
In summation, the multifaceted impact of big data on refining car recycling processes reverberates profoundly. From ameliorating operational effectiveness to ensuring regulatory adherence, its potential merits are monumental. As the auto recycling landscape evolves, big data’s role is poised to grow even more indispensable. Employed judiciously, it has the potential to steer the industry towards a future characterized by both sustainability and profitability. PET Bottles EV Cars

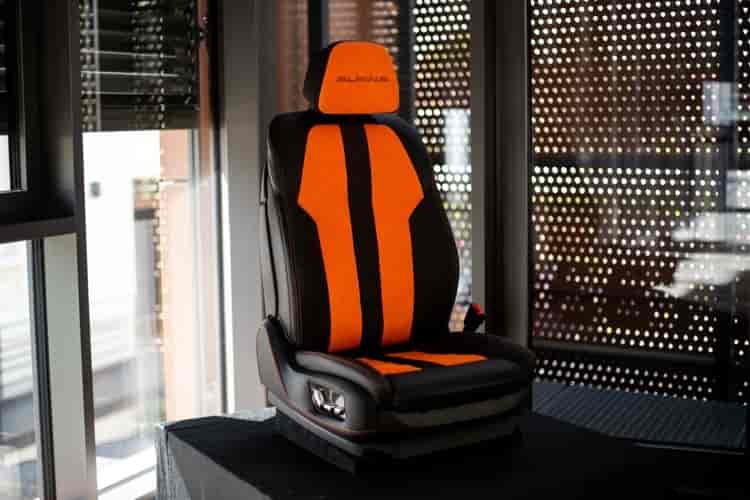
Vibrant Colors Take Center Stage in Upmarket Automotive Interiors, as Alcantara Unveils Innovative Concepts
For decades, the automotive industry’s preference for upmarket car interiors has predominantly revolved around the classic hues of black, grey, and anthracite. However, a striking shift is now reshaping this longstanding trend, as vibrant and bold colors emerge as the new vogue. This transformation was prominently highlighted at a summer festival held in July, where Alcantara, a prominent player in luxury automotive upholstery, unveiled a groundbreaking “screaming orange” concept car seat. This innovative creation emerged from a collaborative effort with Alpina, a renowned components manufacturer headquartered in Buchloe, Germany.
Andrea Boragno, the Chairman and CEO of Alcantara, emphasized the brand’s proactive engagement with the automotive industry to discern nascent trends from their inception. Previously, vibrant colors were relegated to bespoke domains or limited edition models. However, a seismic shift is underway, propelling these vivid shades into the limelight of mainstream design. The summer festival, which also marked the commencement of the 2023 German Car of the Year (GCOTY) award program, served as the perfect platform to showcase this transformative shift. Boragno underscored how an array of fresh patterns is surfacing, complemented by meticulously laser-cut embellishments that breathe new life into interior aesthetics. PET Bottles EV Cars
Among the contenders for the prestigious German Car of the Year title are several car models featuring Alcantara interiors. Notable mentions include the BMW Alpina B5 GT, Alpina’s B4, the Opel Astra GSe, and Peugeot’s E-2008. Boragno expressed immense pride in Alcantara’s capacity to deliver exclusive bespoke solutions, enriched by their adaptable material’s expansive potential for customization. He highlighted the culmination of this collaboration, presenting a final product that boasts an infinite spectrum of colors, textures, and finishes—a tangible testament to the synergistic partnership between Alcantara’s design team and its counterparts within the automotive industry. Boragno stressed that these exclusive and unparalleled custom creations can effortlessly meet the demands of even the most intricate projects.
In alignment with its pioneering stance as a carbon-neutral manufacturer since 2009, Alcantara has also introduced an innovative milestone in its material offerings. A special variant composed of 68% certified post-consumer recycled polyester has made its debut in Germany. This advancement has received certification from the Recycled Claim Standard (RCS), a benchmark established by Textile Exchange. With an eye on the future, Alcantara aims to incrementally augment the proportion of recycled polyester content in the years to come, underscoring their commitment to sustainability and environmental stewardship.
This pursuit of sustainability extends to Alcantara’s carbon neutrality certification, which is rooted in the practice of offsetting greenhouse gas emissions through verified and certified offsetting projects. This enduring dedication to minimizing its carbon footprint is an integral aspect of Alcantara’s corporate ethos, underscoring the brand’s alignment with environmentally conscious practices. PET Bottles EV Cars
In conclusion, the world of luxury automotive interiors is undergoing a vivid transformation, as bold and vibrant colors rise to prominence. Alcantara’s recent collaboration with Alpina has resulted in the unveiling of a “screaming orange” concept car seat, heralding the onset of this transformation. From the perspective of both design and sustainability, Alcantara is at the forefront, championing innovative materials and practices. As the automotive industry evolves, Alcantara continues to set new standards, ensuring that the interiors of tomorrow’s cars are as strikingly unique as they are environmentally responsible.

Enhancing Electric Vehicle Sustainability through Circular Economy Principles
The quest for sustainable transportation has prompted a comparison between internal combustion engine vehicles (ICE) and electric vehicles (EV), revealing that both possess intricate supply chains that cast considerable environmental footprints. Within this context, experts have been advocating for the integration of circular economy principles, which revolve around the concepts of reduction, reuse, and recycling of materials. This strategic approach is perceived as pivotal to augmenting the sustainability of EVs and steering them toward becoming a cornerstone solution for climate change mitigation.
While the automotive industry is a notable contributor to global carbon emissions, accounting for approximately 10% of the total, the imperative shift from ICE to EVs has emerged as a pivotal step in addressing this environmental challenge. Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that both ICE and EVs have substantial environmental ramifications, intricately woven into their supply chains and production processes. In this light, the principles of a circular economy, which envisions a closed-loop supply chain that operates on renewable energy and emphasizes waste minimization, have garnered significant attention as a linchpin to curbing the adverse climate impacts associated with the automotive sector. PET Bottles EV Cars
In the pursuit of a low-carbon mobility ecosystem and the avoidance of catastrophic global warming scenarios, the adoption of circular economy tenets in EV manufacturing becomes paramount. Shifting the focus from the vehicles themselves to their production processes is an essential facet of this transition. A concerted effort to mitigate embedded emissions within EV supply chains, along with a comprehensive strategy to address the carbon footprint associated with the sourcing and fabrication of diverse car components, serves as the cornerstone of the circular approach.
However, circularity’s influence extends beyond the realms of recycling and material loops. The automotive industry’s conventional paradigm, characterized by its heavy reliance on resource-intensive practices, warrants a broader reevaluation. As experts contend, it is imperative to reexamine prevailing vehicle dimensions, foster public transportation systems, encourage vehicle sharing models, and ultimately reduce society’s dependence on private automobiles. By recalibrating societal norms and aspirations, this holistic approach not only curbs material demand but also curtails the overarching environmental repercussions of automotive culture. PET Bottles EV Cars
Presently, the circularity metrics for both ICE sedans and battery EV sedans remain suboptimal, underscoring the pressing need for industry-wide improvements. The augmentation of circular economy practices necessitates a multifaceted strategy that encompasses prolonging the operational lifespan of vehicles, recuperating EV batteries for reuse in secondary applications, and amplifying the recycling rates of end-of-life vehicles. The recycling process itself, although a key aspect of circularity, is not without its challenges. Downcycling, a recycling technique that entails the reuse of materials but at a diminished quality level, presents a substantial hurdle in this trajectory.
Moreover, the global transition to vehicle electrification is characterized by a significant imbalance, disproportionately impacting economically disadvantaged nations with emissions, pollution, and recycling quandaries. Addressing this equity concern is integral to the broader pursuit of sustainable mobility on a global scale.
In sum, the integration of circular economy principles constitutes a linchpin in elevating the sustainability of electric vehicles and ameliorating the environmental toll of the automotive industry. PET Bottles EV Cars
This transformation necessitates comprehensive changes spanning the entire supply chain spectrum – from the initial procurement of raw materials to the intricacies of production processes and, ultimately, the management of end-of-life vehicles. A systemic approach that not only advocates for circularity but also prioritizes public transportation and endeavors to reduce the stranglehold of automobiles on modern society is paramount in achieving substantial emissions reductions and effectively addressing the multifaceted environmental challenges that persist. By adhering to these principles, the automotive industry can genuinely pave the way for a greener and more sustainable future.

PE film recycling r-PET – Will hydrogen cars be important competitors to electric cars? 12-08-2023
PET Bottles EV Cars
