Recyclable packaging
Crude Oil Prices Trend
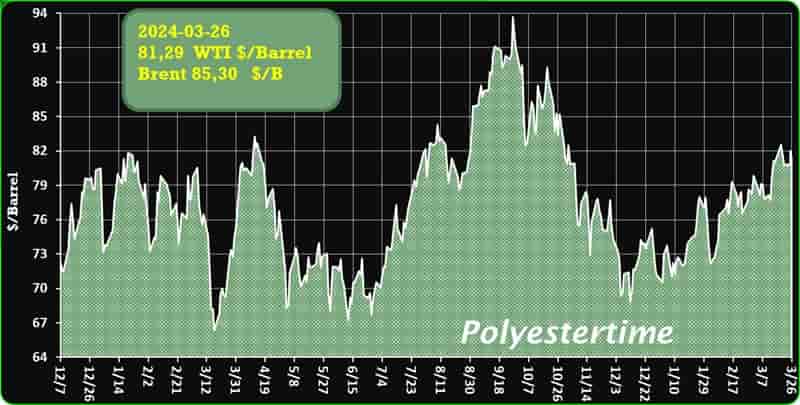
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
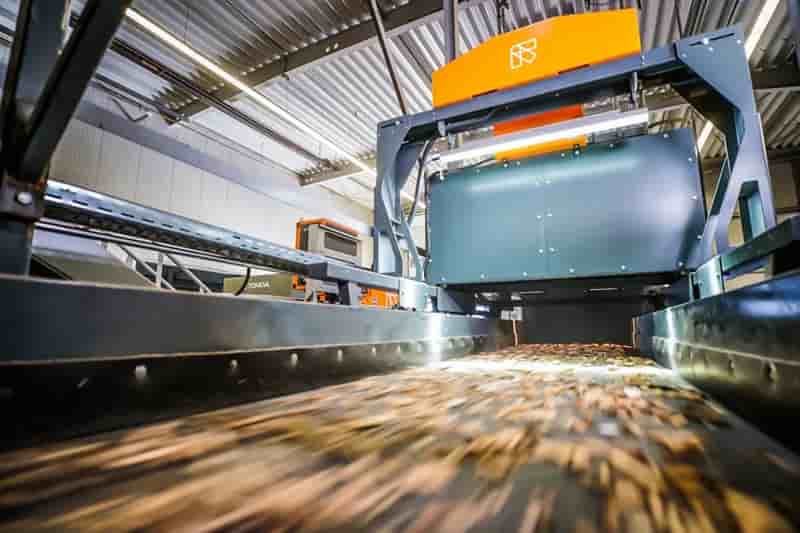
UNSW collaborating with FP Paradigm on new recyclable packaging technique
UNSW researchers, in collaboration with FP Paradigm, have devised a groundbreaking method for recycling plastics, offering a significant advancement in the recycling landscape. This innovative process efficiently converts various forms of plastic waste into polymer nanoparticles suspended in water, presenting a promising avenue for enhanced recycling endeavors.
The resulting nanoparticles can be extracted for reuse in manufacturing new consumer goods or utilized in applications such as asphalting and waterproof coatings, even eliminating the need for separate dye treatment. Recyclable packaging
Spearheaded by Professor Per Zetterlund and Dr. Vipul Agarwal from the School of Chemical Engineering, this collaboration targets PET recycling, a major global challenge. By licensing relevant aspects of the UNSW patent to FP Paradigm, the initiative aims to revolutionize PET recycling, potentially mitigating the significant energy and resource requirements of conventional methods.
Paco Industries, acting as FP Paradigm’s research and development subcontractor, recently secured a deal with the Arnott’s Group to explore implementing this technology across their product range. Recyclable packaging
This method, applicable to a variety of plastics including polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and PET, shows promise in reducing polymer degradation during recycling. UNSW researchers anticipate that their technique could enable multiple cycles of plastic recycling without mechanical or chemical degradation, offering a more sustainable approach. Moreover, it streamlines the recycling process by eliminating the need for extensive cleaning and separating polymers from additives like dyes. Arnott’s Group recognizes the potential of this method to isolate and reclaim PET for food-grade packaging, reflecting their commitment to innovative sustainability practices. PET, a widely used plastic, faces challenges due to contamination, hindering efficient recycling; however, this collaborative effort seeks to address these obstacles and usher in a new era of sustainable plastic reuse. Recyclable packaging

Tomra equips Autosort sorting systems with artificial intelligence
Tomra has implemented artificial intelligence in its Autosort sorting systems, allowing it to separate food packaging from non-food packaging with greater precision and speed. This advancement, presented at the headquarters in Koblenz, Germany, is part of the GAINnext program, which uses deep learning models.
The main objective is to encourage closed-circuit recycling, such as that of plastic bottles, to obtain increasingly pure materials at the end of the selection process. This complies with EU regulations, which require a higher percentage of recycled material in packaging, even those intended for food. Recyclable packaging
Through the use of near-infrared sensors, visual spectrometry and other sensing methods, Autosort can quickly distinguish various types of packaging, including separating films from rigid containers. The addition of an RGB camera and the implementation of AI algorithms enable even more precise separation, distinguishing between food and non-food packaging even within similar plastic fractions.
This system can also be installed on existing machines, guaranteeing a separation accuracy of over 95%. It is capable of learning over time and can be trained to detect specific fractions or contaminants in the waste stream. Recyclable packaging
Artificial intelligence is already operational in numerous sorting plants, demonstrating a notable improvement in overall performance and opening up new opportunities in the field of recycling and resource recovery.
Turkey’s central bank responded to worsening inflation by raising the policy rate from 45% to 50%, a 500 basis point increase
This adjustment aims to address the 67% inflation rate recorded last month, which exceeded expectations. To support this move, the bank emphasized its commitment to maintaining a tight monetary stance until a substantial and consistent decrease in monthly inflation is evident.
Additionally, the bank announced changes to its monetary policy operational framework. The overnight borrowing and lending rates will now be set 300 basis points below and above the one-week repo auction rate, respectively. Recyclable packaging
Despite resilient domestic demand, inflationary pressures persist due to factors such as services inflation stickiness, elevated inflation expectations, geopolitical risks, and food prices. The central bank’s release underscored the necessity of sustaining the tight monetary stance until inflation trends downwards and expectations align with forecasted ranges.
Looking ahead, the central bank anticipates disinflation in the latter half of the year. This forward-looking perspective suggests a cautious optimism regarding the efficacy of the rate hike in stabilizing inflationary pressures. Recyclable packaging

APR report studies pyrolysis as a complement to mechanical recycling for FFP plastic
The Association of Plastic Recyclers (APR) has released a report that models the potential of pyrolysis technologies – as a complement to mechanical recycling – to recycle FFP back into plastic resins to be remanufactured into new plastic products. Prepared by Eunomia Research & Consulting, How to Scale the Recycling of Flexible Film Packaging: Modeling Pyrolysis’ Role in Collection, Quantity and Costs of a Comprehensive Solution, details the opportunities for increased FFP recovery volumes, the logistics, and costs necessary to get materials to pyrolysis and other reprocessor markets, as well as the package design and policy necessary for change. Recyclable packaging
FFP packaging is a significant and growing segment that includes a broad array of snack packaging, pouches, bread bags, and other applications. While the challenges and potential opportunities for recycling FFP packaging have been discussed for nearly a decade, the industry is now at an inflection point for these materials. Several countries and U.S. states are setting recycling goals for FFP, and numerous brand companies have publicly committed to producing only reusable, recyclable, or compostable packaging by 2030.
While over 1.1 billion pounds of polyethylene film were recovered for recycling in 2021, the vast majority of flexible film packaging is not recycled. Recyclable packaging
More…

Electric car manufacturers are actively exploring future technologies to enhance their vehicles, contemplating whether lithium-ion batteries still hold potential for advancement
While current dominance rests with liquid electrolyte lithium-ion batteries, research is shifting towards sodium-ion and solid electrolyte lithium-ion alternatives. However, skepticism exists regarding further enhancements to existing lithium batteries, presumed to have reached near-maximum development.
Despite doubts, scientists persist in refining liquid electrolyte lithium-ion batteries, acknowledging room for improvement in this established yet evolving technology. Safety, charging speed, and capacity retention under low temperatures remain prominent challenges. Recyclable packaging
Addressing these concerns, a team led by Chong Yan and Jia-Qi Huang from the Beijing Institute of Technology, published a breakthrough in Nature. Their research introduces a novel electrolyte solution, showcasing exceptional performance in testing.
Their findings reveal that incorporating organic solvents significantly enhances ion mobility within the electrolyte, leading to accelerated charging. Notably, these solvents mitigate capacity loss even at extreme temperatures, down to -80°C.
Fluoroacetonitrile, a specific solvent employed, features smaller molecules than conventional solvents. These molecules envelop lithium ions, facilitating their swift movement through the electrolyte. Tests demonstrate a remarkable fourfold increase in ionic conductivity compared to standard batteries, with operational capacity unaffected even in freezing conditions. Recyclable packaging
DOMOTEX Middle East is the leading event for the carpet and flooring industry in the Middle East. It focuses on machine-made carpets, textile carpets and handmade carpets. Oerlikon’s Polymer Processing Solutions division and its joint venture partner BB Engineering will also be on hand to provide information about their sustainable machines and plant technologies at the ATAG Export & Import stand E10.
The company will be presenting trade fair visitors with complete solutions ranging from melt to yarn, fibers and nonwovens. Recyclable packaging
“Our customers are showing great interest in factory projects that cover everything from our in-house polycondensation plant or extrusion to textured yarn and the corresponding digital solutions. This holistic approach enables us to supply all process steps from a single source and to guarantee coordinated technology that ensures the high quality of the yarn produced,” explains Sales Director Jilali Lakraa.
More…

“First plastic demonstrated to not create microplastics” has been tested
Even when it’s ground into microparticles, 97% of an algae-based plastic biodegrades in compost and water in under seven months, a new study has reported. The researchers hope their plastic will eventually replace existing petroleum-based ones, which have caused concern due to their effects on health and the environment.
In recent years, there has been a great deal of chatter about – and research into – microplastics, the tiny, almost indestructible fragments shed from everyday plastic products. Much of that research has focused on devising ways of collecting and removing microplastics from the environment to prevent the health problems they can cause. Recyclable packaging
In a new study, researchers from the University of California, San Diego (UC San Diego) and materials-science company Algenesis have attacked the problem from another angle, developing a plant-based polymer that biodegrades, even when it’s ground into a microplastic, in under seven months.
“We’re just starting to understand the implications of microplastics,” said Michael Burkart, professor of chemistry and biochemistry at UC San Diego, Algenesis co-founder and one of the study’s authors. “We’re trying to find replacements for materials that already exist, and make sure these replacements will biodegrade at the end of their useful life instead of collecting in the environment. That’s not easy.” Recyclable packaging
More…

CO2 capture – Composites continue to face challenges in Europe, marked by a notable downturn last year despite global expansion 25-03-2024
Recyclable packaging








