rPET bottles Sustainability – Recycle Revolution in Global PET Bottle 10-07-2023 - Arhive
rPET bottles Sustainability
Petrochemicals BGPET – Slight increase in polyester -Still weak nylon – Oil increase, petrochemical products will also increase?

Crude Oil Prices Trend
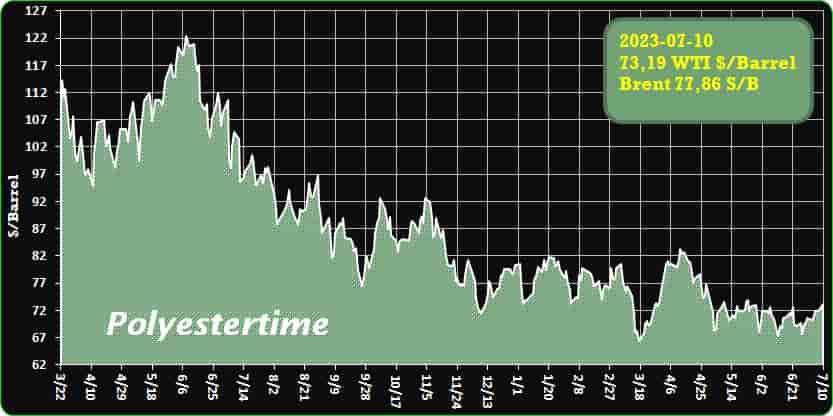
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
rPET bottles Sustainability
LyondellBasell completes acquisition of Mepol Group
LyondellBasell has completed the acquisition of Mepol Group, a manufacturer of recycled, high-performing technical compounds located in Italy and Poland. As a result of the deal, which was announced in March, Mepol S.r.l. and its subsidiaries Polar S.r.l. and Industrial Technology Investments Poland Sp.z.o.o, will be subsidiaries in LyondellBasell’s Advanced Polymer Solutions (APS) business unit.rPET bottles Sustainability
“The acquisition is forward-thinking and aligned with our commitment to a circular economy,” said Torkel Rhenman, executive vice president of the firm’s Advanced Polymer Solutions unit. “With Mepol’s deep expertise in recycled compounds and LyondellBasell’s strategy and scale, we see significant opportunities to accelerate the growth of our APS business by leveraging macro trends in circularity and creating solutions for everyday sustainable living.”
LyondellBasell’s APS segment produces and markets compounding solutions, such as polypropylene compounds, engineered plastics, masterbatches, engineered composites, colours and powders. rPET bottles Sustainability
The company is actively working to build a portfolio of sustainable solutions to meet growing demand from the market. The company is pursuing three different routes to develop these materials: via mechanical recycling, advanced recycling, and through the use of renewable-based feedstocks. Polymers made using these technologies are marketed under the Circulen brand.
The company is committed to producing and marketing at least 2 million metric tons of polymers from recycled or renewable-based sources annually by 2030 to meet its customers’ needs.
To that end, LyondellBasell purchased Veolia’s 50% share in the two companies’ jointly owned Quality Circular Polymers (QCP) BV recycling facilities, which has locations in Belgium and the Netherlands, in April of this year. LyondellBasell offers QCP polymers under its CirculenRecover brand.rPET bottles Sustainability
LyondellBasell is also in the engineering phase of a project that will see the construction of an advanced recycling plant at its Wesseling, Germany, site, based on its proprietary MoReTec technology. Start-up is planned for end of 2025 with a capacity of 50,000 tonnes per year. The feedstock produced will be converted at the LyondellBasell Wesseling site into new CirculenRevive polymers. rPET bottles Sustainability

Renewable energy and nanotechnology have joined forces to create ultra-light solar cells, a groundbreaking innovation by MIT scientists
These solar cells, as thin as a human hair, have the potential to revolutionize the field of photovoltaics by turning any surface into a source of energy.
Traditional photovoltaic systems have often faced challenges due to the weight and size of the panels, along with architectural constraints in certain regions. MIT’s nanotechnology breakthrough addresses these issues, as their ultra-light solar cells are incredibly thin and lightweight, weighing only 13 grams per square meter. The key material used in these cells is Dyneema, which is renowned for its strength and is commonly used in fabrics and bulletproof vests. rPET bottles Sustainability
What sets these solar cells apart is not only their reduced weight but also their enhanced efficiency. They weigh 100 times less than traditional solar panels while producing 18 times more energy per kilogram. This increased efficiency is achieved through the use of printable electronic inks in their creation. Moreover, the flexibility of these cells allows them to be applied to various surfaces such as camping towels, boat sails, and drone wings. rPET bottles Sustainability
The applications of these ultra-thin solar cells are vast. They hold the potential to transform any surface into an energy generator, leading to a widespread adoption of renewable energy and a significant reduction in environmental impact. While full-scale production may require time, the installation, laying, and transportation of these ultralight solar cells will be simpler compared to traditional panels.
The impact of this innovation extends beyond buildings and surfaces. Electric cars could benefit from constant recharging through these solar cells, reducing charging costs. Furthermore, industries with high electricity consumption, such as factories and companies, could cover their surfaces with these cells, potentially revolutionizing the energy transition. rPET bottles Sustainability
In conclusion, MIT’s ultra-light solar cells represent a remarkable advancement in photovoltaics. Their thinness, lightness, and flexibility make them suitable for various applications, paving the way for a future where renewable energy is seamlessly integrated into our everyday lives.
Ampacet, a global leader in masterbatch solutions, has unveiled AA Scavenger 0846, an innovative additive specifically designed to diminish acetaldehyde levels in PET and rPET bottles, while preserving the desirable sensory qualities of water
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is one of the most widely used thermoplastics globally, finding extensive applications in bottles, containers, trays, and various food and beverage packaging. However, the usage of PET for water packaging comes with a potential drawback of acetaldehyde (AA) contamination. AA is a byproduct that can be generated during the thermal degradation of PET, often occurring during the extrusion or injection molding processes. rPET bottles Sustainability
Ampacet’s AA Scavenger 0846 acts as a highly effective agent to scavenge and remove acetaldehyde, allowing manufacturers to control and decrease its presence in bottle walls. This safeguarding action helps protect the contents of the bottles, preventing contamination and maintaining the desired taste. Remarkably, even at low addition rates, Ampacet AA Scavenger 0846 can reduce acetaldehyde migration by up to 80%, ensuring the preservation of product quality and safeguarding the reputation of brands.
In addition to its immediate benefits, AA Scavenger 0846 contributes to the advancement of circular economy initiatives. By controlling acetaldehyde migration, this innovative additive enables the use of higher proportions of recycled PET in preforms and bottles, without compromising the taste of the final product. rPET bottles Sustainability
To learn more about AA Scavenger 0846, please reach out to marketing.europe@ampacet.com.

Scientists at the University of Colorado (CU) Boulder have made a significant breakthrough in recycling polyethylene terephthalate (PET) by harnessing an electrochemical process
Through a combination of chemical reactions and an electrical charge, the researchers were able to break down waste PET into its molecular building blocks within minutes. In their experiments, small bits of PET were mixed with a specialized molecule, and a small electric voltage was applied, resulting in a color change as the PET disintegrated. The findings of this study, published in the journal Chem Catalysis, offer promising prospects for the future of PET recycling. rPET bottles Sustainability
Lead author Phuc Pham and his team ground up PET bottles and blended the powder into a solution, to which they added a molecule called [N-DMBI]+ salt. When electricity was introduced, this molecule acted as a “reactive mediator” that donated an extra electron to the PET, causing the plastic grains to break apart. While the exact mechanisms of these reactions are still being explored, the researchers successfully broke down the PET into its fundamental components, which could be reclaimed and potentially used to create new products.rPET bottles Sustainability
Using simple laboratory equipment, the researchers were able to break down approximately 40 milligrams of PET over a span of several hours. However, they acknowledge that further optimization and scaling up of the process are necessary before it can be implemented on an industrial scale. Co-author Oana Luca envisions the potential of this technology extending beyond PET recycling alone. She imagines a future where various types of plastics could be simultaneously broken down using electrochemical methods, enabling the extraction of valuable molecules from massive garbage patches in the ocean.rPET bottles Sustainability
In summary, the development of an electrochemical process by CU Boulder chemists has revolutionized PET recycling, allowing for the rapid breakdown of waste PET into its molecular building blocks. Although more research and refinement are needed, this breakthrough holds great potential for industrial-scale recycling and the recovery of valuable materials from plastic waste.

In 2023, there has been a growing focus on chemical recycling and its regulation in various states across the United States
The debate revolves around whether chemical recycling should be classified as manufacturing or waste management. Currently, 24 states have passed bills considering chemical recycling as manufacturing, which subjects it to less stringent environmental regulations compared to waste management facilities.
However, some states have attempted to pass laws classifying chemical recycling as waste management, despite the materials not counting towards recycling goals set by each state.rPET bottles Sustainability
Proponents of chemical recycling argue that classifying it as manufacturing reduces barriers for new technologies and better describes the processes involved.
They believe that advanced recycling is necessary alongside mechanical recycling to meet recycling targets, especially for packaging materials like pouches and films. On the other hand, environmentalists who oppose this classification prefer chemical recycling facilities to adhere to higher environmental standards and prove themselves.
Chemical recycling, also known as advanced recycling, encompasses a range of processes that use heat, pressure, and solvents to break down polymer chains into liquids or gases. These byproducts can then be processed into fuels, oils, waxes, new plastics, or other chemical products.rPET bottles Sustainability
The 2023 legislative session has witnessed significant activity regarding chemical recycling. Fifteen bills related to chemical recycling were introduced across the nation. Thirteen of these bills aimed to classify chemical recycling as manufacturing, while two bills in Maine and New Hampshire sought to do the opposite.
Indiana, Kansas, and Utah enacted laws classifying chemical recycling as manufacturing, with nearly identical language. Texas and Louisiana passed bills that not only regulated chemical recycling but also included the products of chemical recycling in future recycled-content mandates.rPET bottles Sustainability
Several bills failed to advance, including those in Alabama, Alaska, Nebraska, Nevada, New York, Maine, and Virginia. The American Chemistry Council (ACC) counters pushback by providing research and information demonstrating that these facilities comply with environmental regulations and have lower emissions. ACC also organizes visits for lawmakers and stakeholders to observe the facilities firsthand.
Some bills are still active in New Hampshire, New Jersey, and North Carolina, which seek to regulate chemical recycling as manufacturing.
ACC supports legislation that recognizes chemical recycling as manufacturing, as these facilities receive sorted plastics and process them into liquid commodities, serving as an alternative to raw materials. They also advocate for including chemical recycling in recycling goals and targets, especially as states consider extended producer responsibility and recycled content mandates. ACC anticipates similar movement at the federal level to establish a national regulatory framework that supports both advanced and mechanical recycling.rPET bottles Sustainability
However, there are also opposing voices at the federal level. The Break Free From Plastic Pollution Act, which has been introduced in different forms, seeks to impose more permitting requirements on chemical recycling facilities without classifying the technology as recycling. Additionally, 35 members of Congress urged the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to regulate chemical recycling as combustion, citing concerns about toxic emissions from these facilities. In response, the EPA decided to continue applying current Clean Air Act requirements for pyrolysis. rPET bottles Sustainability
Critics of chemical recycling argue that the term is broad and covers unproven technologies that have yet to be scaled up. They emphasize the need for innovation in mechanical recycling, such as removing toxic chemicals and addressing microplastics in effluent.
In summary, chemical recycling policy activity is increasing in 2023, with debates focusing on whether it should be classified as manufacturing or waste management. Various states have passed legislation, while others have attempted to regulate chemical recycling differently. Proponents argue that it complements mechanical recycling, while critics raise concerns about environmental and social impacts. The legislative landscape continues to evolve at both the state and federal levels, with ongoing discussions and actions shaping the future of chemical recycling regulation. rPET bottles Sustainability

The global PET bottle recycling market is experiencing remarkable growth, fueled by the increasing demand for sustainable packaging solutions and growing environmental concerns
Government initiatives aimed at promoting recycling activities are also contributing to the market’s expansion. It is projected that the market size for PET bottle recycling will reach USD 6.75 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.5% during the forecast period. The market’s potential in various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Latin America, has been highlighted in the report. The recommendations put forth emphasize the need to enhance collection and sorting infrastructure, raise consumer awareness, and foster collaborations among key stakeholders to improve recycling rates.rPET bottles Sustainability
PET bottle recycling has gained significant popularity due to its environmental advantages and cost-effectiveness. The market can be divided into two segments based on the recycling process: chemical and mechanical methods. The chemical process involves depolymerization of PET bottles to produce new PET products, while the mechanical recycling method entails grinding and melting the bottles to create new packaging materials. rPET bottles Sustainability
The PET bottle recycling market finds applications in various sectors such as food and beverages, personal care, pharmaceuticals, consumer goods, and others. This wide range of applications ensures a steady demand for recycled PET products, thereby contributing to the growth of the recycling industry. rPET bottles Sustainability
Regulatory and legal factors play a crucial role in shaping the PET bottle recycling market. Governments worldwide are implementing stringent regulations to promote recycling and establish a sustainable environment. For instance, some countries have enforced bottle deposit schemes, where consumers are required to pay a deposit for each PET bottle they purchase, which can be redeemed upon returning the empty bottles for recycling. Additionally, initiatives and policies are being implemented to control illegal dumping and encourage responsible waste management. These factors create a favorable market environment, motivating businesses to invest in recycling infrastructure and adopt sustainable practices. rPET bottles Sustainability
In conclusion, the PET bottle recycling market is experiencing significant growth due to various recycling processes and applications across multiple sectors. The support from regulatory and legal frameworks worldwide further enhances market conditions for the recycling industry, driving sustainability and ensuring a greener future.