Red-Sea crisis – Amidst prevailing market weakness, Saudi Arabia has announced a reduction in key crude prices for buyers across all regions in February 08-01-2024
Red-Sea crisis
PET-Bottle Nylon – Germany delays plastic tax to 2025

Crude Oil Prices Trend
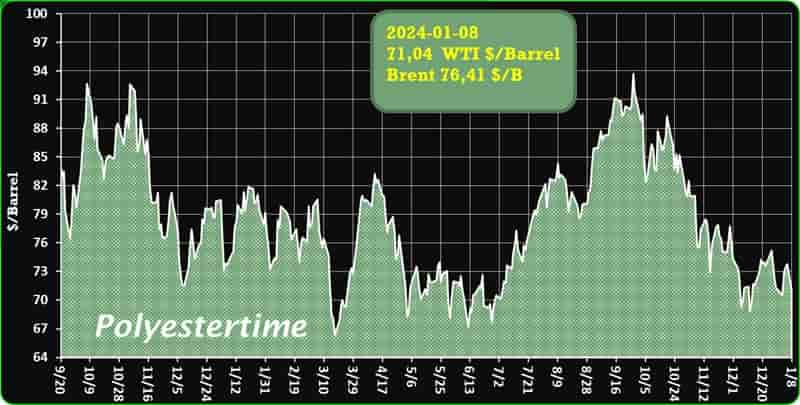
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
Amidst prevailing market weakness, Saudi Arabia has announced a reduction in key crude prices for buyers across all regions in February
This decision encompasses the primary Asian market, where oil prices for the flagship Arab Light have been lowered by $2 to $1.50 above the benchmark. This adjustment is more substantial than the estimated $1.25 reduction projected in a Bloomberg survey of refiners and traders. Saudi Aramco, the state producer, has also implemented price cuts for February deliveries to Northwest Europe, the Mediterranean, and North America.
The oil industry traditionally experiences decreased consumption during February and March, as refiners often conduct periodic maintenance by temporarily shutting down some facilities. Concurrently, a surplus in global supply, including contributions from the United States, heightens the risk of an oversupply. Consequently, the OPEC+ group, led by Saudi Arabia and Russia, extended output cuts into the current year. Red-Sea crisis
In 2023, global crude prices registered a decline for the first time since 2020. Despite ongoing geopolitical concerns such as the Israel-Hamas conflict and escalating turmoil in the Middle East, as well as Houthi militant attacks in the Red Sea, the market has not witnessed significant disruptions in supply.
The OPEC+ group’s production cuts aim to prevent an accumulation of oil in storage amid apprehensions of a sluggish global economy affecting demand. Saudi Arabia bears the major responsibility, voluntarily implementing cuts of 2 million barrels per day through the first quarter, potentially extending into subsequent periods. Red-Sea crisis

Wendel completes sale of Constantia Flexibles to One Rock affiliate
The move follows a definitive agreement signed by the parties in August 2023.
An affiliate of private equity investment management company, One Rock Capital Partners, has completed the acquisition of packaging company Constantia Flexibles.
One Rock acquired Constantia from European investment company Wendel, Maxburg Capital Partners, and other shareholders.
Headquartered in Vienna, Austria, Constantia supplies flexible packaging solutions to more than 4,000 global customers in the pharmaceutical, food, and consumer goods sectors.
The company operates a network of 28 sites in 15 countries, with more than 7,150 employees. Red-Sea crisis
One Rock partner Kurt Beyer said: “Constantia’s commitment to product innovation, sustainability and quality underscores its position as a market leader in the flexible packaging industry.
“We look forward to working alongside Constantia’s management team to enhance its operational capabilities and suite of packaging solutions to maximise its potential.”

Container shipping rates spike as Red Sea crisis draws first blood
Maersk halts Red Sea transits (again) after US military kills Houthi attackers
Maersk, the world’s second-largest ocean carrier, gambled that a U.S.-led military force, Operation Prosperity Guardian, would allow safe passage through the Red Sea. That gamble has failed.
On Tuesday, Maersk said it will suspend Red Sea transits indefinitely and reroute ships around Africa’s Cape of Good Hope. The decision followed attacks on the container ship Maersk Hangzhou, which was struck by a Houthi rebel missile on Saturday and threatened by four Houthi boats on Sunday. Red-Sea crisis
Armed guards on the Maersk Hangzhou exchanged fire with the Houthis, whose boats approached within 70 feet of the container ship before U.S. military helicopters intervened. After the Houthis fired on U.S. forces, the helicopters took out three of the four boats, killing 10 Houthi rebels.
The attacks in the Red Sea continue. U.S. Central Command confirmed that the Houthis fired two anti-ballistic missiles on Tuesday that landed in the vicinity of passing commercial ships. The Houthi spokesperson confirmed Wednesday that the missiles were targeting the container ship CMA CGM Tage.
As supply chain issues mount and missile launches persist, there is an increasing likelihood of ground strikes in Yemen by the U.S.-led coalition. Red-Sea crisis

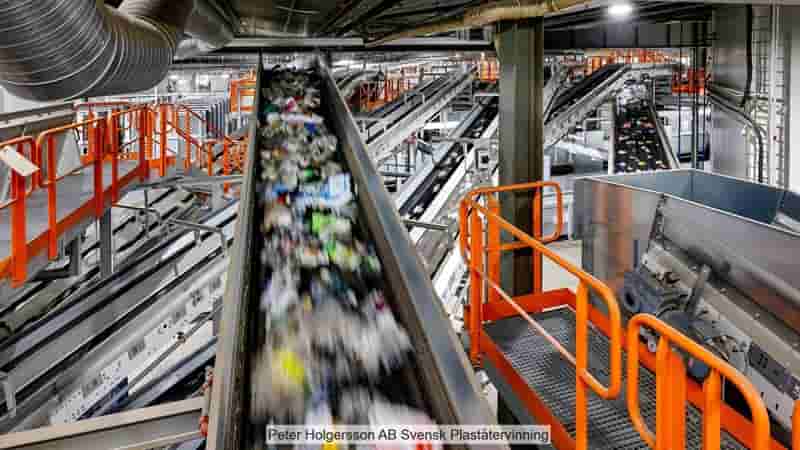
Svensk Plaståtervinning has recently inaugurated “Site Zero,” the world’s largest plastic sorting facility located in Motala, Sweden
Equipped with cutting-edge technology from Sutco and Tomra, this state-of-the-art plant efficiently categorizes all Swedish plastic packaging waste into 12 distinct fractions. WASTE MANAGEMENT WORLD covered the grand opening of this groundbreaking facility.
Motala, with a population of around 30,000, situated on the eastern shore of Lake Vättern, might seem an unlikely choice for the global epicenter of plastic sorting. However, the town’s industrial history, dating back to the 19th century and marked by the construction of the Göta Canal, has paved the way for Site Zero’s establishment. Red-Sea crisis
Housed in a repurposed industrial hall that once manufactured appliances for Elektrolux, the facility spans 60,000 square meters, embodying the principles of a circular economy.
Mattias Philipsson, CEO of Svensk Plaståtervinning, emphasizes the plant’s significance as a pioneer in producing top-tier material quality while minimizing environmental impact. The facility, known as Motala II, is an expansion of the earlier Motala I plant, making it the largest and most advanced plastic sorting plant globally. Red-Sea crisis
Philipsson envisions a future with “no waste, no downcycling, and no emissions.” Currently recycling 33% of plastic packaging in Sweden, the plant’s advanced technology, including 500 tons of steel, nearly five kilometers of conveyor belts, infrared sensors, screening drums, ballistic separators, and state-of-the-art air purification systems, allows it to process 42 tons of material per hour, recovering 12 different plastic types. Plans for additional washing and pelletizing systems by 2025 aim to further enhance recycling capabilities and contribute to Sweden’s journey towards a closed-loop economy.

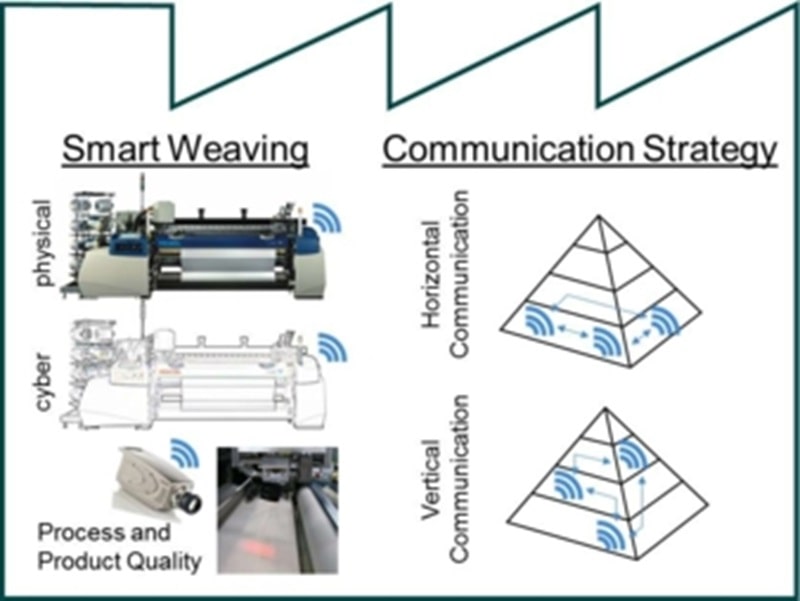
SmartFactory – Developement of Smart Factories in textile industry with Industrie 4.0 approaches
Aim of the project SmartFactory is to frame the special demands of Product and Process Quality Management of Indusrtie 4.0 in Textile Industry and derive concrete approaches and possible potentials. To do this the current status in Production of Home Textiles with Jacquard Weaving is analyzed by Institute of Textile Technology (ITA) of RWTH Aachen University. As result the typical processes and structures for a Smart Textile Fabric of Future are expected. Red-Sea crisis
As shown in the picture the project is divided into two main parallel branches on the mend to Smart Textile Fabric. The first goal is to develop the Smart Weaving Factory. In the smart weaving factory the weaving machines are upgraded to so-called Cyber-physical systems and are able to intelligently interact with their environment. The project is focused on automatic Process and Product Quality Control. The second goal is to develop a consistent Communication Strategy to link the Production Chain as a basis for the Smart Textile Fabric. Red-Sea crisis
To do this an existing strategy from other industrial branches is picked and concretized for a weaving company with an implementation recommendation. It is used as a guideline for further developments and includes vertical and horizontal communication.
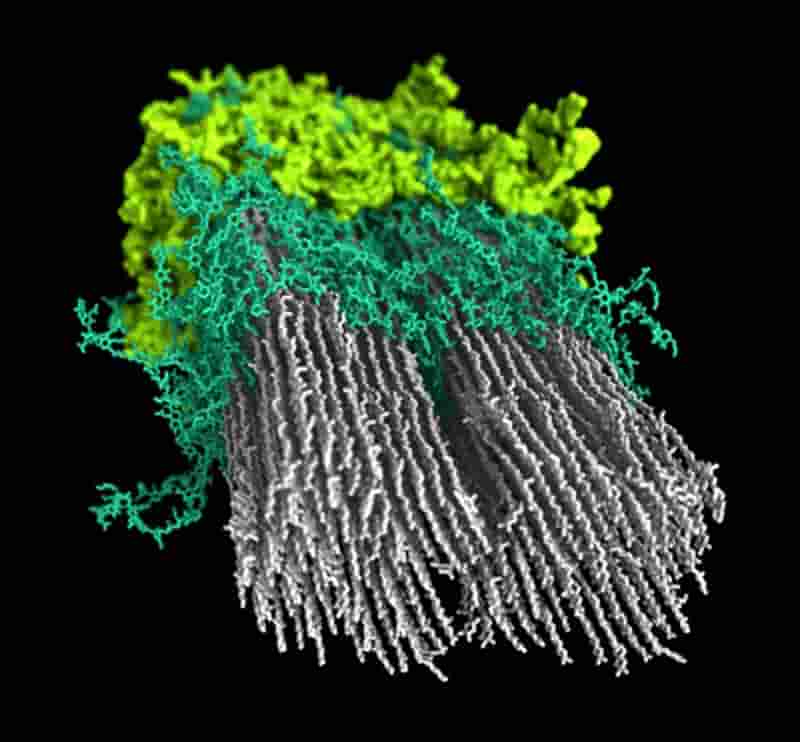
NREL researchers produce first macromolecular model of plant secondary cell wall; more efficient utilization of biomass for fuels, chemicals, and materials
Researchers with the US Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have defined quantitatively the relative positioning and arrangement of the polymers in Populus wood and to create a computer model that details the findings.
The research into solving this macromolecular puzzle, which appears in an open-access paper in the journal Science Advances, may hold the key to disentangle and deconstruct biomass efficiently for conversion to fuels, chemicals, and materials.
Scientists have long known that the secondary cell wall of hardwoods involves three major biopolymers—cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—but detailed and quantitative understanding of how these polymers are arranged relative to each other has remained elusive. Red-Sea crisis
The researchers capitalized on advances in the field of solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (ssNMR) technology to infer refined details about the structural configuration of the cell wall, the intermolecular interactions, and the relative positions of the biopolymers within the wood. Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is an atomic-level method to determine the chemical structure, 3D structure and dynamics of solids and semi-solids.
Red-Sea crisis
