Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling 28-07-2021 - Arhive
Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
Crude Oil Prices Trend
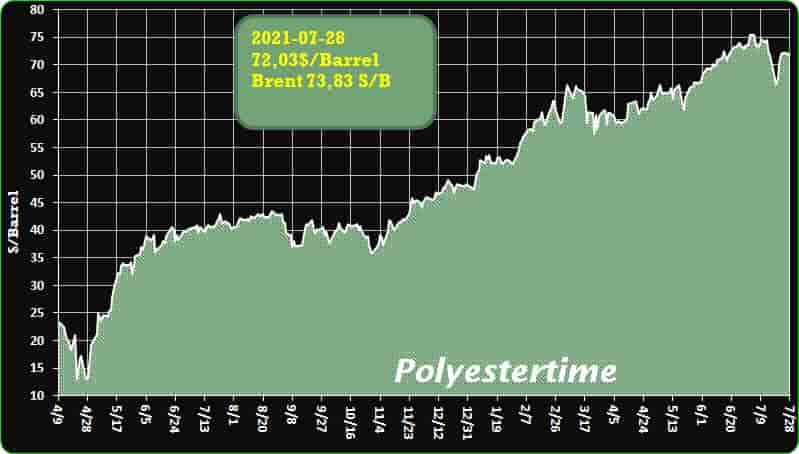
-Nylon 6 CS chip: the worst time is passing
Coming to the end of July 2021, the price gap between nylon 6 conventional spinning (CS) chip and caprolactam has been narrowed to as low as 200yuan/mt. And consider cost difference between the payment (around 250yuan/mt), CPL RMB spot and nylon 6 CS chip spot price spread still lingers low around 450yuan/mt, the same low and profit-losing rate seen in early July. Nylon 6 CS chip plants have been through a difficult time, but they are about to go out of the worst time.
The demand for the conventional spinning chip in July has been obviously weak. Of its major downstream sectors, only cord fabric market has maintained a healthy status, but cord fabric plants only uses high-viscosity CS chip, which is independent from the majority, medium-viscosity CS chip.
Medium-viscosity CS chip market has three major downstream sectors: modified plastics, staple fiber and film.
Film: Prices of BOPA film 15μhas been falling since June and continued through July. Its related end user’s market, food packaging was not as good as the previous year. However, film plants are still certain about returning orders in the third quarter of 2021, and they maintain optimistic look toward August.

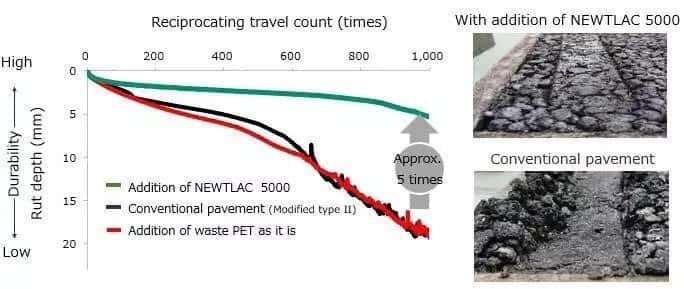
-Kao developes technology that incorporates rPET into asphalt
A newly developed technology that will “pave” the way to sustainability has been adopted by Iwata City, a growing city in Japan. Kao Specialties Americas, a US subsidiary of Tokyo-based Kao Corporation, announced this year the revolutionary technology that incorporates recycled PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastic and makes asphalt nearly 5 times more durable than traditional asphalt in the paving industry. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
NEWTLAC 5000 quickly grabbed the attention of city officials that have now used the new additive made from discarded PET plastic, like clear single use water bottles, to repair roads. A popular Japan-based pharmacy chain, Welcia, also used NEWTLAC 5000 to pave their parking lot.
Finding a new use for PET plastic can divert millions of tons of plastic from landfills globally. For instance, a 1000 m2 surface area with NEWTLAC reuses approximately 15,000 discarded PET bottles. This unique way of thinking drives Kao’s goal to support sustainable lifestyles throughout the world with “positive recycling”—creating a new market for recycled materials.
-Enzyme-based plastic recycling can be better for environment, study finds
a team of international researchers, through their recent study found that enzymes-based recycling is a more sustainable approach for recycling polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a common plastic in single-use beverage bottles, clothing, and food packaging and suggested that its becoming increasingly relevant in addressing the environmental challenge of plastic pollution.
A team of international researchers, through their recent study found that enzymes-based recycling is a more sustainable approach for recycling polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a common plastic in single-use beverage bottles, clothing, and food packaging and suggested that its becoming increasingly relevant in addressing the environmental challenge of plastic pollution. The study by researchers in the BOTTLE Consortium, including from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the University of Portsmouth, was published in the journal Joule. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
The analysis shows enzyme-recycled PET has potential improvement over conventional, fossil-based methods of PET production across a broad spectrum of energy, carbon, and socioeconomic impacts. The concept, if further developed and implemented at scale, could lead to new opportunities for PET recycling and create a mechanism for recycling textiles and other materials also made from PET that is traditionally not recycled today.

-What to know about PHA biodegradable plastic and how it could help Southeast Asia
PHA may provide a solution for the plastic pollution problem.
South Korean conglomerate CJ Cheiljedang is jumping into the global market to begin mass production of PHA biodegradable plastic, or polyhydroxyalkanoates.
PHA is considered a viable alternative to petroleum-based plastic because the new technology allows its plastic waste to decompose completely in the ocean and soil in a significantly shorter period of time. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
“Plastics made from crude oil are said to take over 500 years to completely decompose, while biodegradable plastics take decades at most,” SungYeon Hwang, Head of Bio-based Chemistry Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, told ABC News. “Biodegradable plastic does not pollute the sea even if it accidentally flows into the shore.”
This next generation of plastic, PHA — made from microorganism fermentation — is currently manufactured by U.S. company Danimer, based in Bainbridge Georgia, and Japanese company, Kaneka.

-Ecoblue’s second recycling facility for PET, HDPE and PP
Last year, EcoBlue had committed to set up a world-class second recycling facility for PET, HDPE, and PP in Thailand, which will be completed later this year. The progress at the site is going well. Equipment from the best technology suppliers like Starlinger and Tomra is now on its way. The upcoming facility will help brands achieve their 2025 sustainability targets. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
Some of the key features to look out for at the facility are as follows:
EcoBlue’s food-grade rPET
High-quality food-grade rPET made from 100% PCR waste. Thailand’s first recycling company to receive the Letter of No Objection by the US FDA for its 3D Pure rPET for Bottle and PET Film manufacturing.
Compliance to regulations such as Regulation (EU)
3D Pure Filtration Technology for high-end applications like PET film and filament yarn.
HDPE and PP recycling with de-odoring process
Sustainable alternative to virgin resin
Diverting ocean-bound plastics with the new facility.
Ecoblue is a recycling company that has developed capabilities to produce high-quality rPET and rPP from post-consumer and industrial waste, providing a sustainable substitute to virgin resin. It is a pioneer in offering high-quality rPET with FDA approval for the PET film application, which has been proven to work well for films with 90% rPET content. EcoBlue’s High IV Bottle grade rPET can be used up to 100% for clear bottles suitable for food contact.

-Magna acquiring Swedish driver technology firm Veoneer for $3.8 billion
The deal aims to strengthen and broaden Magna’s ADAS portfolio and industry position. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
In a deal that aims to strengthen its offerings in advanced driver assistance technology, Canadian auto parts maker Magna International Inc. is acquiring Swedish automotive safety technology firm Veoneer for US$3.8 billion including debt.
In a July 22 news release, Aurora, Ont.-based Magna said the deal “builds on [its] strengths and positions the company’s advanced driver assistance systems (“ADAS”) business as a global leader with comprehensive capabilities.”
“The acquisition also expands Magna’s ADAS business with major customers and provides access to new customers and regions, including in Asia,” it said.
Magna said it plans to operate Veoneer’s Arriver sensor perception and drive policy software platform as an independent business unit, consistent with Veoneer’s current practice.

-New Standard to Help Prevent Plastic Pellet Loss
BSI, in its role as the UK National Standards Body, has today published a new standard to help organizations achieve and maintain zero plastic pellet loss across their pellet handling operations (See the press release on BSI website here).
The new standard, named PAS 510: Plastic pellets, flakes and powders – Handling and management throughout the supply chain to prevent their leakage to the environment – Specification, sets out requirements for the handling and management of plastic pellets, flakes and powders throughout the supply chain to prevent spills, leaks and loss to the environment. It covers topics such as organizational responsibilities, leadership and commitment, competence and training, risk assessment and operational controls. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
Read a Factsheet on the PAS 510 Here
Plastic pellets, flakes and powders are the raw materials used to make plastic products, including mouldings, pipes and packaging. As a result of handling and management practices, pellets can be lost to the environment at every stage of the plastic supply chain from production and manufacturing to transport and storage1. Once in the environment, pellets and other types of microplastics, are known to be eaten by a range of animals and are known be harmful2.

-ExxonMobil and SABIC reach mechanical completion of MEG and two PE plants in Texas
ExxonMobil and SABIC hasve announced that their joint venture, Gulf Coast Growth Ventures located near Corpus Christi, Texas, has reached mechanical completion of a monoethylene glycol (MEG) unit and two polyethylene (PE) units, according to Hydrocarbonprocessing.
Project startup is expected to begin ahead of schedule, likely in the fourth quarter of 2021. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
“Gulf Coast Growth Ventures is a key development of our plan to serve growing demand for our high value performance products,” said Karen McKee, president of ExxonMobil Chemical Company. “This is truly a best-in-class project, as demonstrated in schedule acceleration and cost competitiveness, despite the many challenges related to the COVID-19 pandemic.”
“We are very proud to bring GCGV one step closer to operations,” said Abdulrahman Al-Fageeh, SABIC’s executive vice president of petrochemicals. “Not only are we ahead of schedule, but we have executed this project with the highest commitment and emphasis on safety with nearly 18 million safe person-hours worked, all while acting on the promises we made to the community when we started this journey four years ago.”
The project, which includes a 1.8 million metric ton ethane steam cracker, is expected to be delivered under budget and approximately 25% less than the average cost of similar projects along the US Gulf Coast. When completed, GCGV will produce 1,100 kilotons of MEG and 1,300 kilotons of PE per year.

-Piovan to build new automation/hq facility in Suzhou
Italian auxiliary equipment group Piovan, which has been in the Chinese market for over 20 years, is building a 10,000 sq m facility in Suzhou, China, to produce automation systems for the plastics, food powders and refrigeration markets. The new site in Suzhou will also be the regional headquarters for all the group’s branches in the Asian region including Piovan Thailand in Bangkok, Piovan Vietnam in Ho Chi Minh City, Piovan Japan in Kobe, and ToBa PNC in Seoul, South Korea.
The signing ceremony of the agreement with the local government that will lead to the construction of the new Piovan plant in China took place recently.
Piovan opened its first commercial office in Hong Kong in 2000, while the opening of the first production plant was in 2005 in Zhuhai, in the Guangdong province, and then in 2008 in Suzhou, in the Jiangsu province. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling

-Eni will use biofuels from Kenya for plants in Italy
Eni and the Ministry of Petroleum and Mining of Kenya signed an MoU to promote the decarbonization process to tackle climate change through new industrial models of fully-integrated circular economy along the whole bio-fuel production value chain, said Hydrocarbonprocessing.
The parties will jointly conduct feasibility studies to develop waste and residue collection as well as agricultural projects, with the purpose of establishing a wide range of feedstock sources that do not compete with food cycles, to be transformed into bio-fuels and bio-products that might contribute to feed Eni’s bio-refineries in Gela and Venice, Italy. The parties will also assess the opportunity of converting Mombasa refinery into a bio-refinery, as well as the construction of a new plant for second-generation bio-ethanol from waste biomass, leveraging on Eni technologies Ecofining™ e Proesa. Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
The agricultural development project focuses on the development of sustainable oil crop cultivations – namely, low ILUC (indirect land use change) feedstock such as cover crops, castor in degraded lands, croton trees in agro-forestry systems and other agro-industrial co-products. The waste and residue collection would be focused to promote and implement a collection system for used cooked oil (UCO) and of other agro-processing residues.

Petrochemicals Enzyme Recycling
