R-PET market
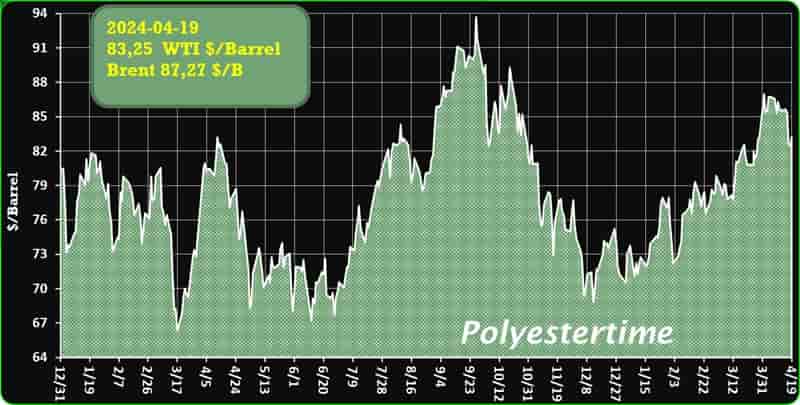
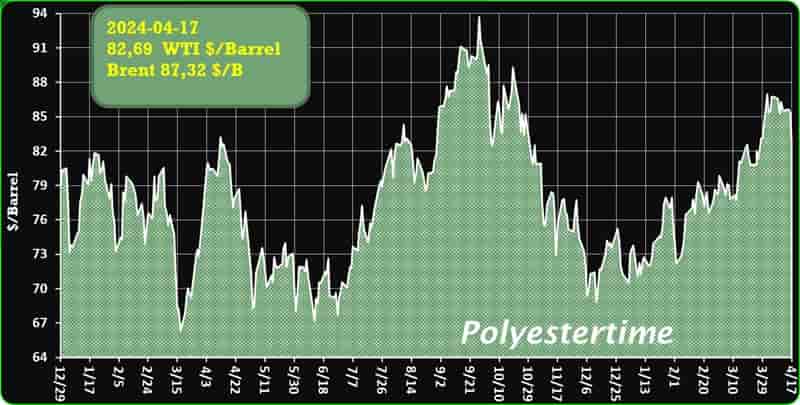
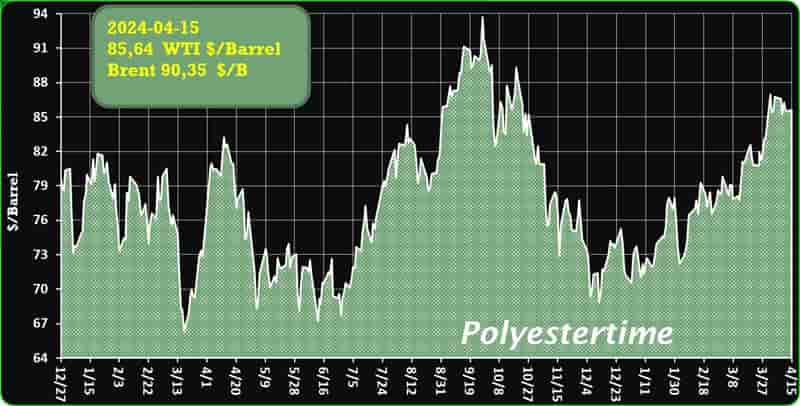
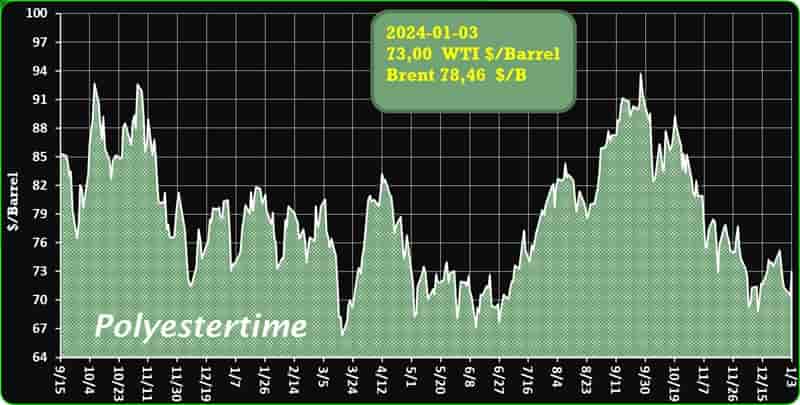
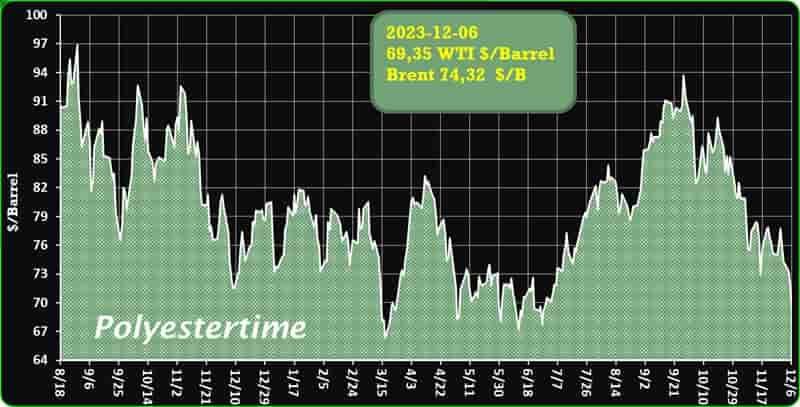
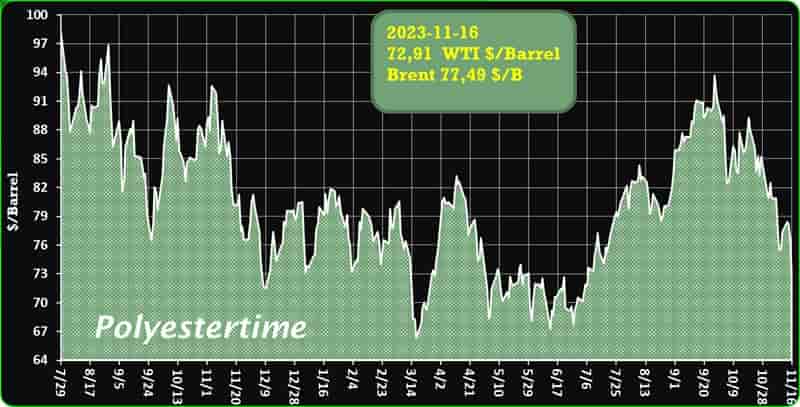
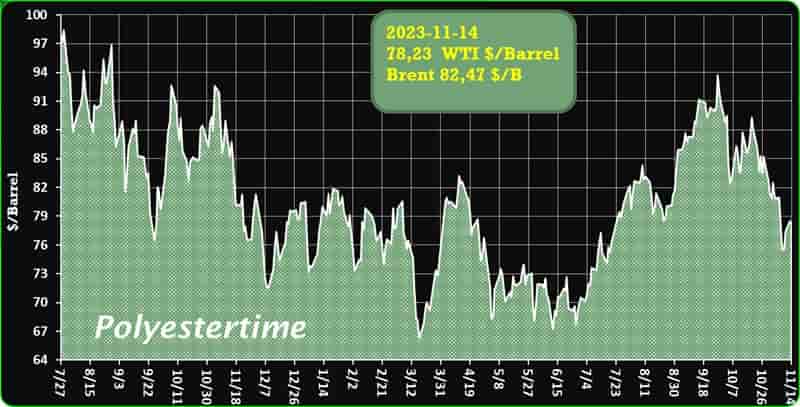
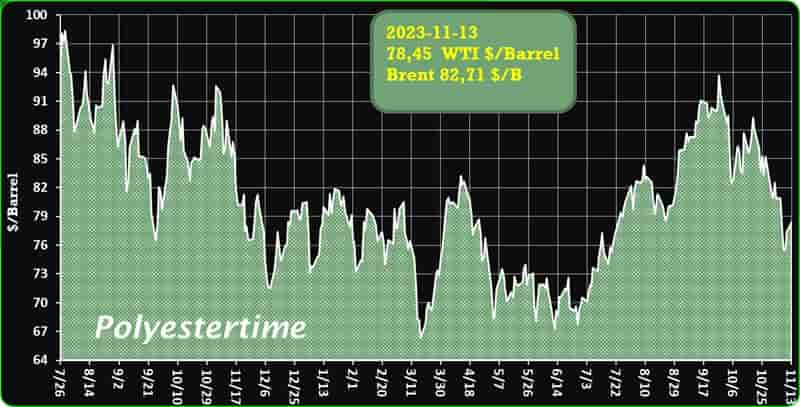
Crude Oil Prices Trend
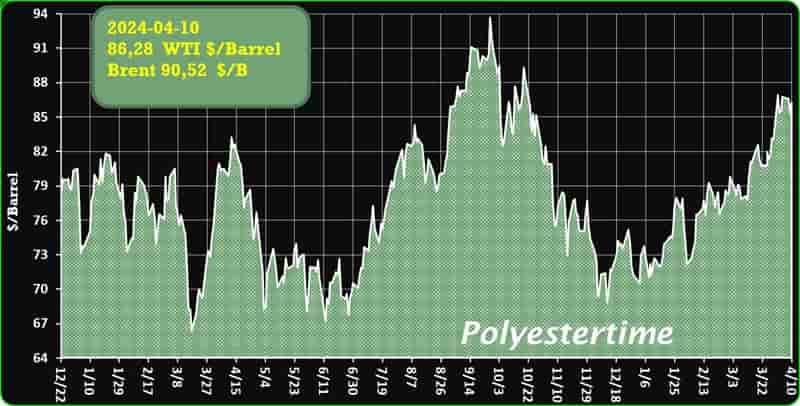
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
U.S. R-PET Market Exhibits Remarkable Stability Amid Global and Domestic Shifts
Throughout March 2024, the U.S. R-PET (Recycled – Polyethylene Terephthalate) market has proven to be a bastion of stability in the fluctuating global economy. With its cornerstone product, the Clear Flakes, steadfastly priced, the sector has navigated through varying degrees of demand with a calm that belies the undercurrents shaping its trajectory.
As the month commenced, industry players were bracing for potential shifts in consumption patterns. Downstream sectors, notably textiles and bottle manufacturing, were adjusting to a softer demand environment. R-PET market
Yet, the R-PET market held its ground, maintaining a steady price point that was reflective of a finely tuned balance between supply and the demands of the market. Manufacturers found themselves in a cautious stance with the spot market, where the pace of trade was subdued, and the pulse of transactions was measured.
The domestic stability in the R-PET market was juxtaposed with a global backdrop where external demand pressures and international market sentiments exerted their influence. The U.S. Manufacturing PMI indicated an uptick in activity, suggesting a recovery in the industrial sector that could potentially ripple into increased demand for R-PET. Export orders, too, showed signs of vigour, marking a reversal from previous trends, and injecting a dose of optimism into market outlooks. R-PET market
More…

Lombardy (Italy) offers substantial incentives for eco-friendly plastics
Lombardy Region is dedicating 5 million euros towards fostering sustainability in the plastics and textile industries. Eligible businesses can receive non-repayable contributions of up to 300,000 euros, covering half of their sustainable expenses.
Open to small and medium-sized enterprises in Lombardy, the application window for accessing these incentives runs from May 7 to June 18, 2024.
Giorgio Maione, the Councilor for Environment and Climate, applauds Lombard companies’ progress over the past decade in balancing environmental and economic sustainability through strategic investments. R-PET market
These funds will further enhance waste management in plastics and textile supply chains through circular economy initiatives.
Eligible expenses encompass various stages of the supply chain lifecycle, including procurement, design, production, distribution, use, collection, and end-of-life management:
- Repurposing production residues for material use, promoting industrial symbiosis and by-product integration.
- Implementing measures for packaging reuse, including the establishment of returnable systems.
- Initiating product reuse or extending their lifespan.
- Adapting production lines to minimize raw material usage.
- Modifying production processes to reduce waste.
- Incorporating “end of waste” materials into production lines.
- Adjusting production lines for product redesign to enhance durability and recyclability. R-PET market
- Supporting innovative waste collection projects for efficient reuse or recycling preparation.
- Backing innovative projects for plastic, compostable bioplastic, and textile waste reuse or recycling preparation, with scalability and transferability.
Lombardy’s incentives signal a commitment to sustainable development, fostering greener practices in key industries.

Revolutionizing Waste: The Plastic Recycling Machine
- Introduction
Plastic pollution has become an ever-growing threat to our planet’s ecosystems. With landfills overflowing and marine life suffering, the need for effective waste management solutions has never been more urgent. Recycling stands as a beacon of hope in this crisis, offering a way to reduce the environmental impact of plastic consumption. Among the innovations leading the charge is the Plastic Recycling Machine (PRM), a revolutionary technology designed to streamline the recycling process and maximize efficiency.
- Understanding the Plastic Recycling Machine
The Plastic Recycling Machine represents a paradigm shift in waste management. Unlike traditional recycling methods, which often rely on manual sorting and processing, the PRM automates much of the recycling process. R-PET market
At its core, the machine consists of several key components: a shredder, a washer, a dryer, and an extruder. These components work in tandem to transform discarded plastic waste into reusable material.
The process begins with the shredder, which breaks down plastic items into smaller pieces, facilitating the recycling process. These shredded pieces then pass through the washer, where they are cleaned to remove any contaminants or impurities. Once cleaned, the plastic undergoes drying to prepare it for the next stage.
Finally, the dried plastic is fed into the extruder, where it is melted down and formed into pellets or other reusable forms. R-PET market
More…

China’s spunlace nonwovens export experiences robust growth amidst intense price rivalry
Customs data reveal a 15% year-on-year surge in Jan-Feb 2024, totaling 59.514kt—nearly rivaling 2021’s annual volume. However, the average price plummeted by 7% to $2,264/mt, indicative of stiff competition among fabric mills despite ample orders.
During the same period, exports to key destinations—Republic of Korea, United States, Japan, Vietnam, and Brazil—reached 33.851kt, marking a 10% uptick and constituting 57% of total exports. While shipments to the US and Brazil flourished, those to Republic of Korea and Japan saw marginal declines. R-PET market
Originating mainly from Zhejiang, Shandong, Jiangsu, Guangdong, and Fujian, Jan-Feb exports hit 51.53kt, escalating by 15% year-on-year and accounting for 87% of total exports.
Although Jan-Feb exports slightly surpassed expectations, fierce pricing competition persists, with many mills hovering near break-even levels. The surge in export volume is chiefly propelled by the US, Brazil, Indonesia, Mexico, and Russia, while exports to Republic of Korea and Japan saw declines. Zhejiang remains China’s primary source of spunlace nonwovens. R-PET market

Stellantis CEO Carlos Tavares aims to halve the weight of EV batteries within a decade, addressing environmental concerns and lithium scarcity
Current electric vehicles, with a 250-mile range, carry around 1,000 lbs more in raw materials than traditional ICE models. Tavares envisions slashing this weight by 50%, reducing environmental impact and raw material usage significantly.
Speaking at Stellantis’ Freedom of Mobility Forum, Tavares emphasized the need for lighter battery packs, hinting at breakthroughs to achieve this goal. Although specifics on how Stellantis plans to achieve this weren’t provided, the company is heavily investing in electrification. It targets 100% of European sales being electric by the decade’s end and aims for BEVs to constitute 50% of its U.S. sales. R-PET market
Moreover, Stellantis plans to sell 5 million BEVs annually by 2030 and will introduce over 75 BEVs by then.
Stellantis’ electric lineup will rest on four platforms: STLA Small, Medium, Large, and Frame, the latter embracing a body-on-frame design. Additionally, the company is developing three electric drive modules, multiple battery chemistries, and various drivetrain configurations, offering ranges from 300 to 500 miles.
Despite the buzz around hydrogen, Tavares remains skeptical about its viability due to high costs, suggesting it may only be practical for large company fleets in the foreseeable future, not for average consumers. R-PET market

UPM Raflatac’s BOPP labels recognized for HDPE, PP recycling
UPM Raflatac’s BOPP Labels Acknowledged by APR for HDPE & PP Packaging Recyclability Supporting Circular Economy with Certified Sustainable Labeling Solutions UPM Raflatac, a global provider of eco-friendly self-adhesive paper and film products, has received formal recognition from the Association of Plastic Recyclers (APR) for three variants of biaxially-oriented polypropylene (BOPP) labels suitable for recycling in HDPE and PP packaging. These variants encompass Undecorated BOPP with hotmelt adhesive, Undecorated BOPP with RW85C, and Metalized undecorated BOPP with general purpose acrylic adhesive.
Kyle Strenski, Business Director of UPM Raflatac Americas, expressed gratitude for the acknowledgment, highlighting their dedication to fostering a circular economy.
He stated, “This validation enables us to offer even more sustainable solutions to our clientele and brand proprietors.” R-PET market
APR Design® for Recyclability Recognition serves as third-party validation, confirming a package or its components’ compatibility with North American recycling systems.
UPM Raflatac’s BOPP products have successfully met the stringent recyclability criteria outlined in the APR Design® Guide, specifically tailored for HDPE and PP recycling.
Steve Alexander, President & CEO of APR, commended UPM Raflatac’s efforts, emphasizing the importance of recyclable packaging in minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. R-PET market
He remarked, “Recyclable packaging translates to reduced waste, optimized use of scarce resources, and a greater supply of high-quality post-consumer resin for manufacturing new goods.” 
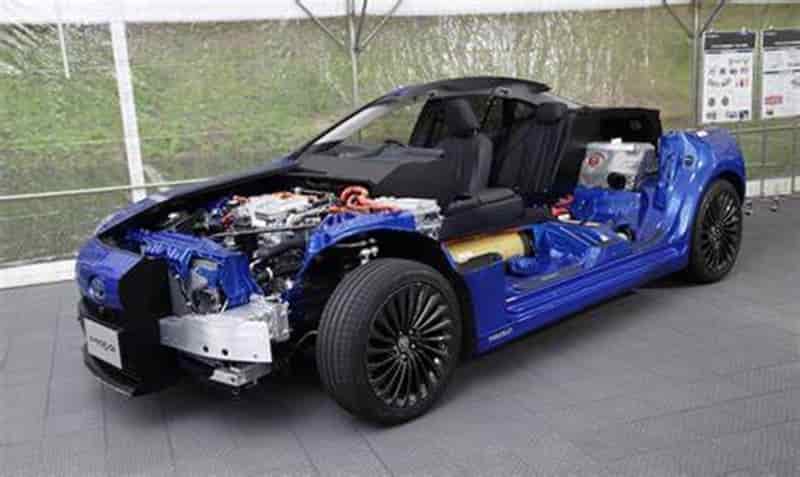
Utilizing modular battery configurations, manufacturers such as Tesla, GM, and Porsche have capitalized on the efficiency of 800-volt electric vehicles
Unlike cell-to-pack structures, which directly integrate cells into the battery pack, modular designs divide the battery into separate units. Examples include the Tesla Cybertruck and GMC Hummer EV, both employing a “split” battery approach.
In the case of the Hummer EV, its dual modules, when connected in series, achieve an 800-volt capacity, enabling rapid charging of up to 350 kW. Similarly, the Cybertruck utilizes four 200-volt modules, enabling it to reach 800 volts during charging, offering similar rapid charging capabilities. R-PET market
Notably, the Cybertruck, besides its 800-volt platform, supports vehicle-to-load functionality. When connected to a Supercharger V3, it seamlessly switches to 400 volts, optimizing performance. The absence of a DC-DC converter simplifies the architecture, reducing costs and space requirements.
This modular approach also facilitates future upgrades. Tesla has hinted at a potential 1,000-volt Cybertruck variant, achieved by adding another module. Other manufacturers, such as Porsche with the Macan EV and Audi with the Q6 e-tron, are adopting similar 800-volt architectures. R-PET market
Ford has even patented designs for 800-volt electric vehicles, further indicating the industry’s shift towards modular battery configurations.
Circular Plastic – NILIT, a global leader in Nylon 6.6 production for apparel and the owner of the SENSIL® brand, introduces SENSIL® Flow, an innovative approach to Nylon 6.6 circularity 09-04-2024
R-PET market