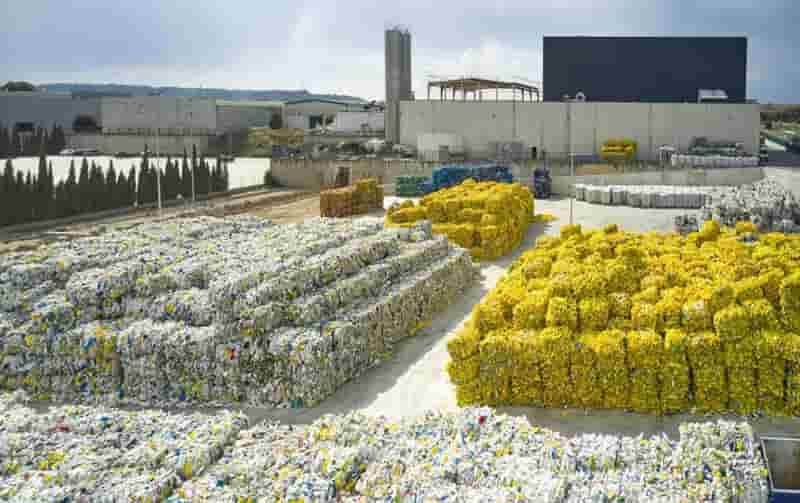
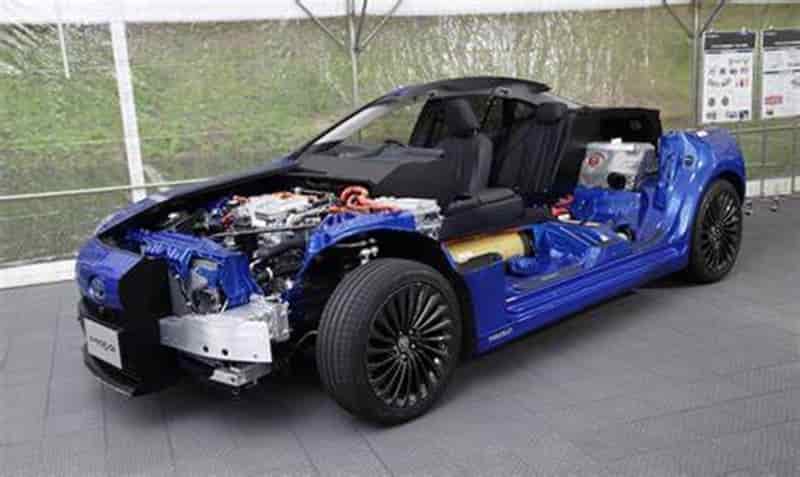
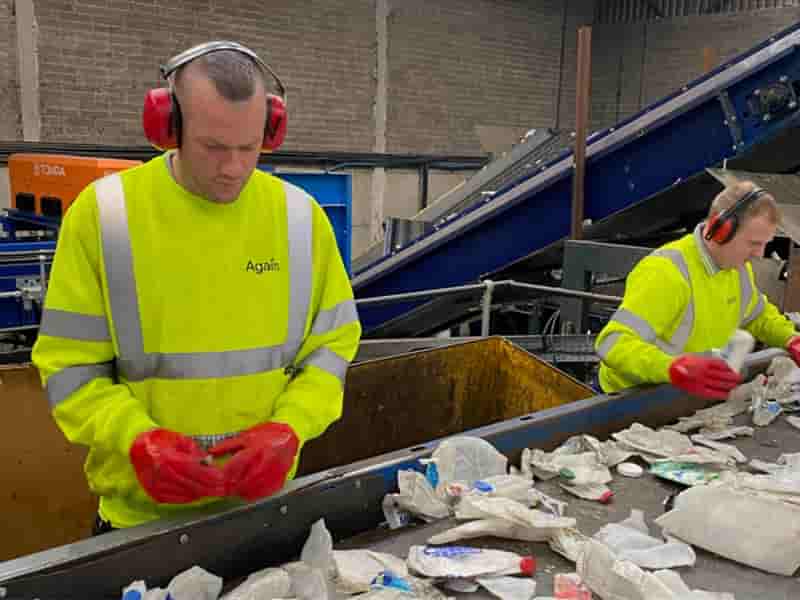
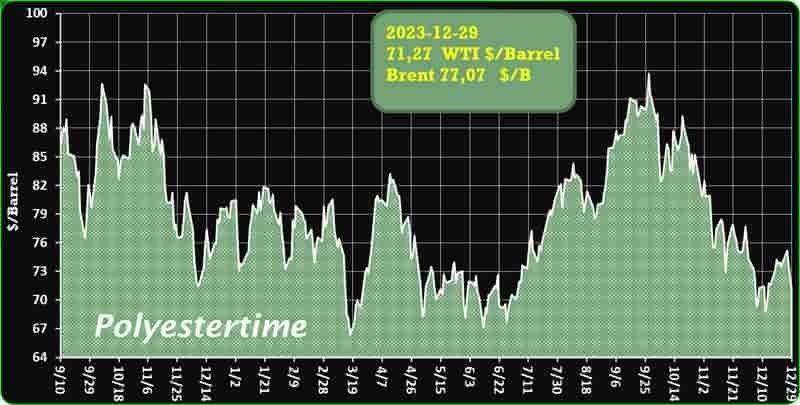
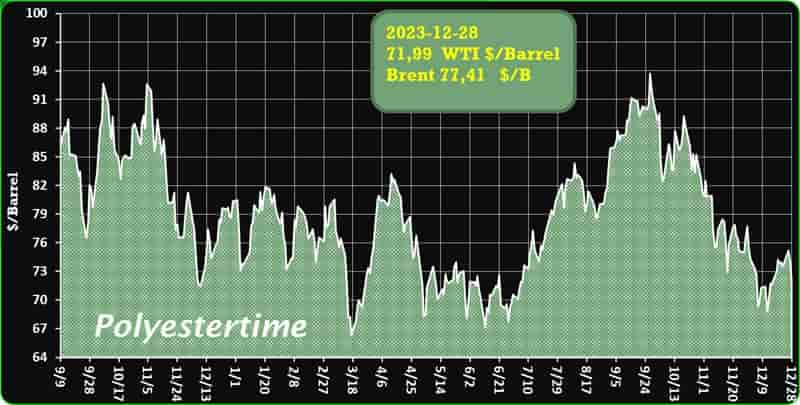
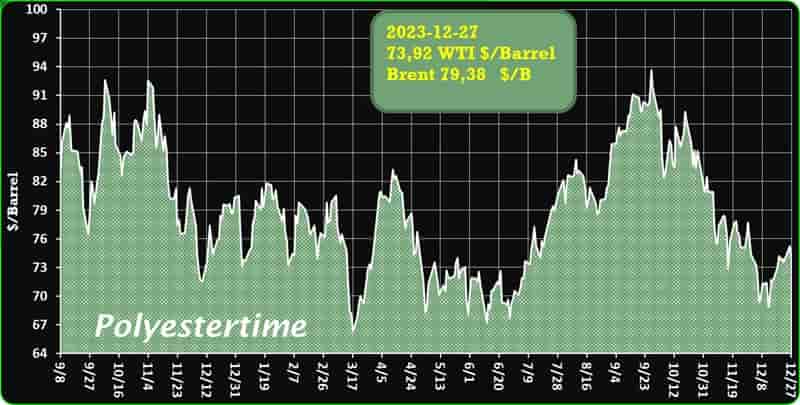
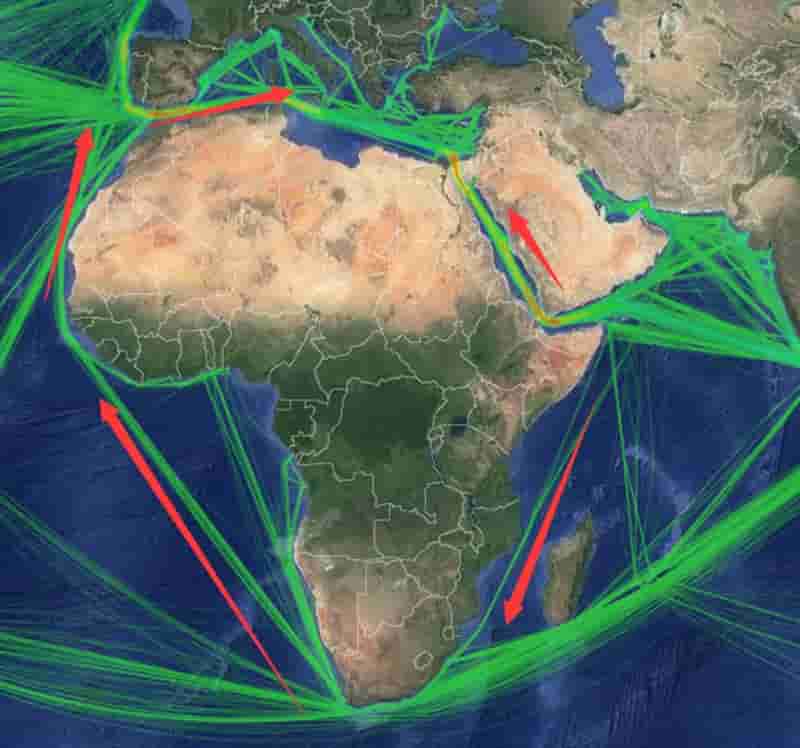
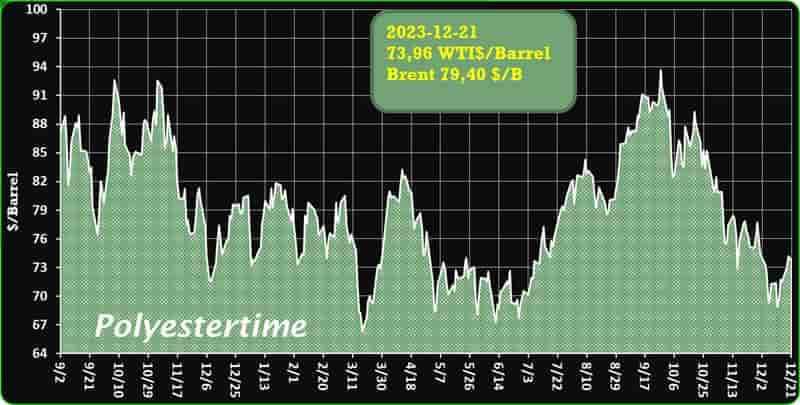
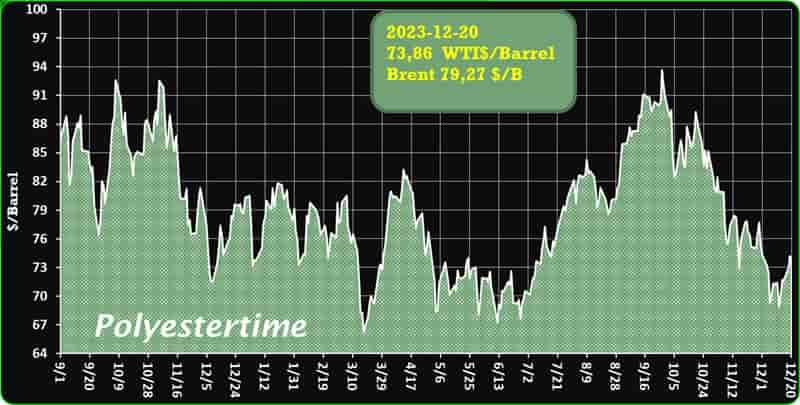
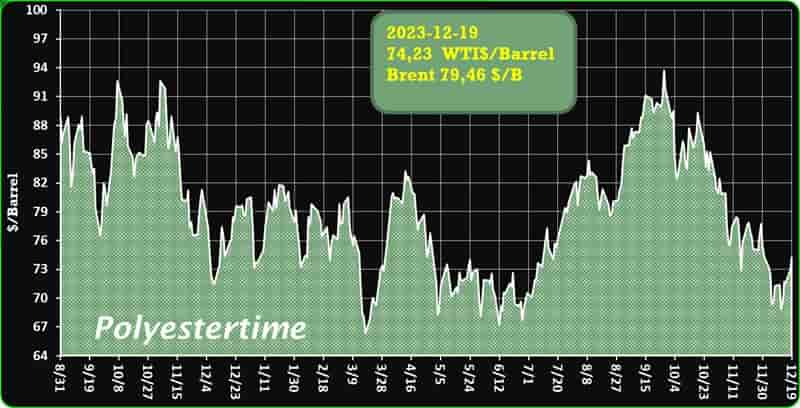
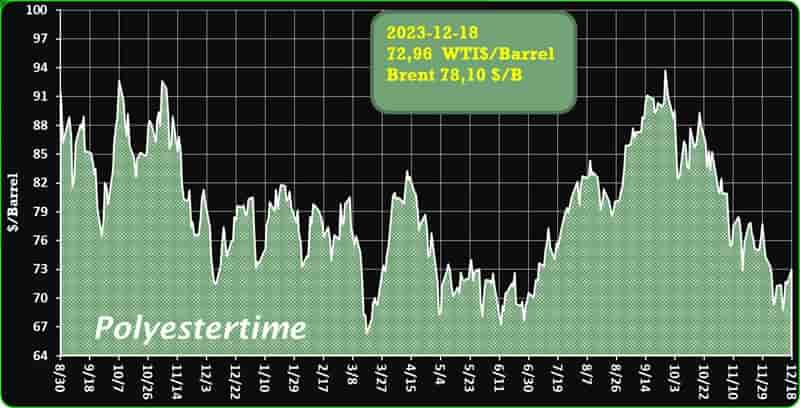
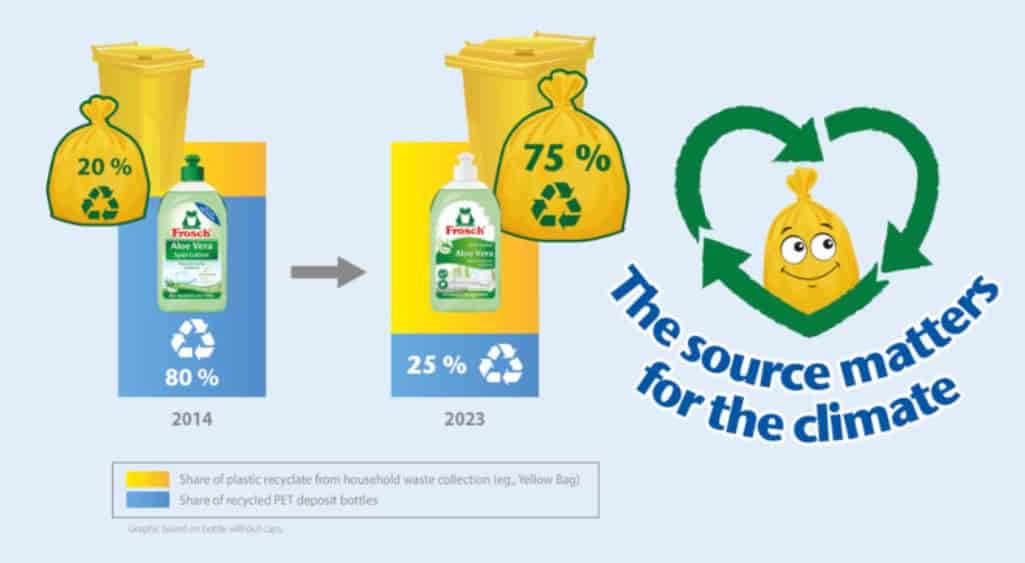
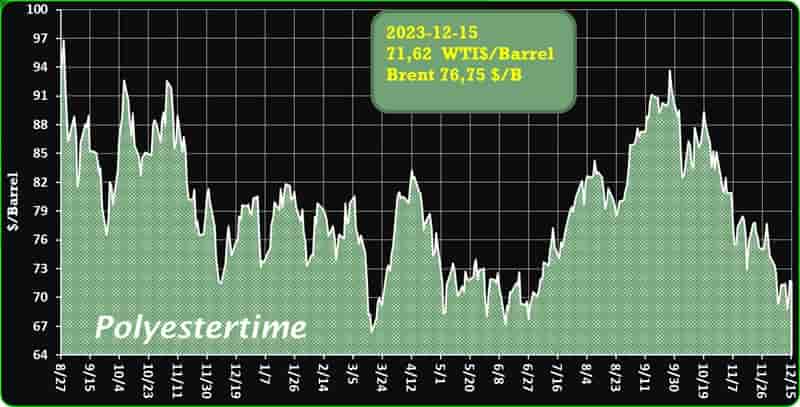
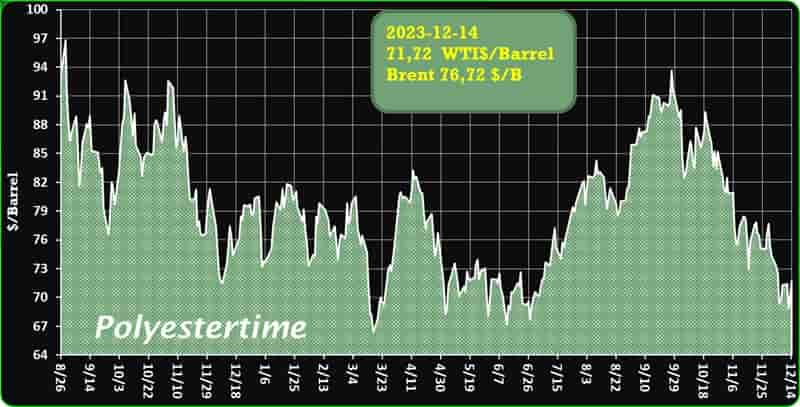
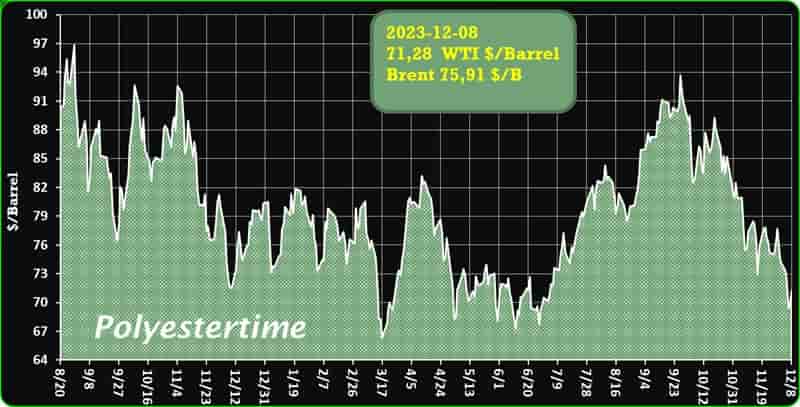
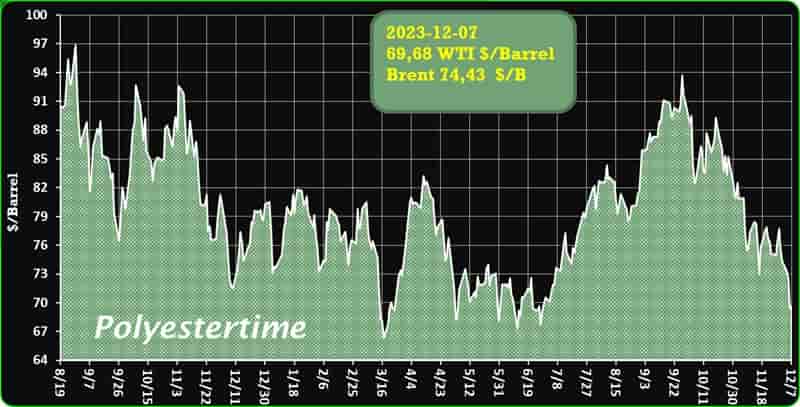
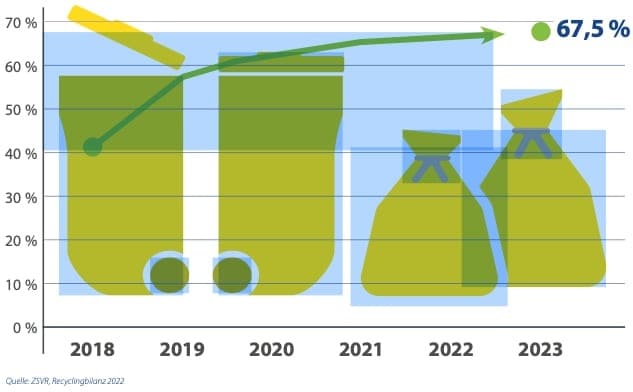
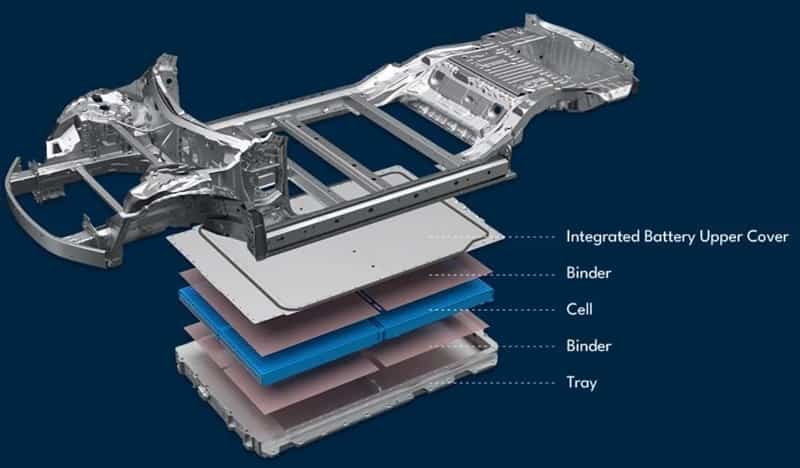
India is expected to remain on top in Asia for demand of petrochemical in 2024 given its strong economic growth and resilient industrial production, said Exportgenius.
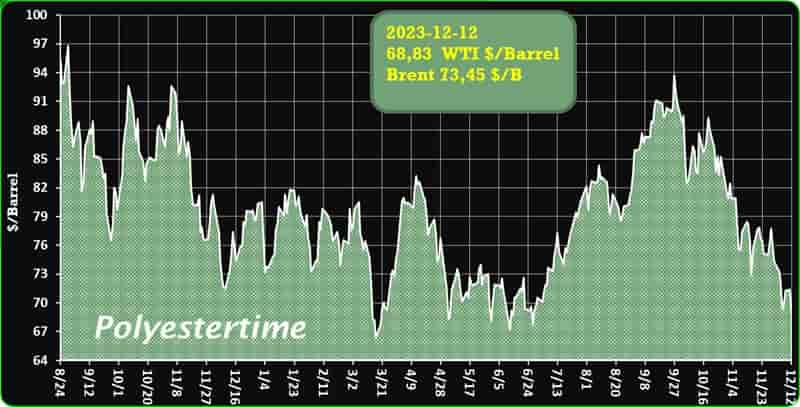
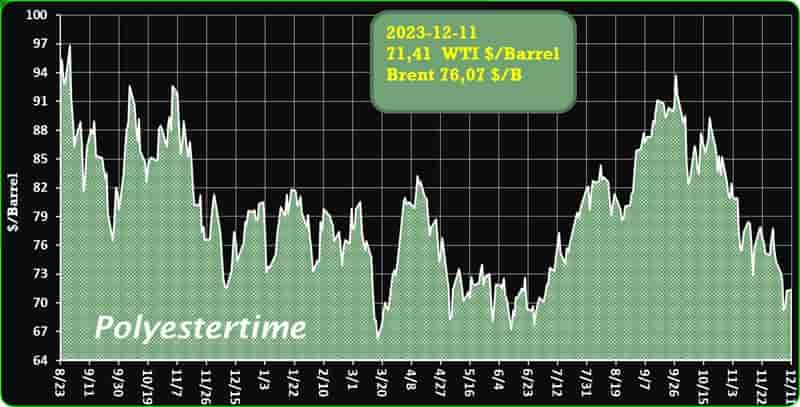
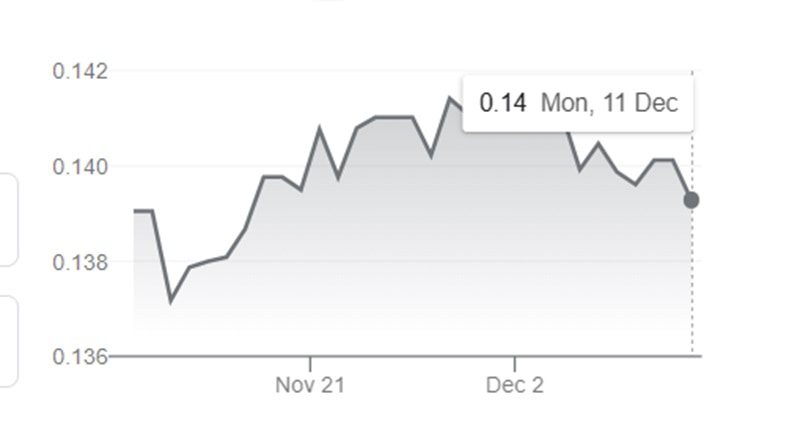
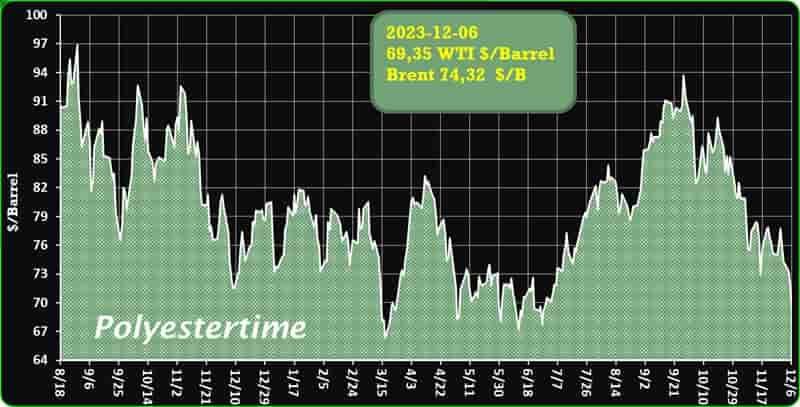
However, the greater demand is unlikely ro bring much relief to domestic producers struggling with pressure on margins as prices of key chemicals in bulk are expected to remain suppressed due to ample supplies and new capacities coming on stream. According to a report, India’s market for chemical commodities is predicted to grow at around 7% in 2023 and 8% in 2024. Biomass-derived PET
The robust demand of India’s chemical products is being driven by a sharp flow of economic activities after the country emerged from COVID-19 lockdowns. While India’s domestic chemicals demand is expected to stay strong in 2024, price expectations will not be very robust as the market struggles to find the right balance. This is due to new production capacities on stream in the country and in the rest of Asia, weak global demand, changing trade flows and volatile upstream prices.
India’s import of polyolefins – the largest chunk of its petrochemical import market surged significantly in 2023, crossed USD 200 million mark in first half of the year itself. This led by higher demand and increased imports from China, where downstream demand scenario stood weak. India’s imports of polyolefins from the world totalled USD 159 million in 2020, that increased to USD 360 million in 2022. Biomass-derived PET
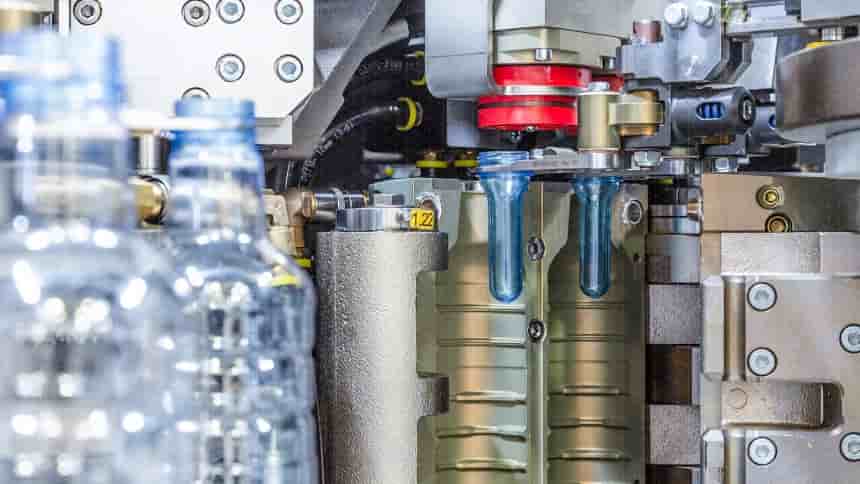
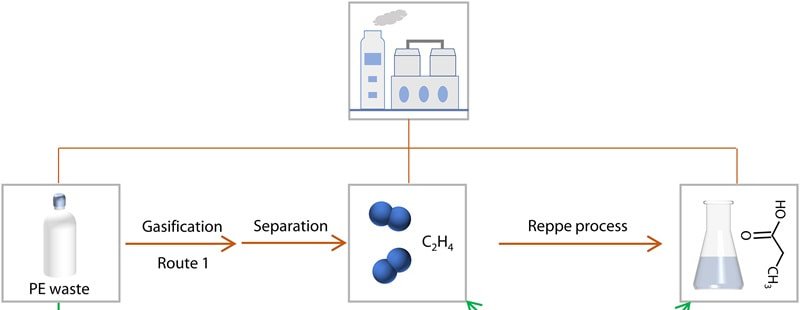
Photocatalytic recycling: University of Adelaide researchers use light to upcycle PE into ethylene
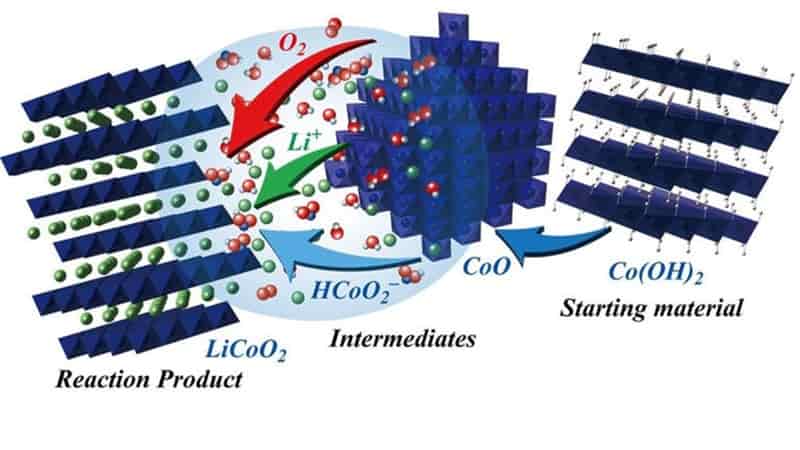
An international team of researchers, led by Professor Shizhang Qiao from the University of Adelaide, Australia, has developed a way to convert PE waste into ethylene (C2H4) and propionic acid, which has antiseptic and antibacterial properties, using a light-driven photocatalysis method. Biomass-derived PET
The study outlines a method involving the atomic engineering of a titanium dioxide (TiO2) photocatalyst with reversible palladium (Pd) species. This modification enables the selective conversion of PE under mild conditions.
“We have upcycled polyethylene plastic waste into ethylene and propionic acid with high selectivity using atomically dispersed metal catalysts,” shares Qiao, chair of Nanotechnology and director of the Centre for Materials in Energy and Catalysis at the School of Chemical Engineering, University of Adelaide. Biomass-derived PET
“Plastic waste is an untapped resource that can be recycled and processed into new plastics and other commercial products. Catalytic recycling of PE waste is still in early development. It is practically challenging because of the chemical inertness of polymers and side reactions arising from structural complexities of reactant molecules.”
The process involves room-temperature, oxidation-coupled photocatalysis. The team achieved a 98.8% selectivity in propionic acid, which can be used as preservatives to extend the shelf life in food packaging or as plasticizers in producing certain packaging materials. Biomass-derived PET
itled “Photocatalytic Production of Ethylene and Propionic Acid from Plastic Waste by Titania-Supported Atomically Dispersed Pd Species,” the research was published in the journal Science Advances.
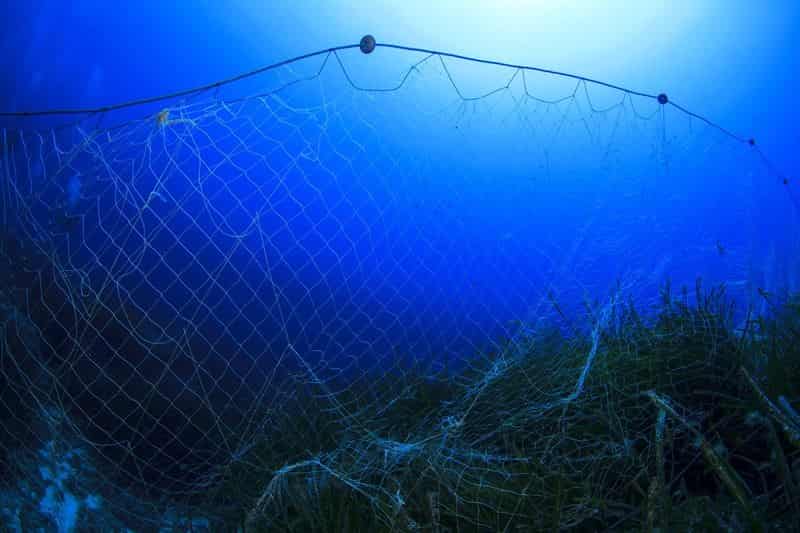
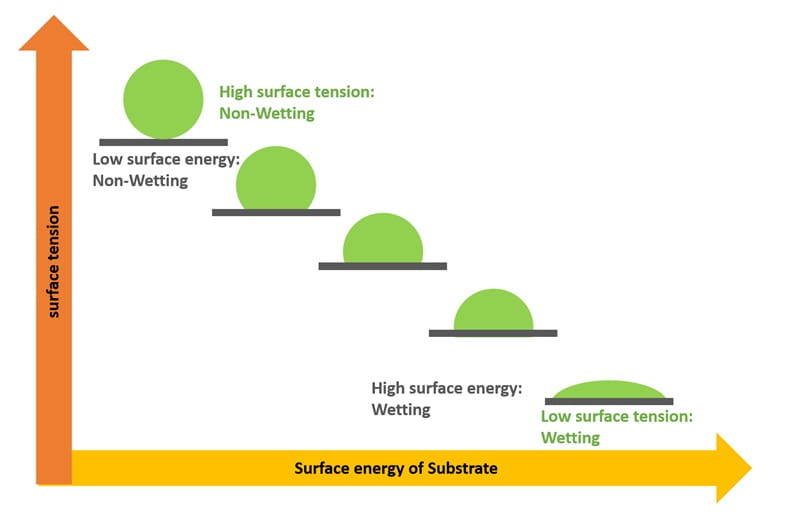
Garware Technical Fibres has introduced an innovative coatable High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) braided knotted net, marking a significant milestone in the industry
This pioneering product allows the application of traditional water-based antifouling paints, overcoming the challenge posed by HDPE fibers’ inherent low surface energy, which impedes paint adhesion. Unlike nylon nets with higher surface energy, HDPE nets typically resist water-based antifouling paints.
The breakthrough lies in Garware’s V4 technology, which selectively modifies the surface properties of polyolefin material without altering its bulk properties. By increasing the surface energy of the polyolefin fibers, the V4 Technology facilitates the spreading and adhesion of water-based antifouling paints on the net surface. Biomass-derived PET
Extensive trials in Scotland demonstrated comparable antifouling performance over a 100-day period in peak summer for both V4-treated CBN-CFR nets (braided knotted net) and nylon knotless nets. Pål Korneliussen, Country Manager for Norway, hailed this as a significant achievement.
While Garware’s Sapphire CFR nets have proven effective against dogfish attacks in Norway, a notable limitation for fish farmers has been the inability to antifoul the nets. The introduction of Garware’s polyethylene nets with antifouling properties addresses this challenge, offering fish farmers greater flexibility to alternate between antifouling painting and in-situ cleaning strategies based on site and regulatory conditions. With over 100 Coatable Braided HDPE Nets sold to the salmon farming industry, Garware continues to deliver exceptional performance in terms of antifouling paint efficacy and protection against predator attacks. Biomass-derived PET
Baxter Expands PVC Intravenous Bag Recycling Program
Baxter International has successfully completed the initial phase of its groundbreaking intravenous (IV) bag recycling pilot program, conducted in collaboration with Northwestern Medicine. This pioneering initiative has diverted over six tons of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) IV bag waste away from landfills, demonstrating a significant stride towards sustainable healthcare practices. 100% biomass-derived PET
Cecilia Soriano, President of Baxter’s Infusion Therapies and Technologies division, underscores the importance of IV bags in healthcare, emphasizing their widespread use in hospitals for administering clinically essential solutions such as fluids, nutrition, and medicines. The conventional disposal method for non-hazardous IV bags involves draining residual fluids and discarding them as waste, contributing to landfill accumulation. Baxter’s pilot program, however, introduces a novel approach by integrating material separation for recycling into the nursing workflow. This innovative process addresses common space constraints in hospital settings and engages stakeholders from various Northwestern Memorial Hospital departments. 100% biomass-derived PET
Partnering with dedicated third-party logistics and recycling firms, the collected PVC IV bags undergo transportation and inspection before being recycled into diverse products, including industrial floor mats and protective edging for docks and landscaping. The success of this pilot phase is attributed to the collaboration with Northwestern Medicine and the active involvement of hospital departments in developing and implementing an efficient recycling process. All IV bags involved in the pilot were composed of PVC.