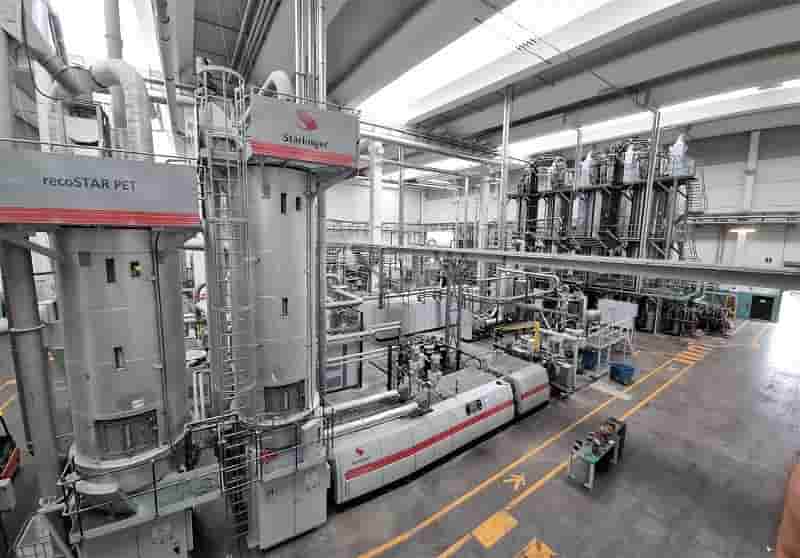
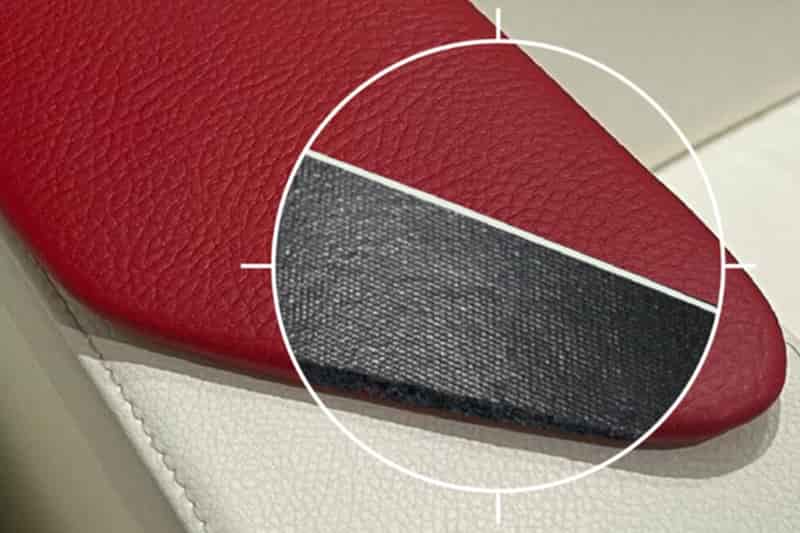
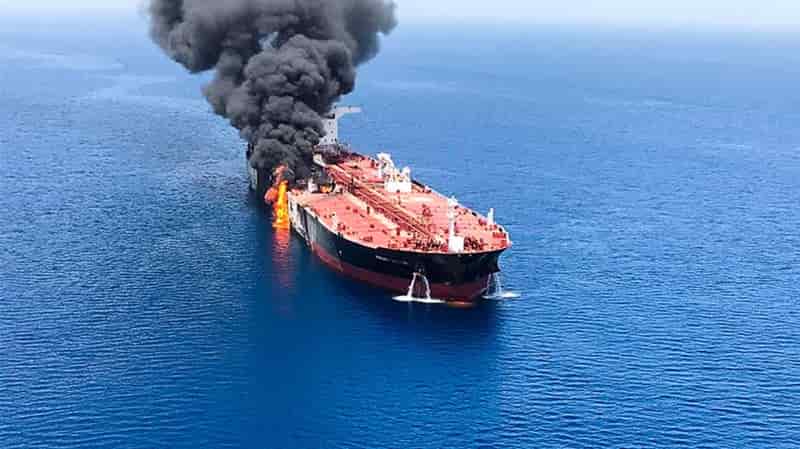
Red Sea Crisis
Maritime Security and Geopolitical Tensions: A Comprehensive Overview
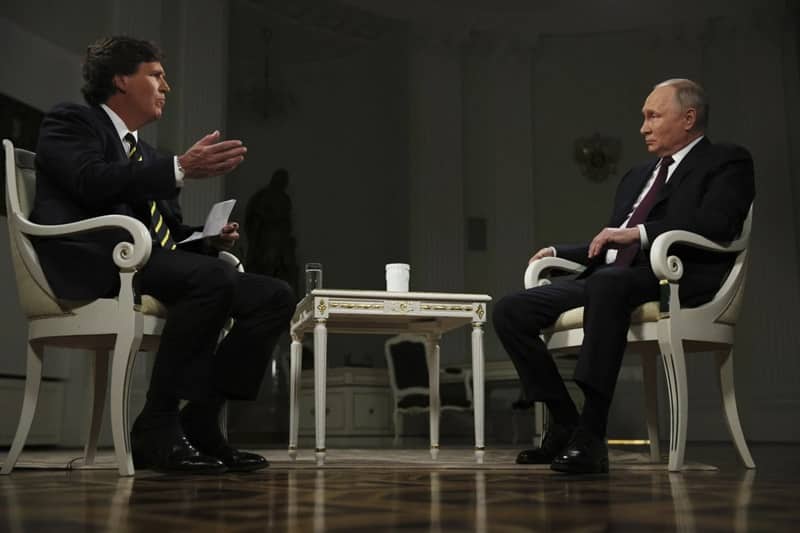
In recent developments, the Houthi rebels in Yemen have assured the safe passage of Russian and Chinese ships transiting through the Red Sea. Mohammed al-Bukhaiti, a senior Houthi official, emphasized in an interview with the Russian agency Izvestia that the waters around Yemen remain safe for navigation, provided the ships are not connected to certain countries, particularly Israel. Al-Bukhaiti’s assurance underscores the Houthi commitment to ensuring free navigation, a crucial aspect for their country.
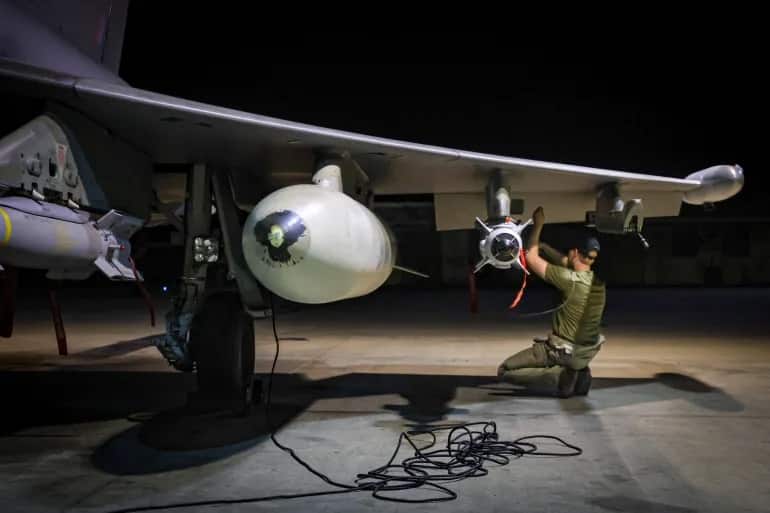
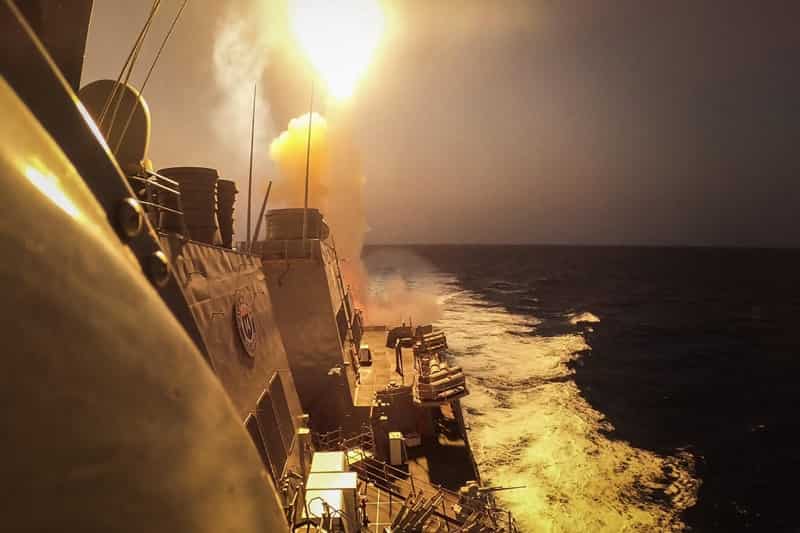
However, amidst these assurances, the Houthi rebels claimed responsibility for a missile attack on the American ship Chem Ranger off the coast of Yemen. They asserted that the attack was in retaliation for American and British actions, warning of further aggression if their interests are targeted. Red Sea Crisis
The United States Central Command confirmed the attack, stating that two anti-ship ballistic missiles were launched, but fortunately, no injuries or damage to the vessel were reported, allowing the tanker to continue its journey.
Despite the Houthi leader Abdel-Malek al-Houthi’s vow to continue naval attacks in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden, he specifically highlighted their intention to strike ships linked to Israel. This follows recent air attacks by the United States and Britain on Houthi targets in Yemen, escalating tensions in the region.
In a surprising turn of events, the Houthi rebels, whose attacks have disrupted maritime traffic in the Red Sea, offered a guarantee of “safe passage” to Chinese and Russian ships on this strategically important route. This move raises questions about the geopolitical dynamics at play, with the Houthi leadership seemingly distinguishing between nations and their vessels based on political affiliations.
The Houthi leadership criticized the military actions of the United States and the United Kingdom, claiming that their “folly and idiocy” have backfired, resulting in losses greater than those suffered by Yemen. According to Mohammed al-Bukhaiti, member of the Houthi political leadership, ships from China and Russia are not under threat, and the rebels are prepared to ensure the safe passage of their vessels in the Red Sea.
The exclusion of Israeli ships or those with any link to Israel from safe passage through the Red Sea reflects the Houthi rebels’ strategic objective of increasing the economic cost for the state of Israel, aiming to draw attention to the situation in Gaza and curb what they perceive as a humanitarian crisis. Red Sea Crisis
As tensions escalate, Al-Bukhaiti also warned of various scenarios, including the possibility of an American ground operation in Yemen. This highlights the complex and precarious nature of the geopolitical landscape in the region and the potential for further military engagements.
In conclusion, the assurance of safe passage for Russian and Chinese ships, coupled with the Houthi rebels’ continued naval attacks and warnings of potential scenarios, underscores the volatile situation in the Red Sea and the broader implications for maritime security and international relations. The geopolitical complexities in the region demand careful consideration and diplomatic efforts to prevent further escalation and protect the interests of all nations involved. Red Sea Crisis

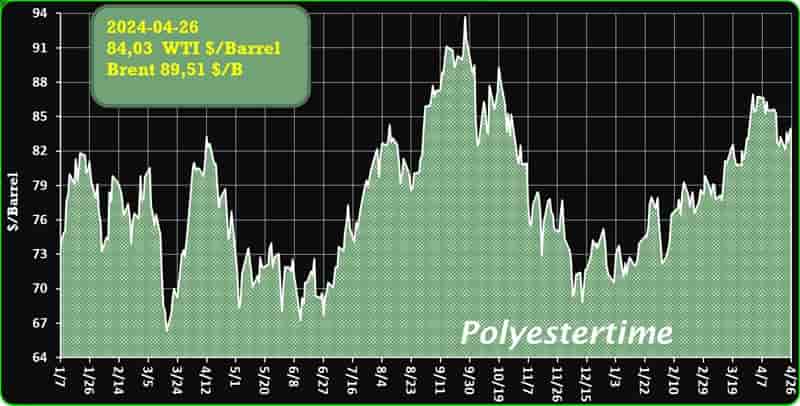
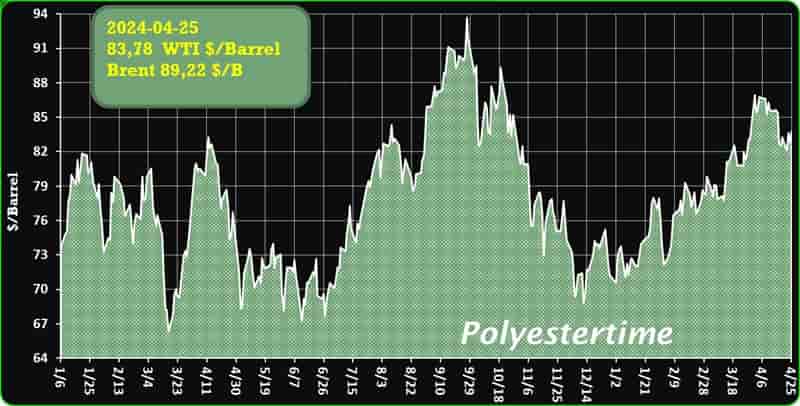
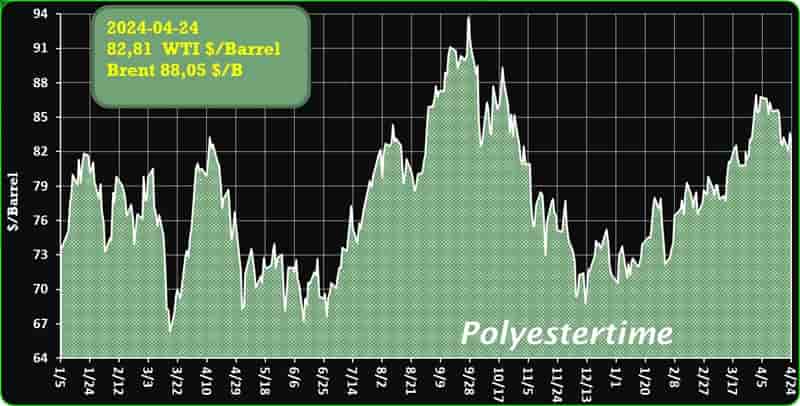
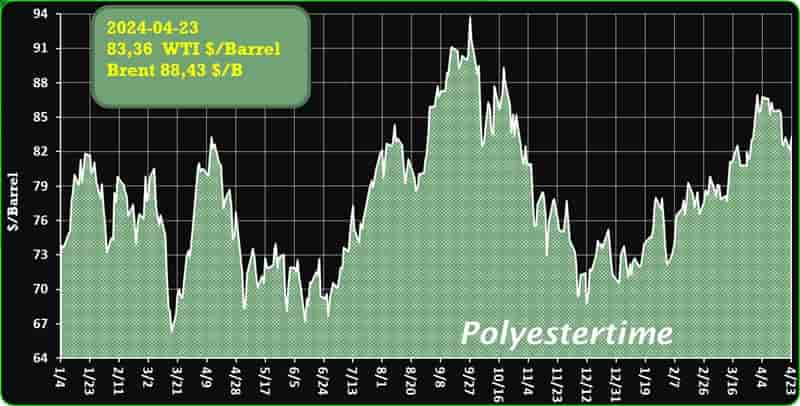
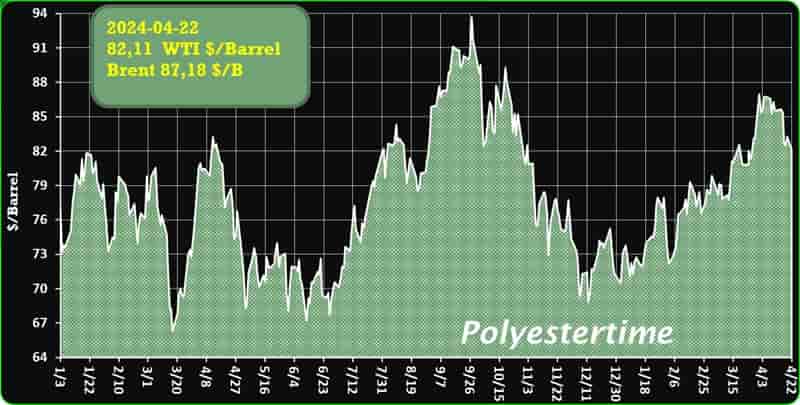
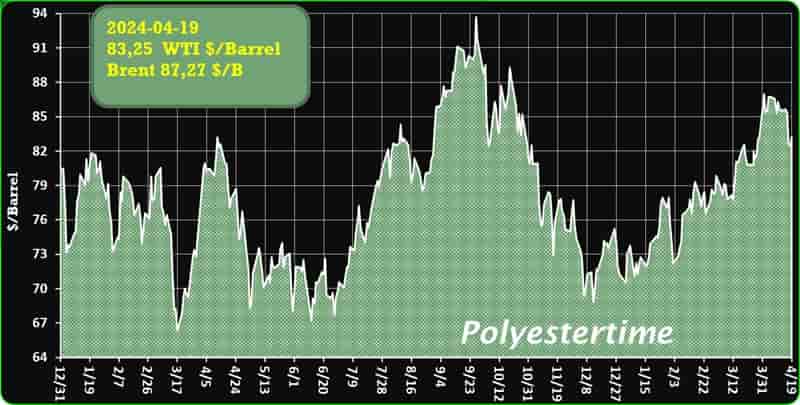
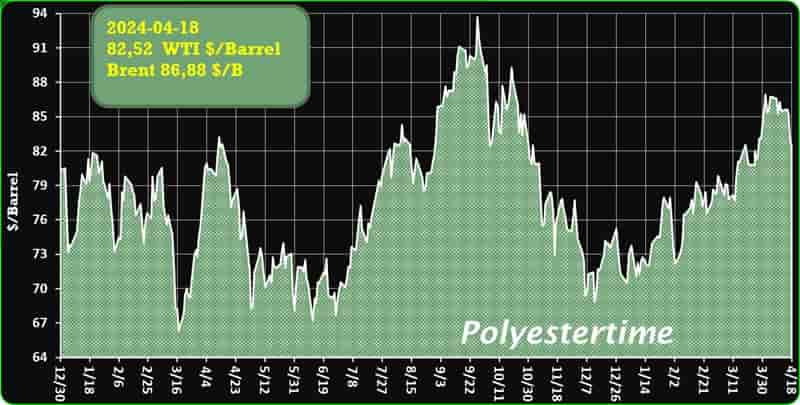
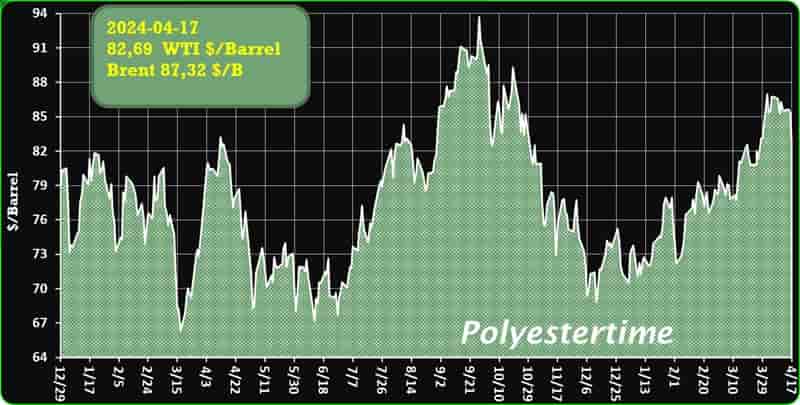
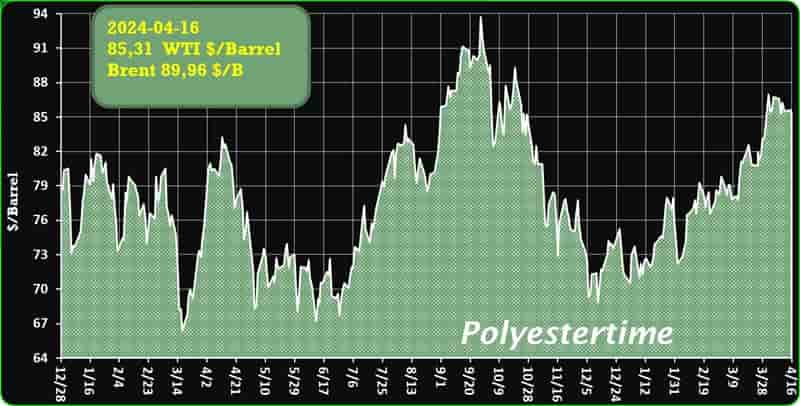
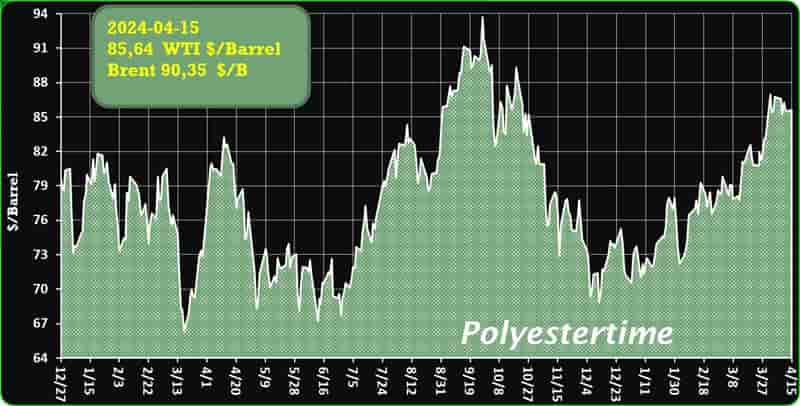
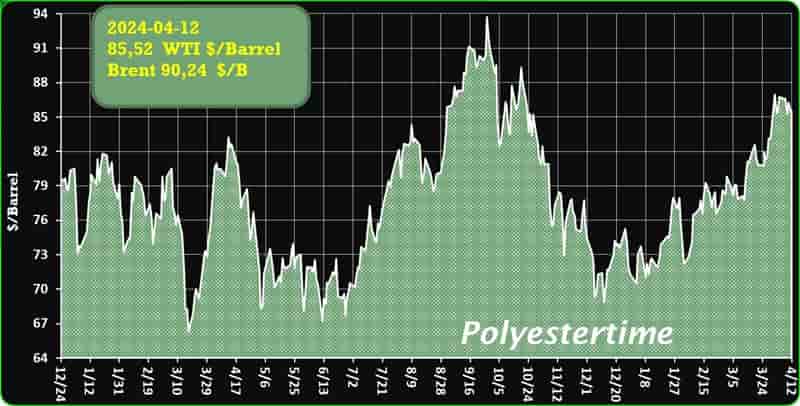
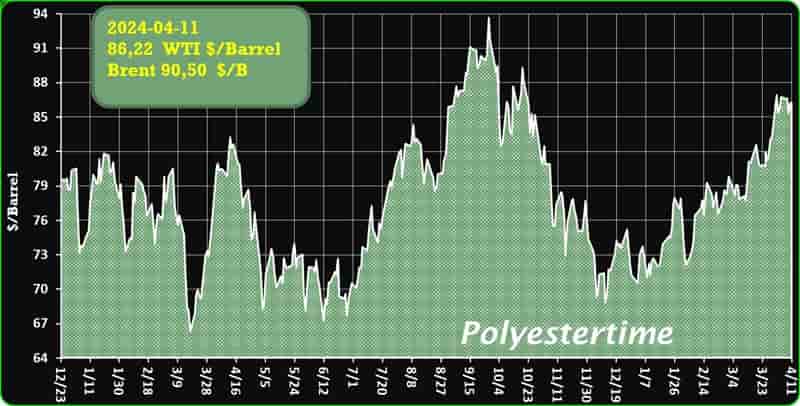
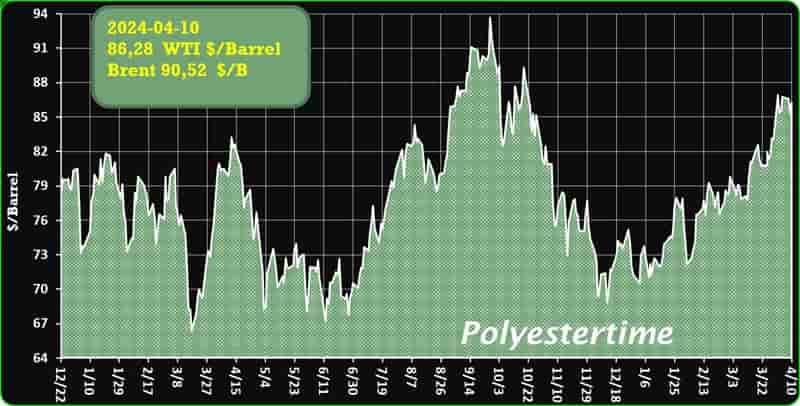
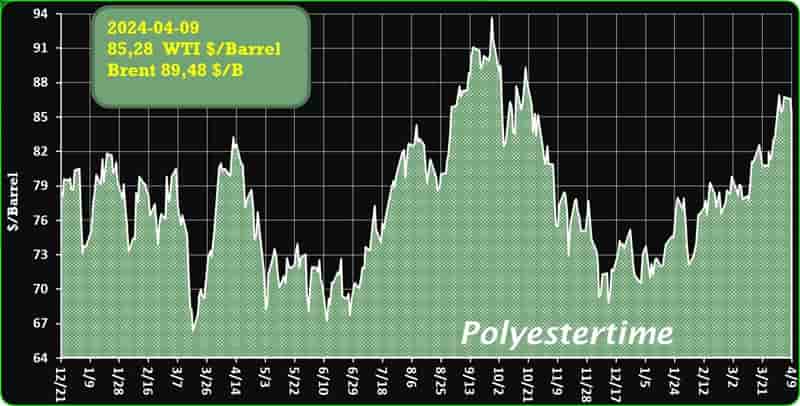
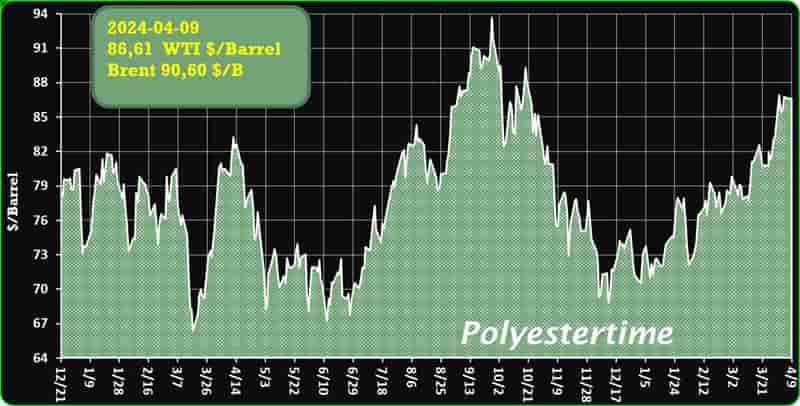
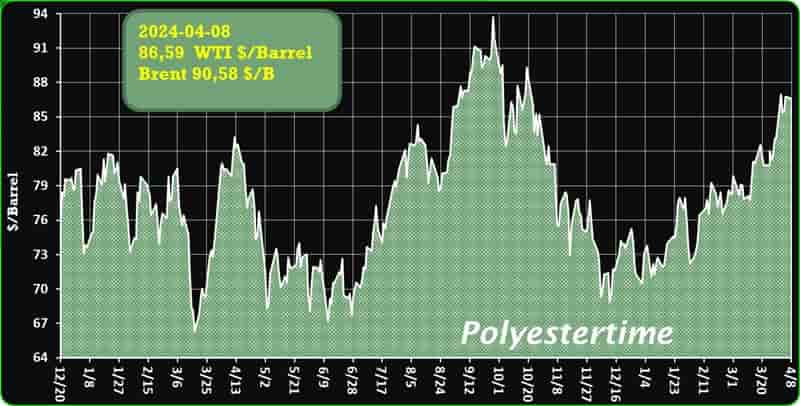
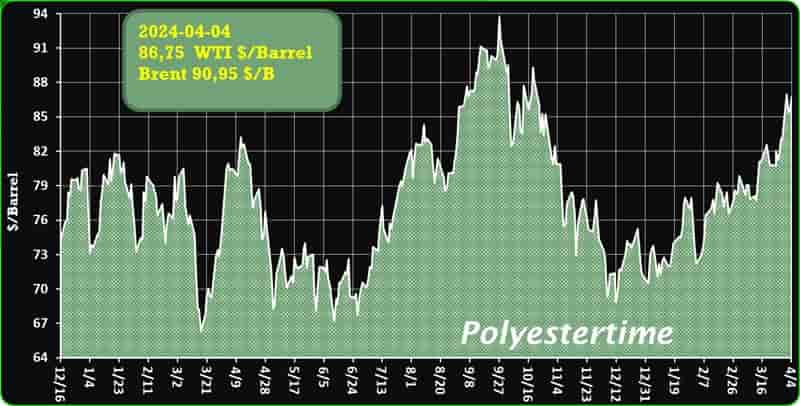
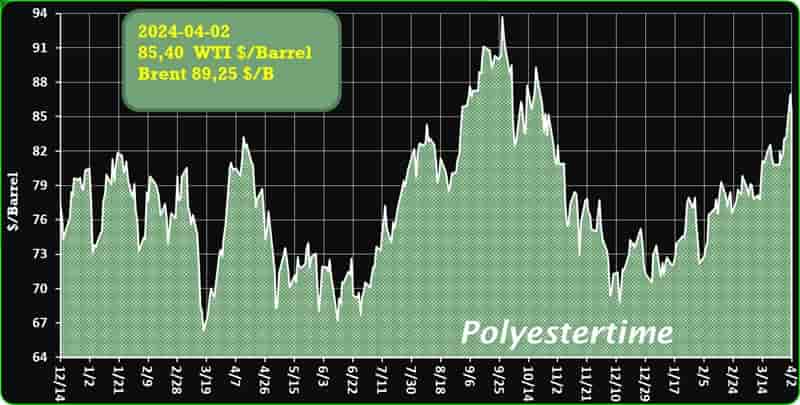
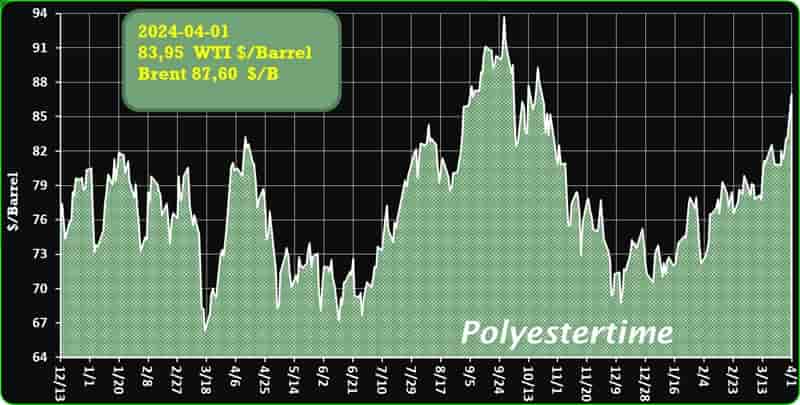
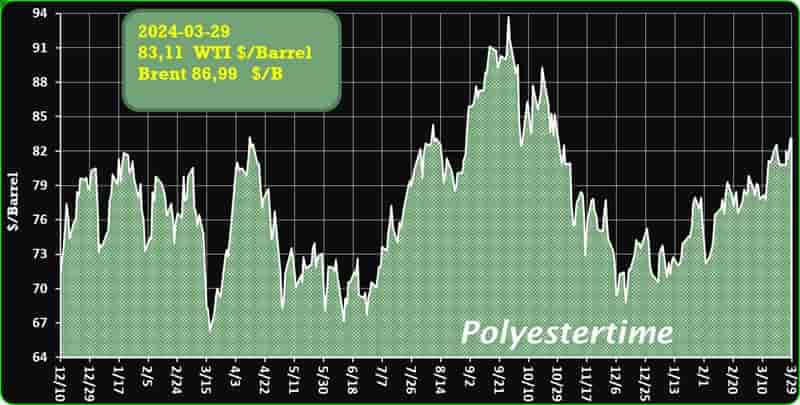
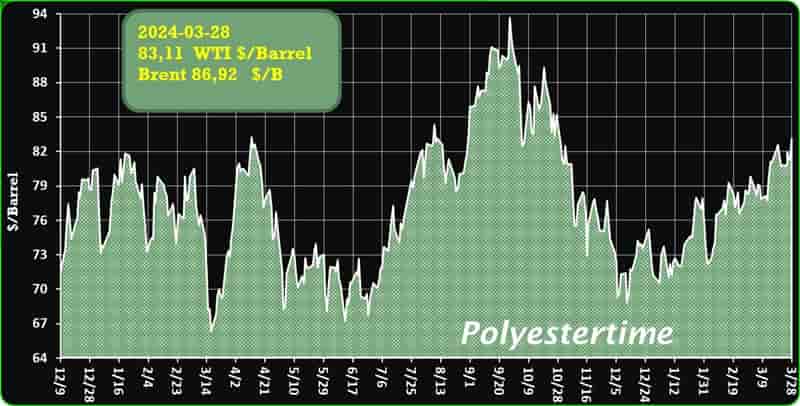
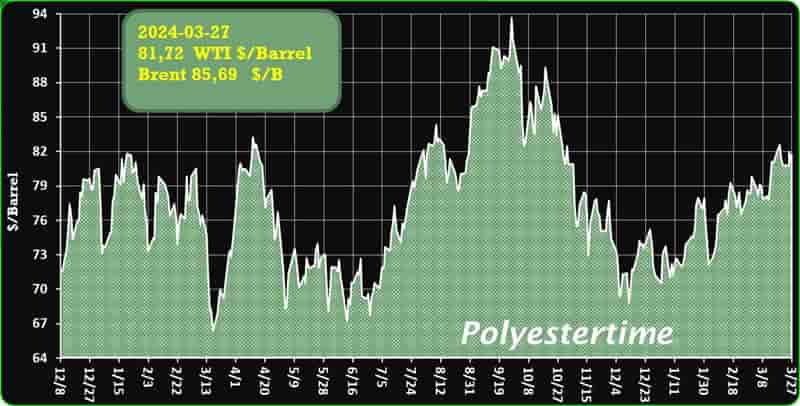
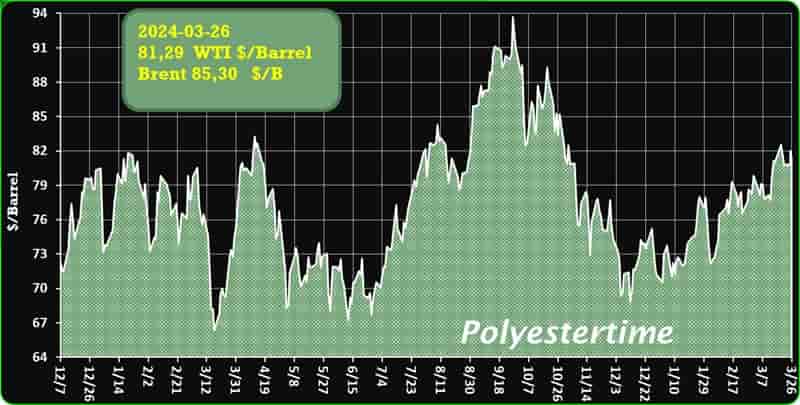
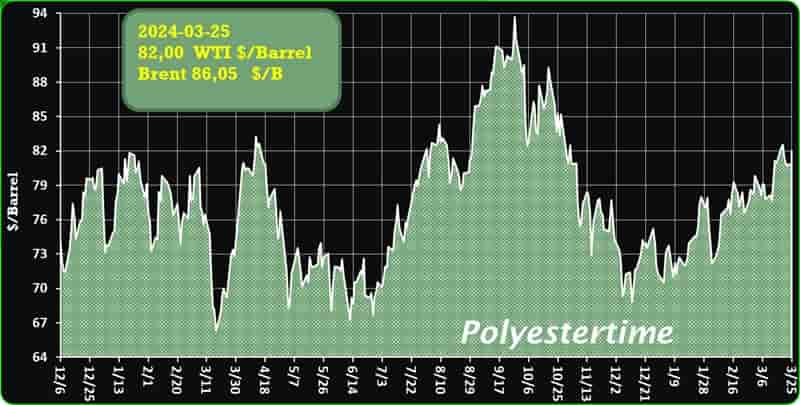
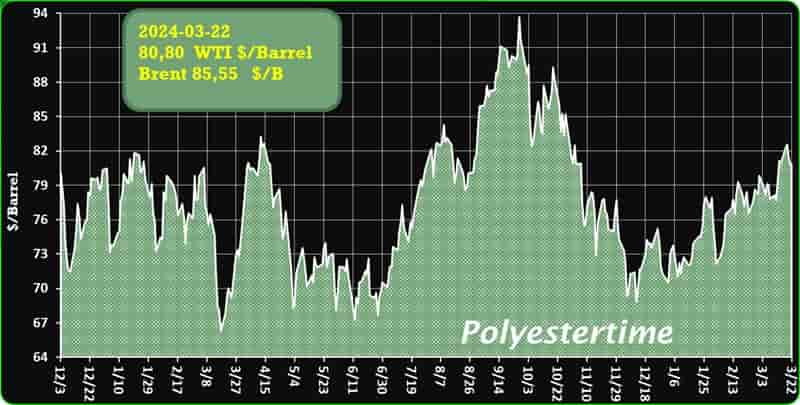
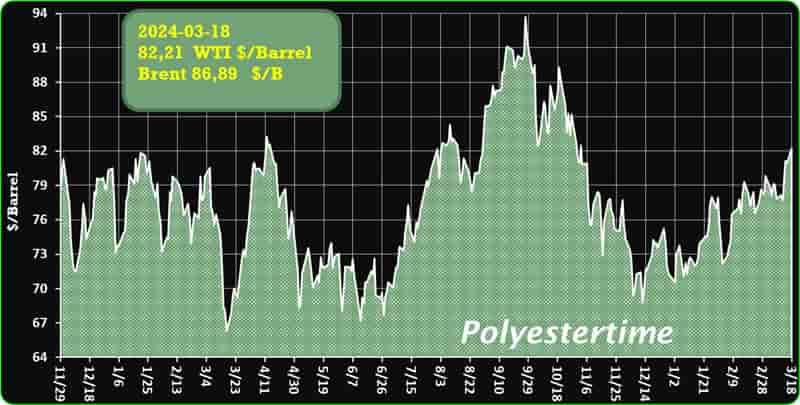
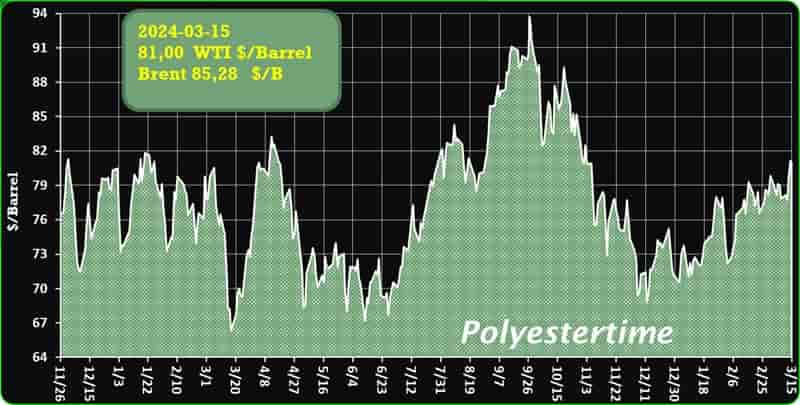
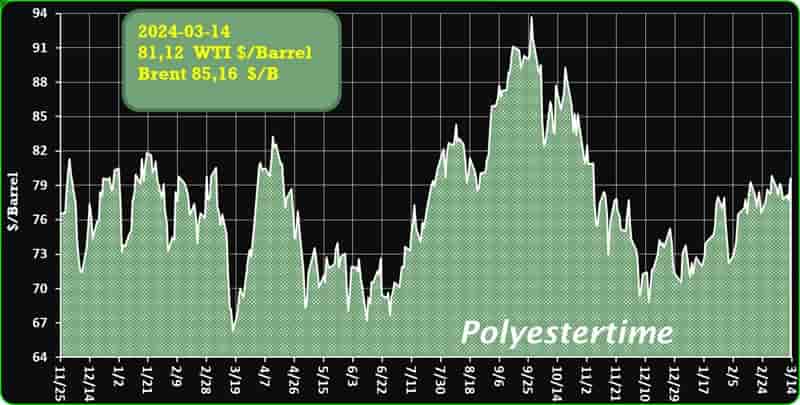
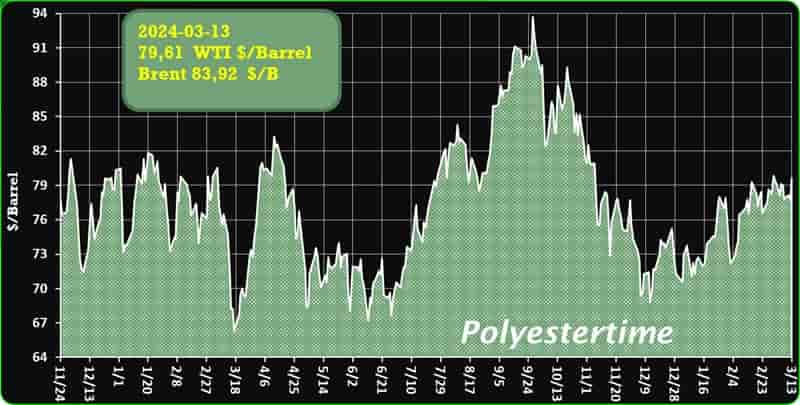
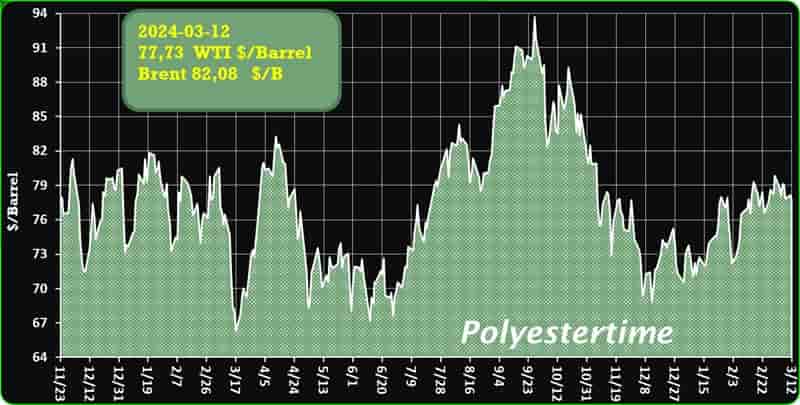
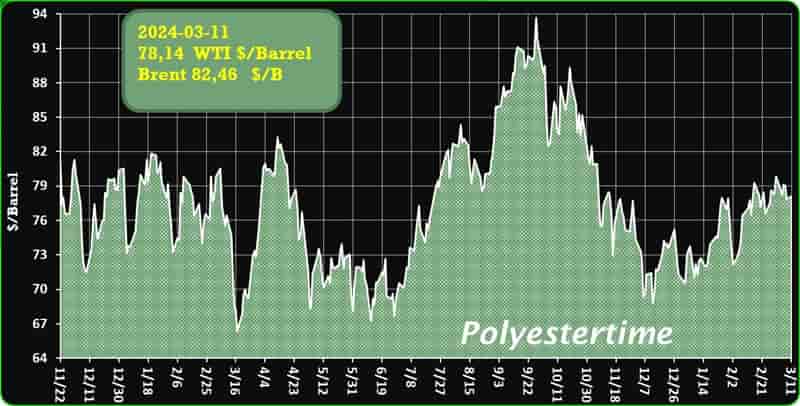
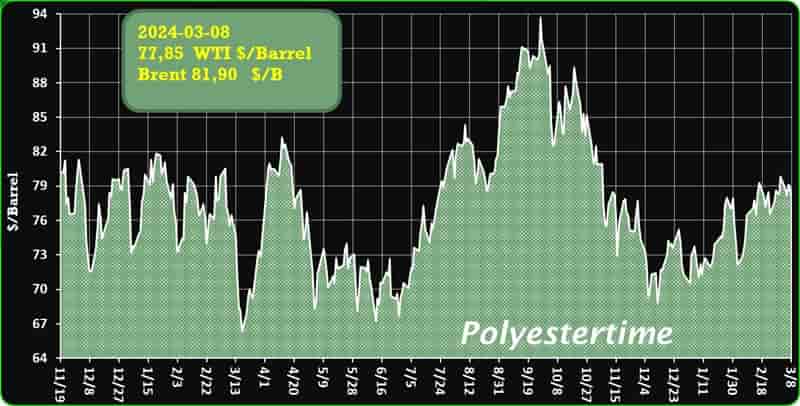
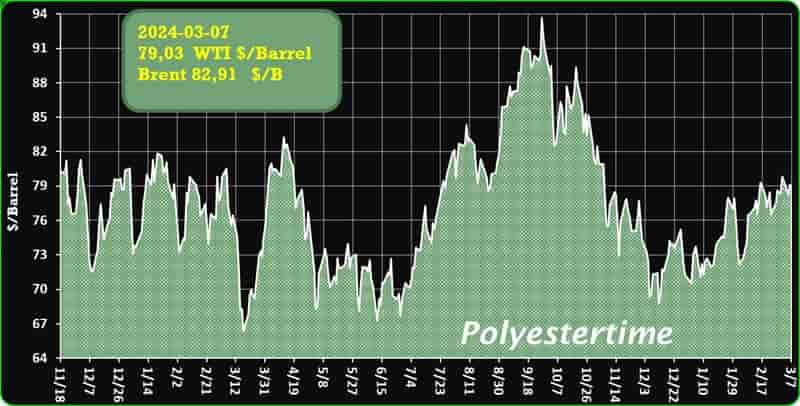
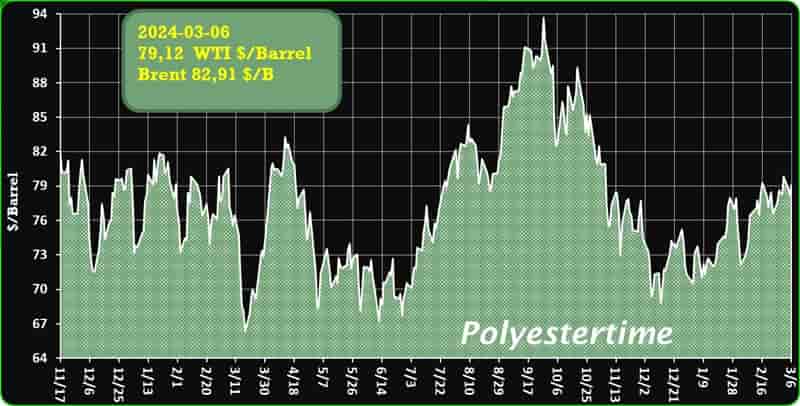
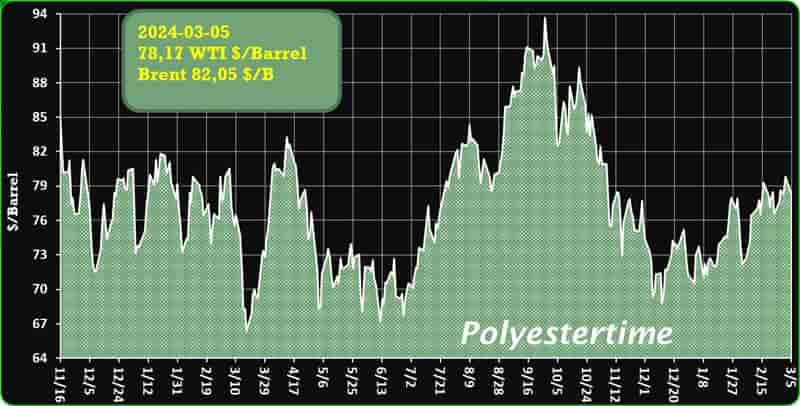
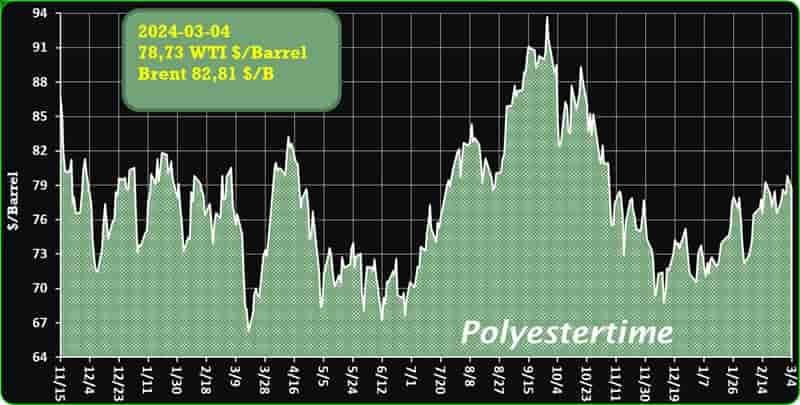
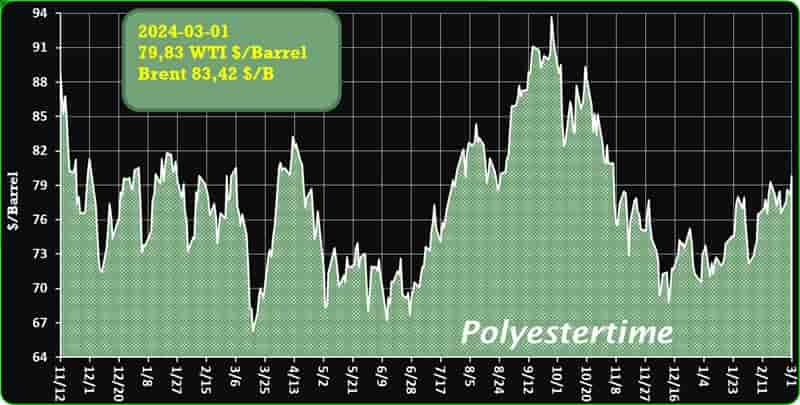
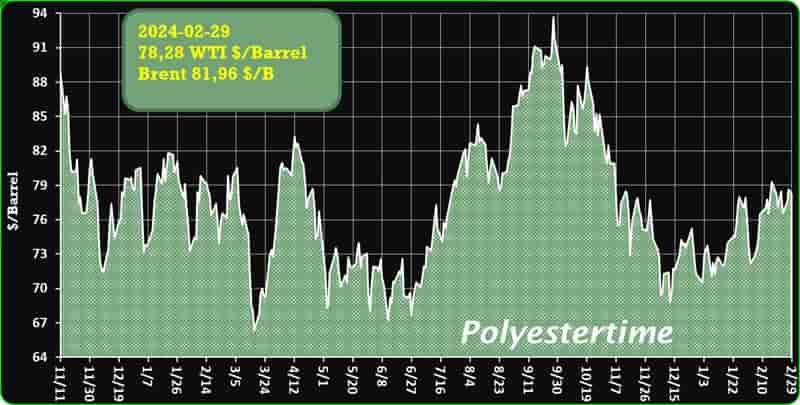
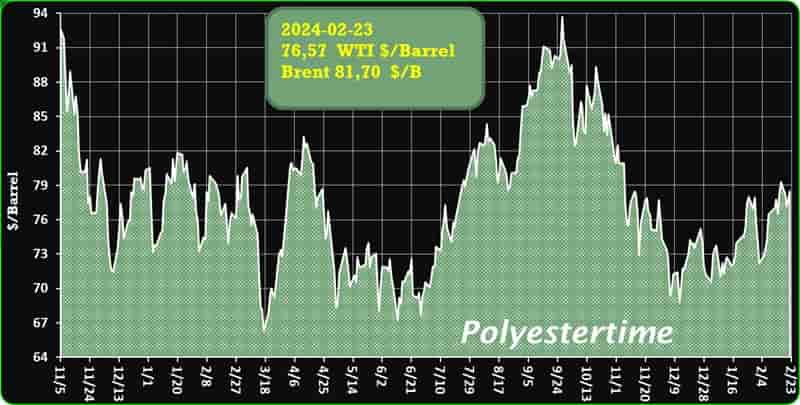
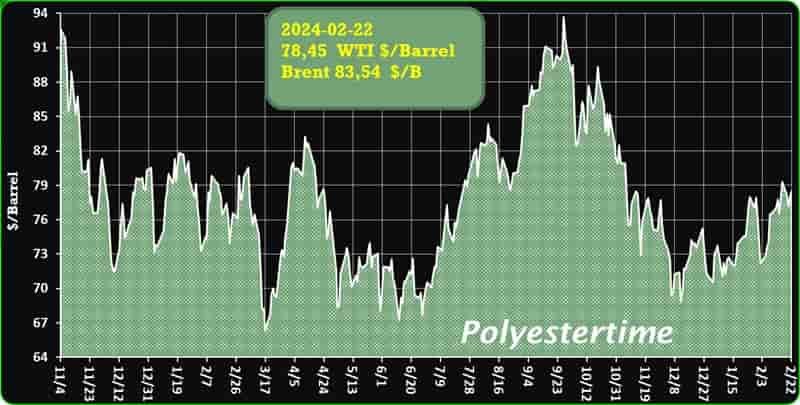
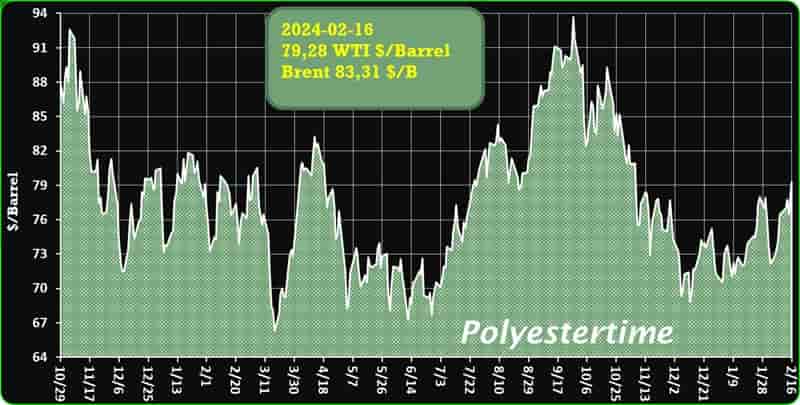
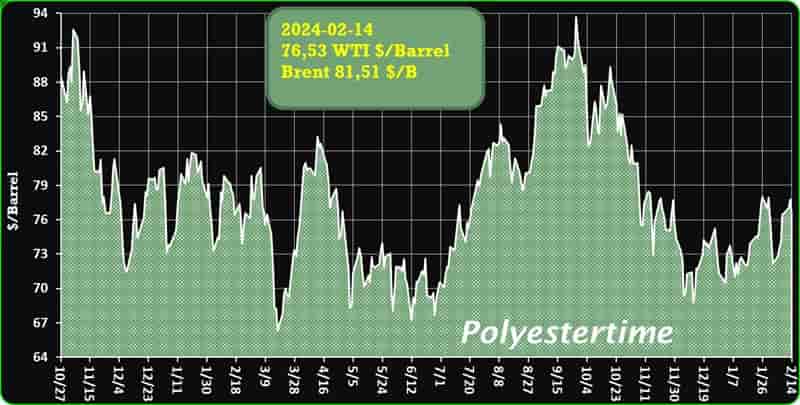
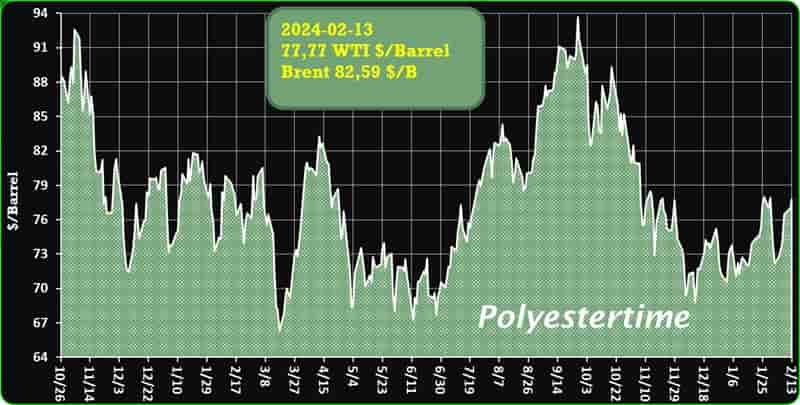
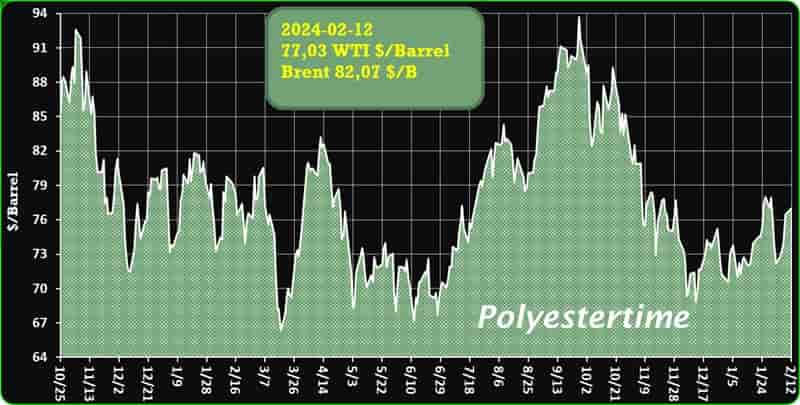
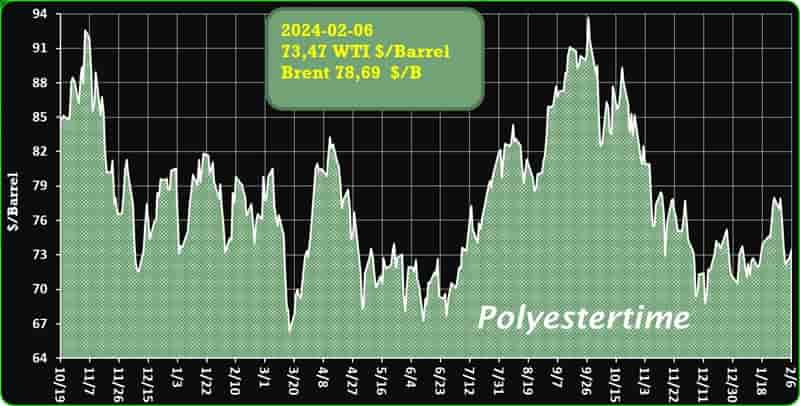
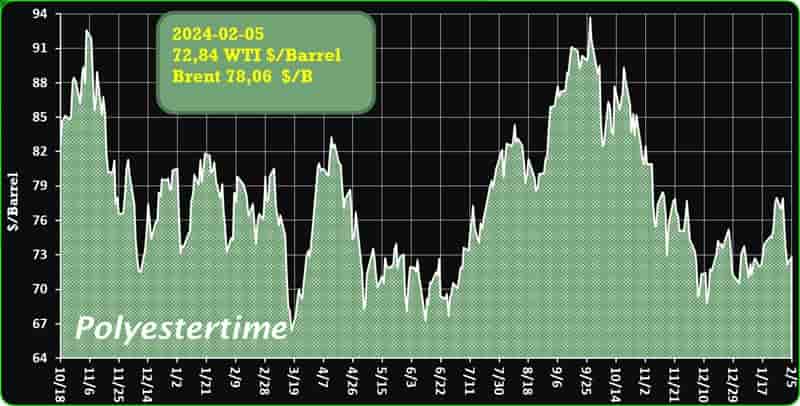
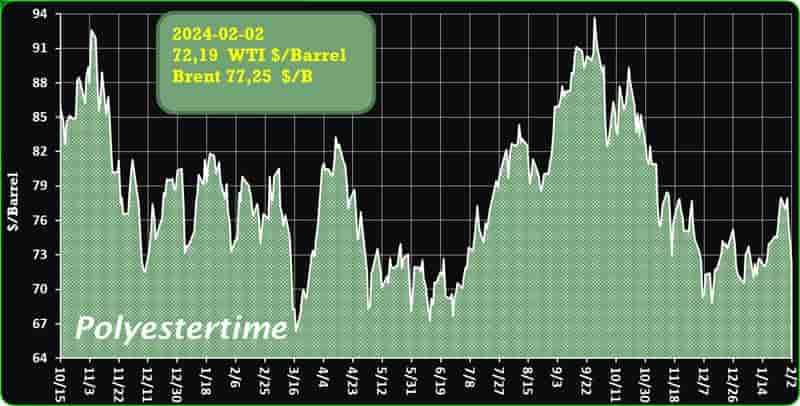
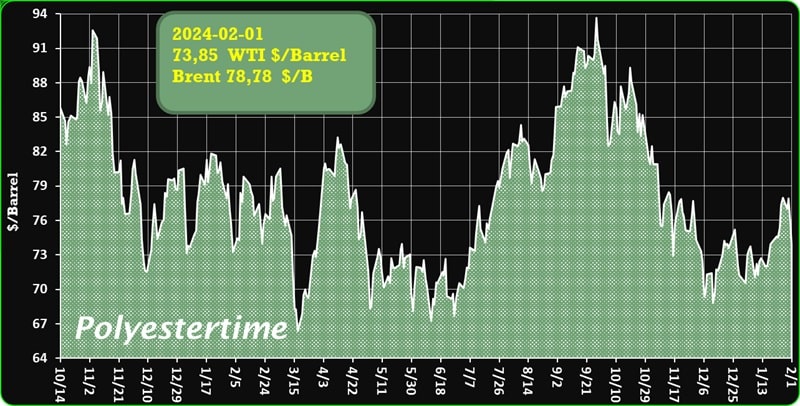
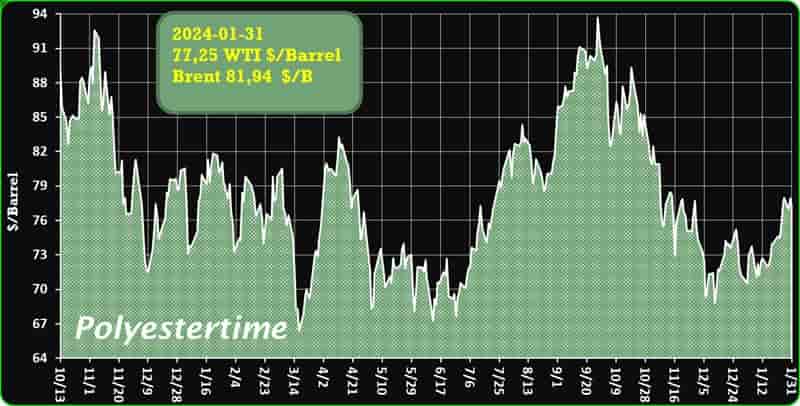
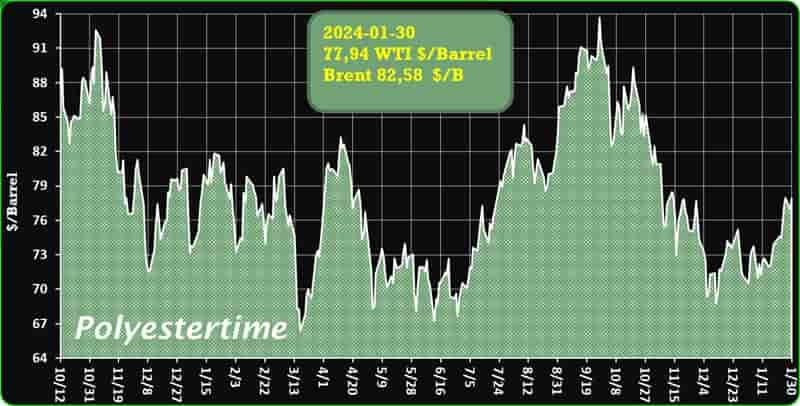
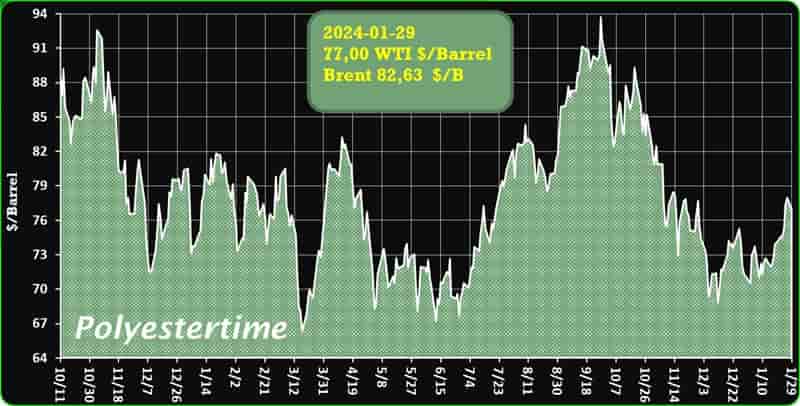
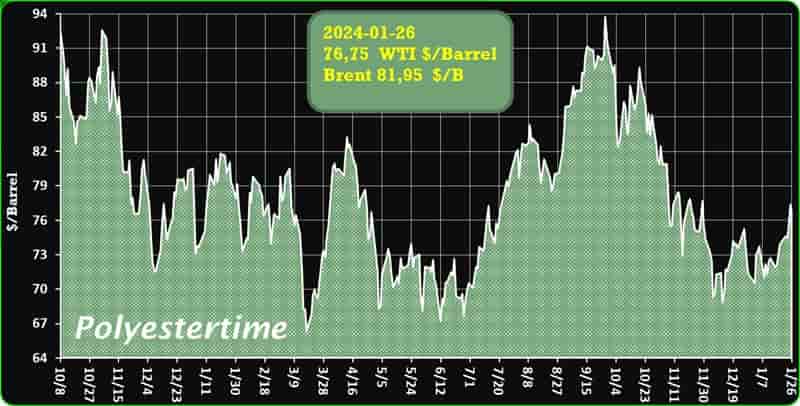
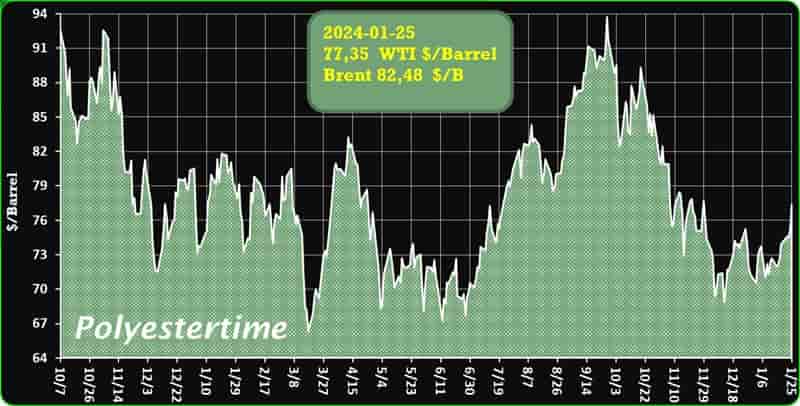
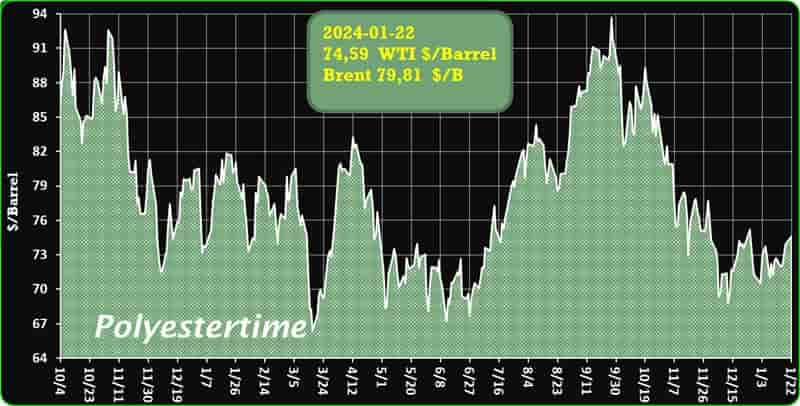
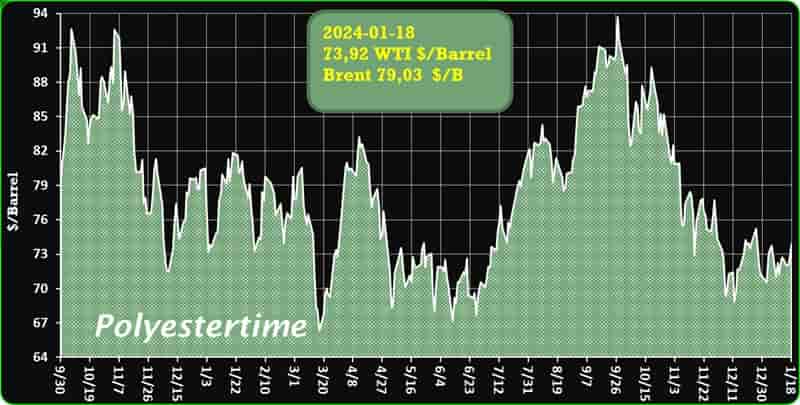
Crude Oil Prices Trend
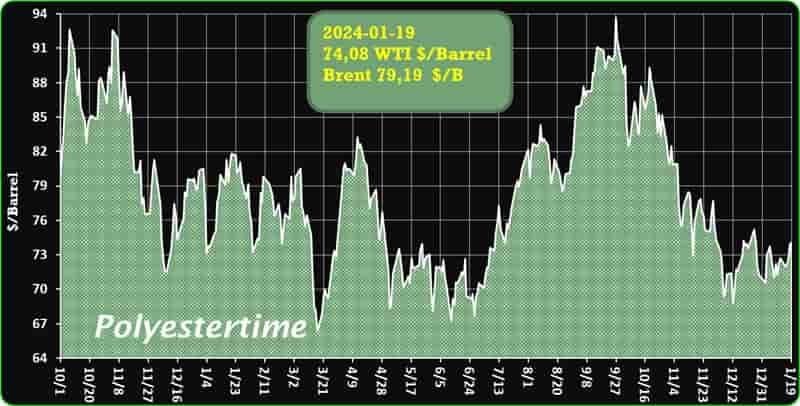
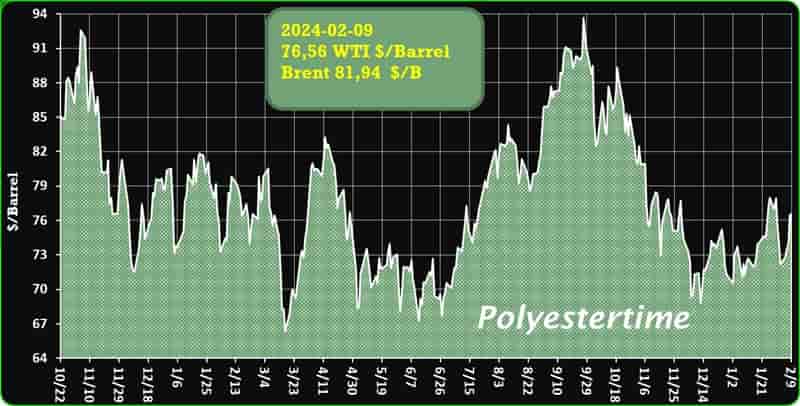
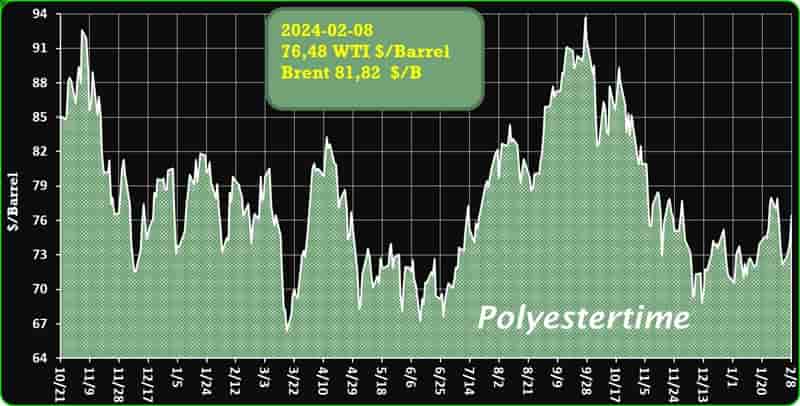
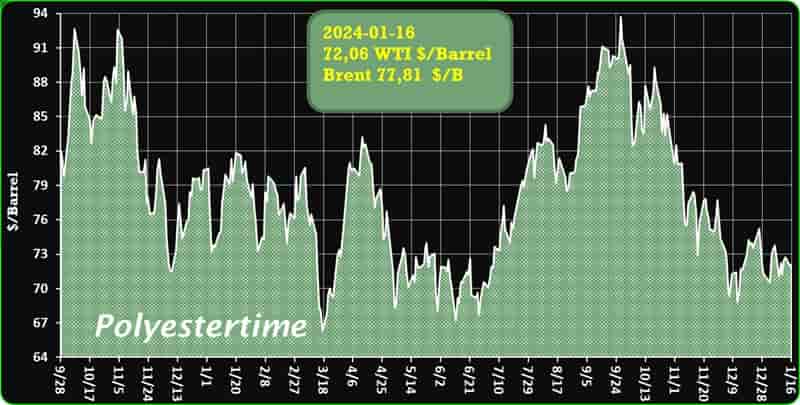
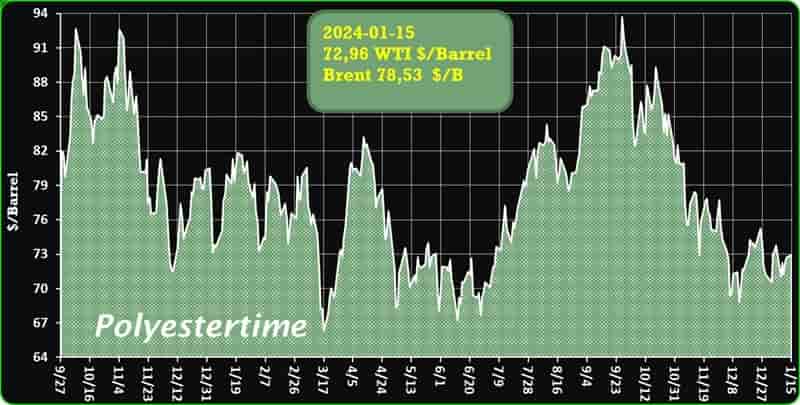
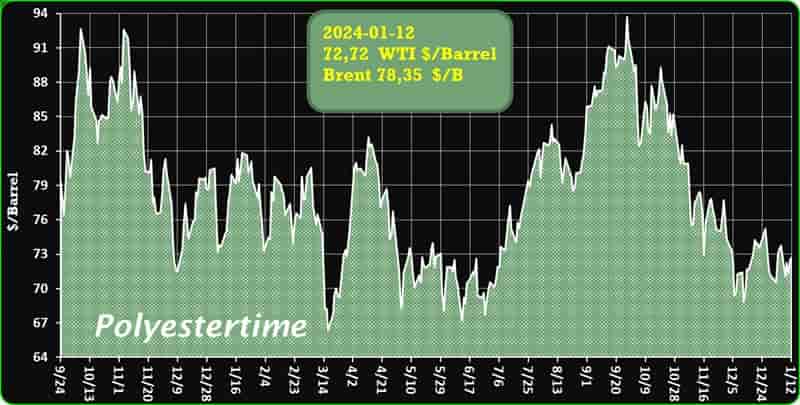
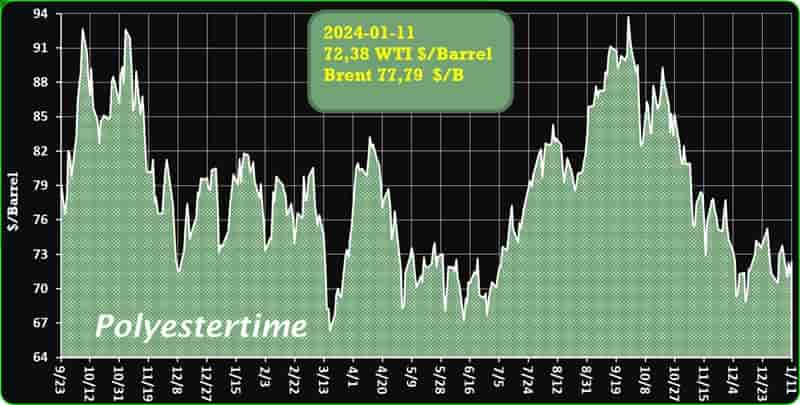
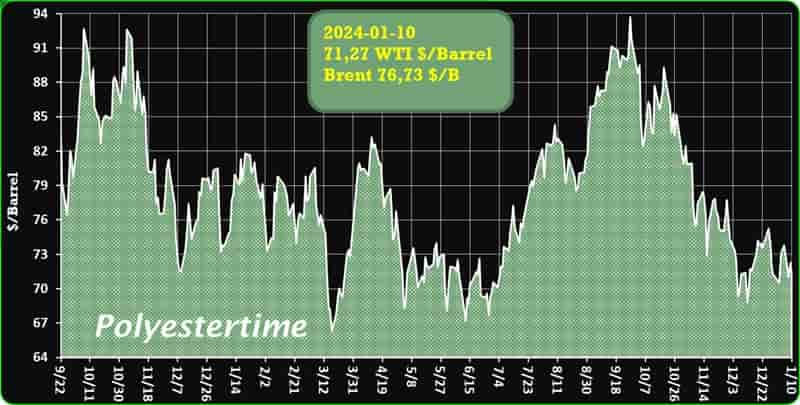
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
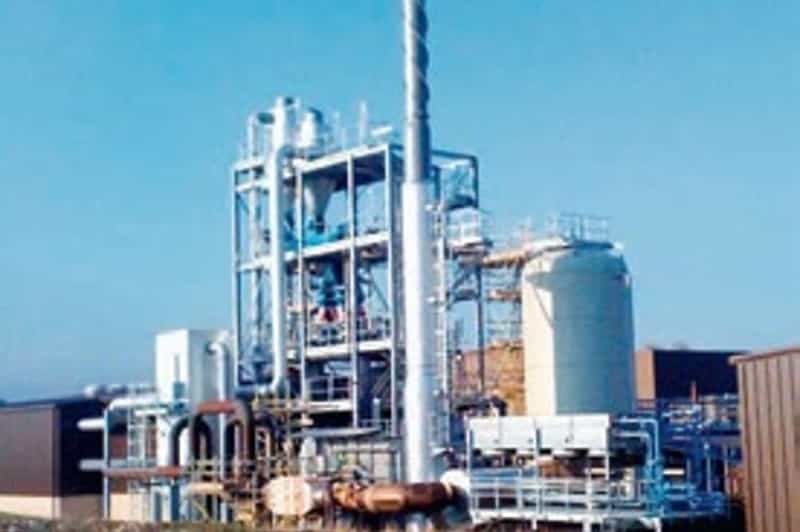
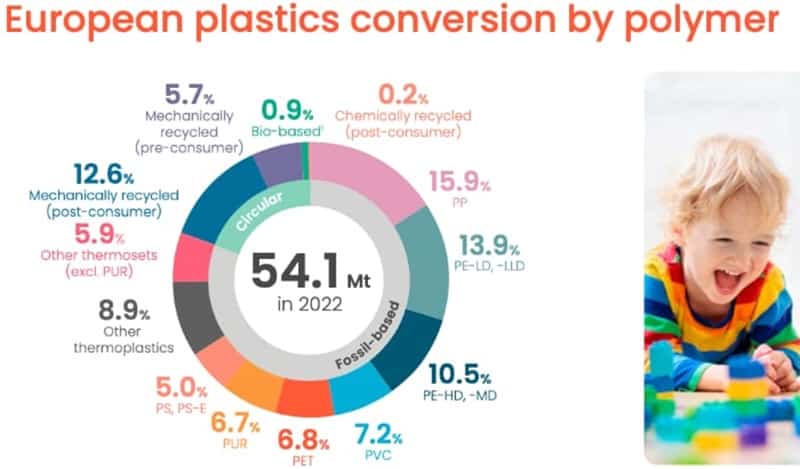
MEGlobal has announced a $10/tonne increase in the Asian Contract Price (ACP) for monoethylene glycol (MEG) for February 2024
The new nominated price stands at $850/tonne, reflecting a rise from the previous month’s ACP, as reported by the company. This adjustment is based on the CFR (cost & freight) Asia basis.
In January 2024, MEGlobal had set the ACP for MEG at $840/tonne, maintaining stability compared to the December ACP, according to information provided by a company source. During that period, the ACP was also determined on a CFR Asia basis.
The decision to raise the February ACP by $10/tonne aligns with market dynamics and may be influenced by factors such as production costs, supply and demand trends, and global economic conditions. MEGlobal’s proactive approach to periodic pricing adjustments reflects its responsiveness to the dynamic nature of the MEG market.
As MEGlobal continues to navigate market fluctuations, stakeholders will monitor how these adjustments impact the broader industry and whether they are indicative of wider trends in the global MEG market.

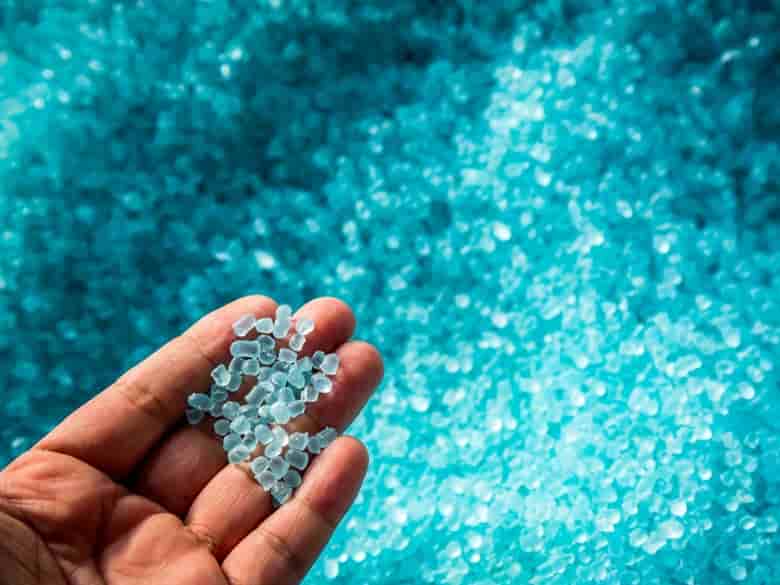
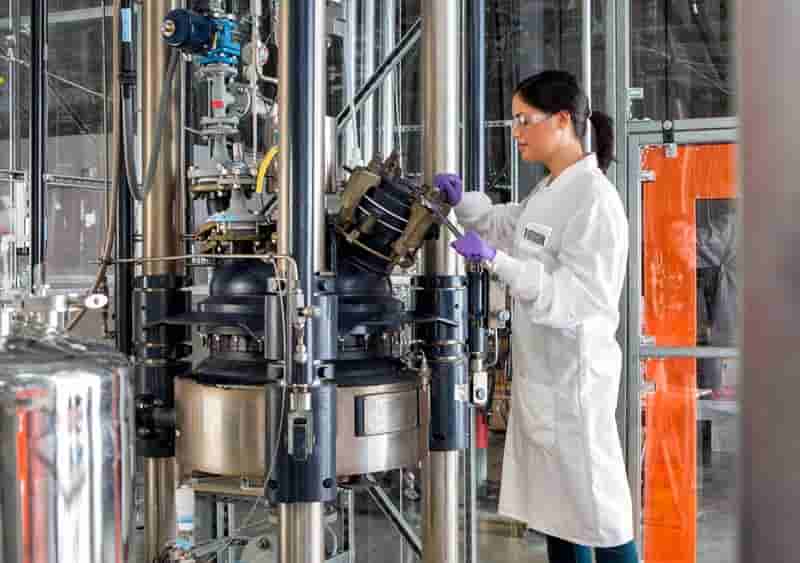
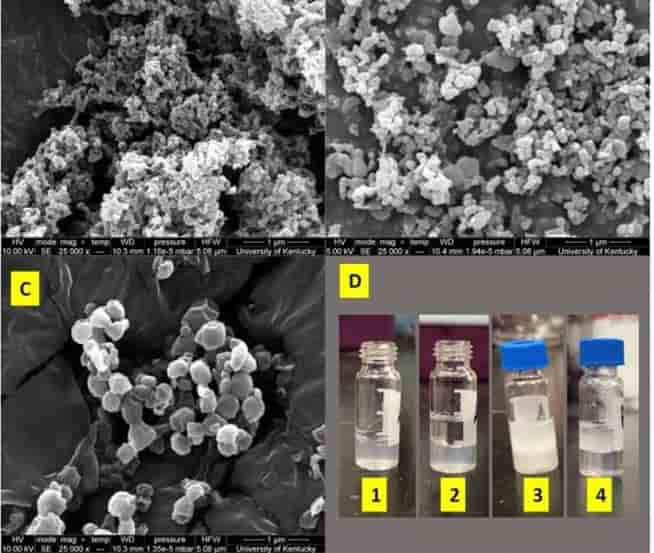
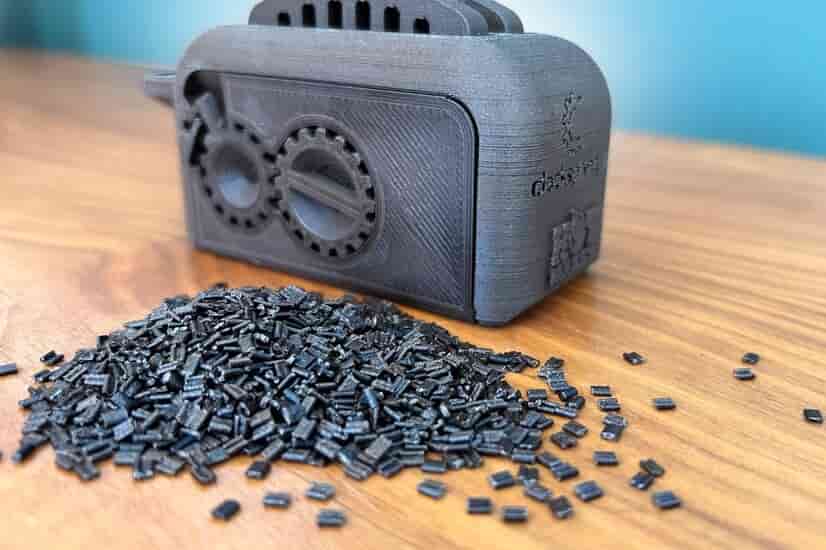
TotalEnergies Corbion, based in Gorinchem, Netherlands, has unveiled the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) for recycled Luminy® PLA, titled “Life Cycle Assessment of PLA through Advanced Recycling – Utilizing Waste Streams as Feedstock for a Biobased Polyester”
The study reveals that the advanced recycling of PLA significantly reduces environmental impact compared to its production from virgin feedstock.
Specifically, the Global Warming Potential (GWP) of Luminy 30% rPLA, factoring in its biogenic carbon content, stands at 0.19 kgCO2/kg of PLA, whereas virgin Luminy PLA emits 0.51 kgCO2/kg of PLA. Seven impact categories were assessed in the report, including GWP, water consumption, and land use. Luminy recycled PLA, with 20% and 30% recycled content, effectively mitigates impacts across these categories, showcasing environmental benefits over traditional virgin production methods.
The report underscores the significance of considering temporary carbon storage in biobased materials, emphasizing the role of biogenic carbon content in PLA. Recycling PLA extends the storage of biogenic carbon from the atmosphere, contributing to reduced GWP. Notably, the GWP of 30% recycled PLA is reduced by 300 kgCO2/tPLA compared to virgin PLA, marking a substantial stride towards global climate targets.
Maelenn Ravard, Regulatory and Sustainability Manager at TotalEnergies Corbion, emphasizes the energy-efficient depolymerization process via hydrolysis in advanced recycling, closing the loop and enhancing circularity for biobased materials. The LCA results validate the efficiency of this process.
The LCAs evaluate the environmental impact of a product across its defined life scope. TotalEnergies Corbion’s commitment to sustainability aligns with its recent announcement of aligning with the United Nations Global Compact initiative. This collaboration emphasizes the company’s dedication to universal sustainability principles, actively supporting the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals through responsible production practices and collaborative initiatives across its value chain.
For those interested in the comprehensive analysis, the Life Cycle Assessment of PLA through Advanced Recycling can be accessed through the provided link.

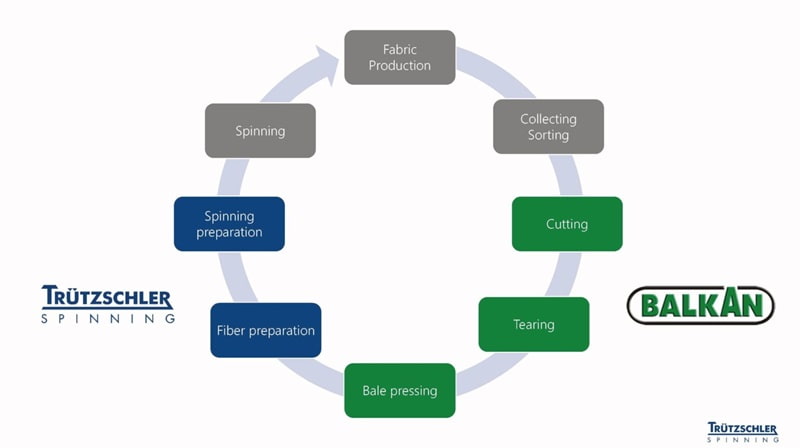
In a significant development, ERCA Textile Chemical Solutions (TCS) has officially emerged as an independent entity within the ERCA Group, exclusively dedicated to the textile industry
Fabio Locatelli, CEO of ERCA TCS and an Associate of the ERCA Group, announced the decision, highlighting the company’s commitment to focusing solely on textile solutions while maintaining a robust foundation from ERCA S.p.A.
The strategic move to establish ERCA TCS as a distinct company is driven by the aspiration to prioritize the textile industry, fostering agility in research and production with a steadfast commitment to ethical, social, environmental, and economic responsibility. With an agile organizational structure and an amplified research and development department, ERCA TCS aims to swiftly address customer needs, fostering an engaging dialogue that results in pioneering developments and innovative chemical solutions.
As a pioneering force, ERCA TCS seeks to be the premier global reference for sustainable innovation in the textile sector, contributing to reducing the industry’s environmental impact while upholding performance and competitiveness. Red Sea Crisis
Fabio Locatelli emphasizes the company’s dedication to well-being, responsible resource usage, and the initiation of education and training initiatives, ensuring transparent and professional communication.
ERCA TCS employs “green chemistry” principles in its operations, exemplified by its flagship product, REVECOL®. This innovative chemical auxiliary, derived from critical waste materials like used vegetable oils, demonstrates immediate success in the textile industry. The establishment of ERCA TCS will further propel research and investment, expanding the product range available to the textile industry.
ERCA Group, with six plants across Europe, Latin America, and Asia, embodies responsible innovation in chemical specialties and auxiliaries, covering diverse markets. With a turnover of 150 million euros and a global workforce of 350 employees, ERCA Group is poised to address the challenges and opportunities in the textile industry, positioning ERCA TCS as a catalyst for responsible and high-quality productions. Red Sea Crisis

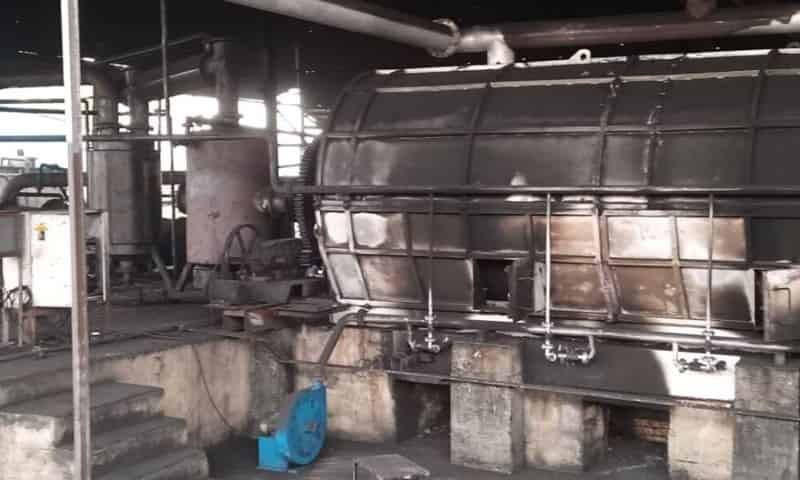
Baltex Plans to Expand Polyamide Fabric Manufacturing in Russia
Baltex, also known as Balashovsky Textile Plant situated in Saratov, Russia, has embarked on a substantial investment project with a total value exceeding 800 million rubles to augment the production of polyamide fabrics. The inaugural phase of this expansive initiative, surpassing 300 million rubles, was successfully executed in 2023. This initial phase involved the installation of cutting-edge equipment, renovation of both production and residential facilities, and endeavors to enhance operational processes.
Citing a robust domestic demand for technological fabrics coupled with state support in the form of preferential financing from the Industrial Development Fund (IDF) of Russia, Baltex foresees commencing the second stage of production modernization in 2024. The projected investment for this stage focuses primarily on main equipment and is estimated to reach 500 million rubles. Red Sea Crisis
The anticipated outcome of this ambitious investment project is a noteworthy 50% increase in production capacity, fortifying Baltex’s standing in the consumer market, particularly within the Saratov region.
It is noteworthy that the company’s strategic vision aligns with the broader industry trend of expansion and modernization. Recently, the Kotovsky Plant of Nonwovens in the Tambov Region announced plans to double the production of polyester, signalling a collective effort within the Russian textile sector to meet growing market demands.
Financial commitments to Baltex’s project are substantial, amounting to almost 141 million rubles. Notably, 91 million rubles of this sum are sourced from a preferential loan provided by VEB.RF, carrying an interest rate of merely 1% per annum. These funds are earmarked for the acquisition and deployment of state-of-the-art equipment critical to the success of the modernization efforts. Red Sea Crisis
Baltex, as a comprehensive textile enterprise, boasts a full-cycle operational model, covering the spectrum from material development to the serial production of functional textiles. The company specializes specifically in the manufacturing and supply of high-strength polyamide fabrics, a niche that aligns with the increasing demand for advanced and durable materials in various industries.
More..

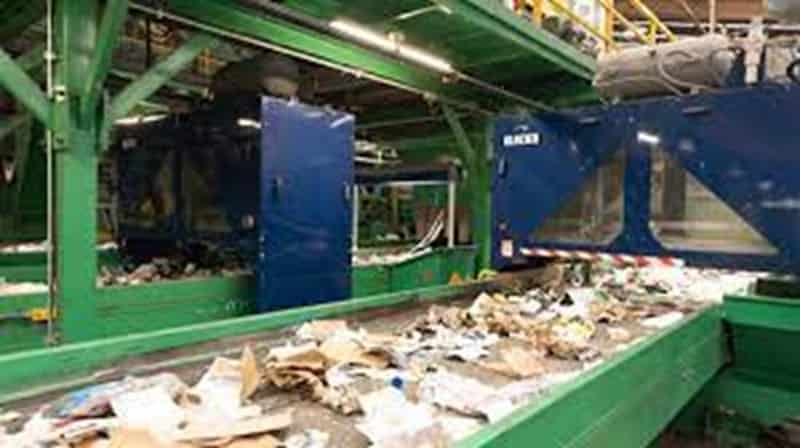
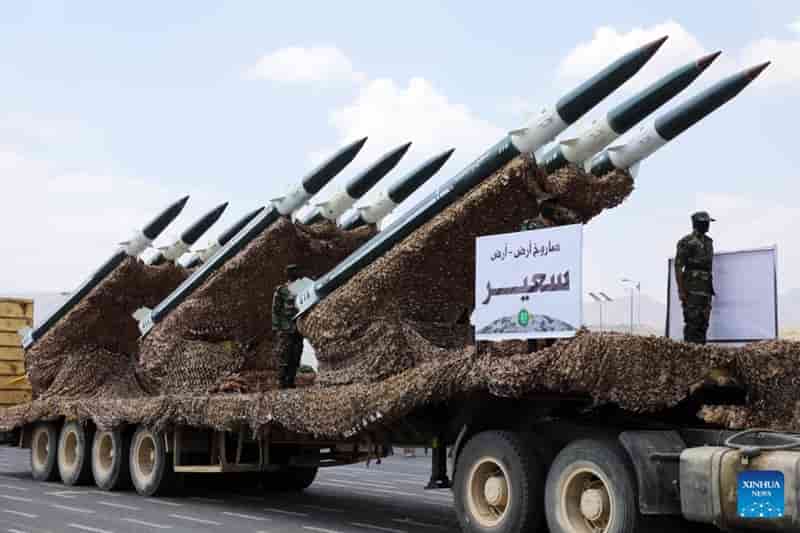
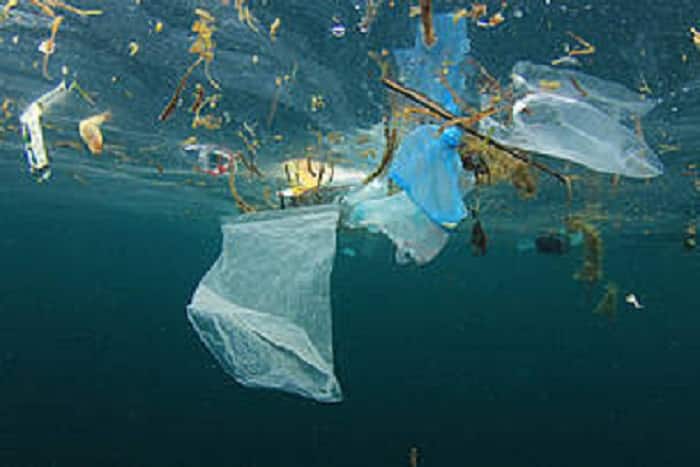
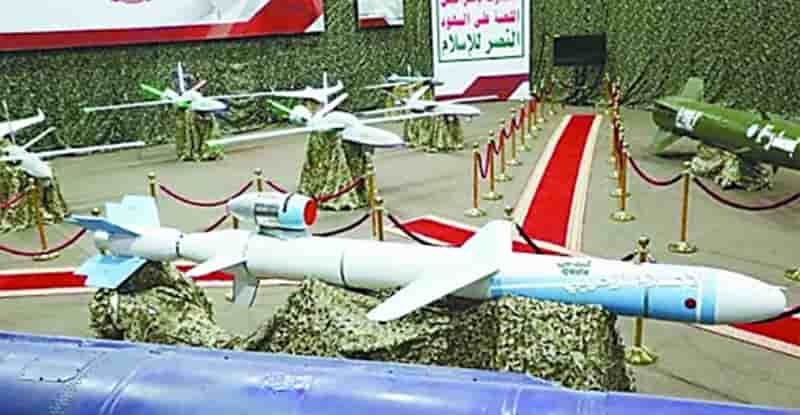
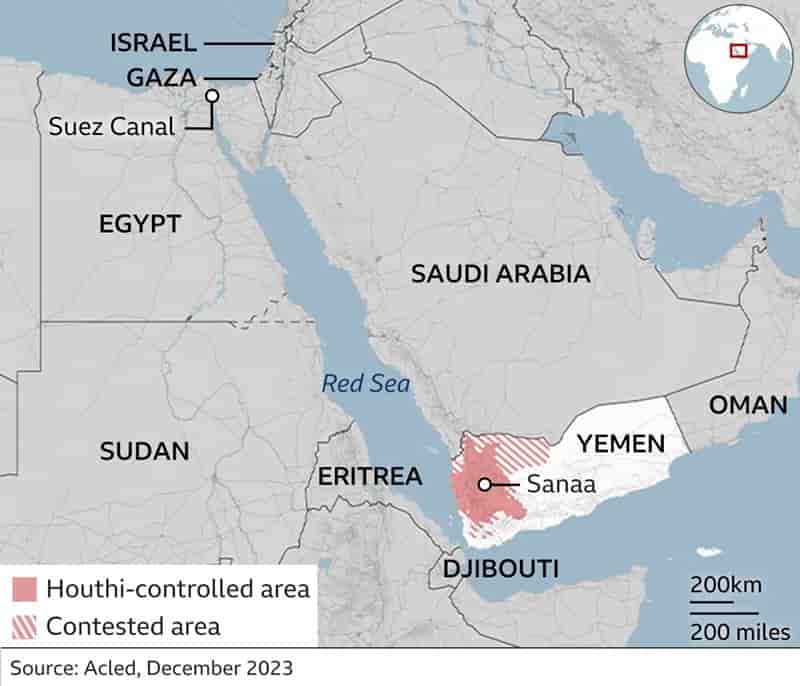
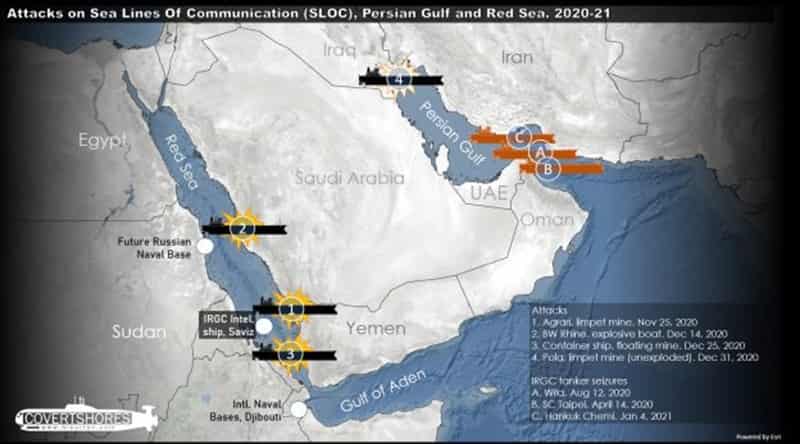
Red Sea Crisis Casts a Shadow on Asian Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) Exports in Early 2024
The recent crisis in the Red Sea and the subsequent changes in shipping routes through the Suez Canal are posing significant challenges on the export of Asian garments and textiles, particularly those made from Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF). This development comes at a time when these nations had anticipated improved prospects for 2024, but the crisis threatens to extend the slowdown in garment and textile exports due to the surge in freight charges, particularly to Europe. Red Sea Crisis
Shinhan Securities Vietnam reports that Vietnamese firms exporting PSF to Europe and the East Coast of North America are facing disruptions due to the altered Red Sea routes. Vietnamese PSF exporters are expressing concerns about escalating transportation fees as shipping lines divert their routes to ensure safety amidst tensions in the Red Sea. This situation places an additional burden on exporters of PSF who were already grappling with the repercussions of the global economic slowdown in 2023.
Truong Dinh Hoe, the general secretary of the Vietnam Association of Seafood Exporters and Producers (VASEP), notes that transport fees to the West Coast of the US surged by approximately 55-60% in January compared to the previous month. For the East Coast, the increase ranges from 58-73%. Notably, transportation fees to Hamburg, Germany, have skyrocketed to 3-4 times higher, jumping from USD 1200-1300 to USD 4350-4450.
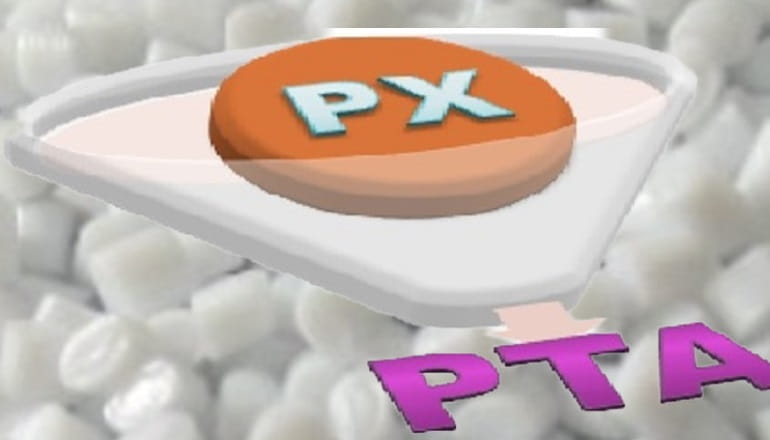
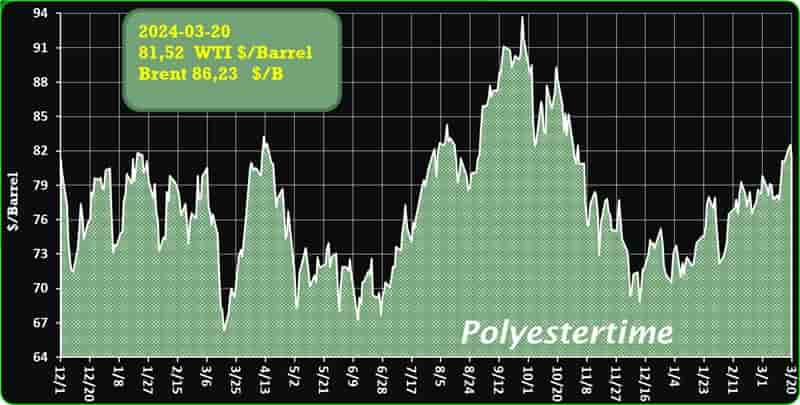
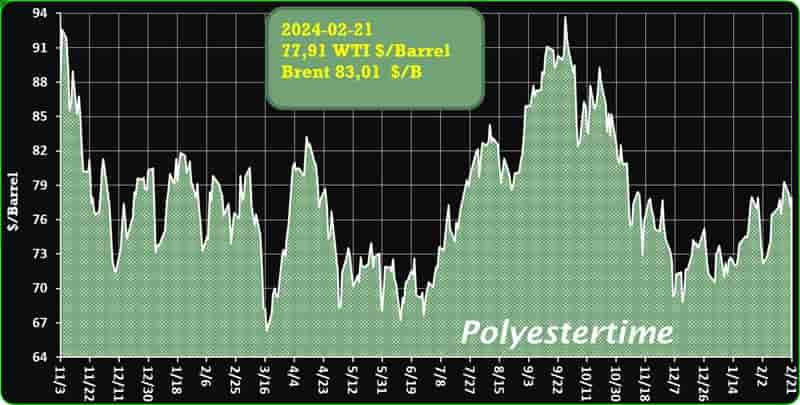
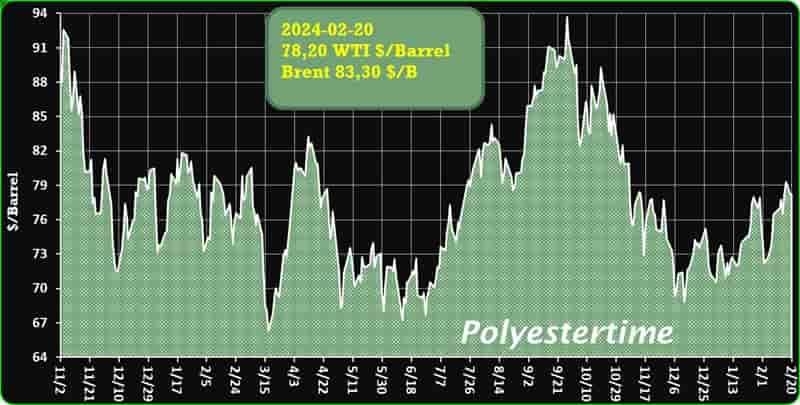
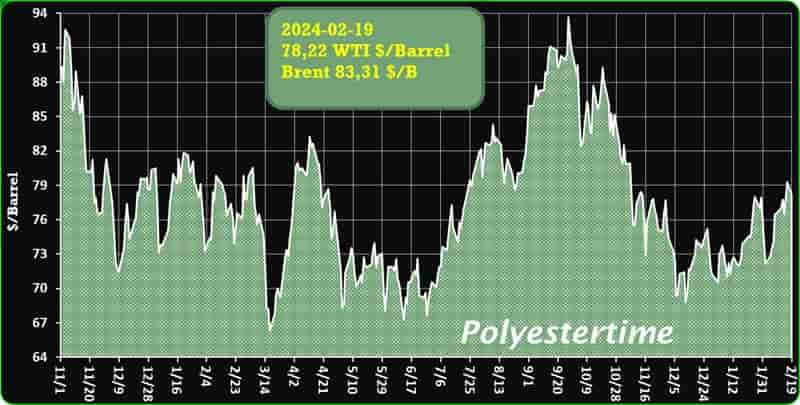
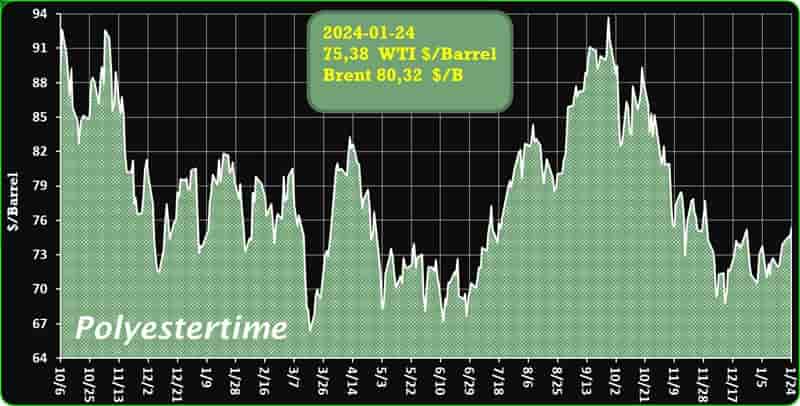
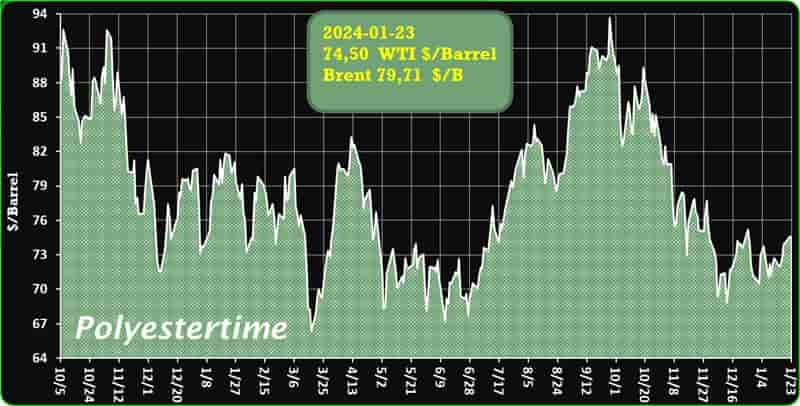
The prevailing tension in the Red Sea area is causing an increase in oil prices, thereby positively affecting the upstream sector, and feedstock linked to oil like Purified Terephthalic Acid (PTA) and Mono-Ethylene Glycol (MEG), which serve as crucial feedstock for PSF.
At the beginning of 2024, there is a slowdown in the rate of growth in the demand for PSF in Asia, specifically in the home textiles sector. Nonetheless, there is an anticipated continuation of replenishment demand across the PSF industrial chain.
Concurrently, the outlook for foreign trade to Europe and the US is cautiously optimistic, marked by sluggish growth in PSF market, weakened economic strength, and an anticipation of reduced prices. Red Sea Crisis
More.. 
Newcleo and Naarea partners for fourth generation nuclear power
Newcleo and Naarea, two companies that are working on fourth generation nuclear reactors that can use waste as fuel, have announced a strategic and industrial partnership with the goal of “helping all the stakeholders involved in the fourth nuclear generation in their industrial, technological, scientific and regulatory progress”.
The partnership, according to a statement, is in line with the industrial alliance for Small Modular Reactors, which the European Commission will launch soon. Red Sea Crisis
The two companies, which were the first to win the France 2030 competition for innovative nuclear reactor projects, will collaborate to speed up the development of their technologies: newcleo is working on a mini-reactor with lead cooling and fast neutrons (a 30MWe prototype and a 200MWe commercial unit) and NAAREA is working on a micro-generator with molten salt and fast neutrons (40MWe, 80MWth).
Although they are different technologies, both solutions are fourth generation and can use the spent fuel from conventional reactors, ensuring the full closure of the fuel cycle. Newcleo and Naarea aim to bring their solutions to the market by 2030.
The partnership, the statement adds, “will enable the creation of joint initiatives with the whole French nuclear sector to make the decision-making process easier for the successful completion of the energy transition through a mix that includes sustainable and innovative nuclear energy”. Red Sea Crisis

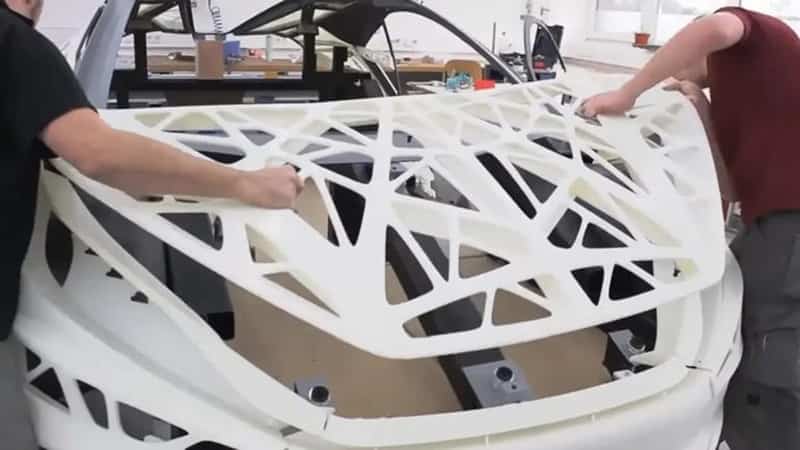
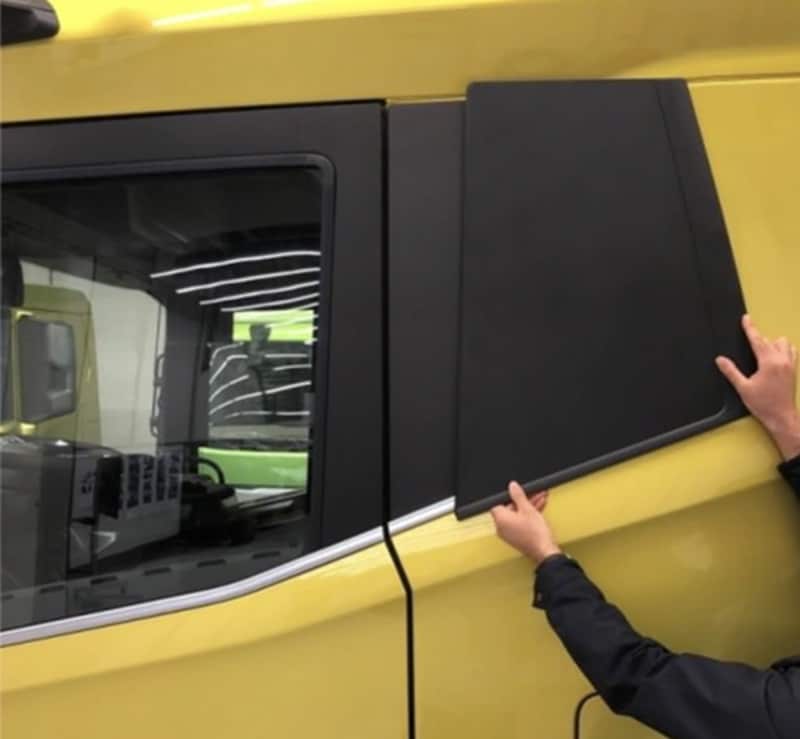
Braskem And WEAV3D Automotive Component To Showcase At The 2024 JEC World Trade Show In Paris, France, March 5-7, 2024
Braskem, a leading producer of polyolefins and biopolymers in the Americas, and WEAV3D, a startup specializing in advanced materials and manufacturing, have announced that their novel automotive door component prototype has been chosen as one of the top three finalists in the JEC Composites Innovation Awards 2024, under the Automotive and Road Transportation – Process category. Red Sea Crisis
The prototype uses WEAV3D composite lattice reinforcement with Braskem PP to create lighter and cheaper thermoplastic solutions than traditional organosheet, opening up new possibilities for replacing sheet metal structures with thermoplastics in vehicles.
“We are very proud to be a finalist for the JEC World Innovation Awards and to offer our clients innovative solutions and partnerships based on high-performance polypropylene materials with the WEAV3D lattice technology, which we launched in 2023.
The automotive industry needs to adopt new performance materials and sustainable end-of-life options as it develops new electric vehicle designs.
The WEAV3D technology can be used for both thermoforming and injection molding of parts, depending on the complexity.
By combining Braskem’s PP portfolio with WEAV3D composite lattices, we achieve a ‘win-win’ situation of improved material performance and reduced environmental impact, with the possibility of incorporating natural fibers,” said Amanda Zani, Technology Platform Manager, Braskem. Red Sea Crisis
Advantages of using WEAV3D’s Rebar for Plastics® and Braskem Polypropylene over conventional composite organosheet:
• LIGHTWEIGHT – Cuts sheet blank weight by ~50% and final part weight by ~23%
• COST EFFECTIVE – Lowers costs by ~50%
• EFFICIENT – Boosts sheet yield from 25% to 45% by weight, resulting in a 62% decrease in trim waste “WEAV3D and Braskem are showing the great potential of the WEAV3D lattice material with this automotive door prototype and we are delighted to be selected a finalist by the Innovation Awards jury,” said Chris Oberste, President of WEAV3D.
“With the help of Altair Engineering, we developed a simulation workflow that allowed us to optimize the lattice structure for cost and performance, using the same organosheet tooling and forming process equipment at the Clemson Composites Center at Clemson University.” Red Sea Crisis
The winners of the JEC Composites Award 2024 will be revealed during an online ceremony on February 8, 2024, from 13:30 to 15:30 CET, at www.jec-world.events. The Braskem-WEAV3D prototype part will also be exhibited in the JEC Innovation Planets section of JEC World, in Paris, France, from March 5-7, 2024.
To learn more about the prototype part, visit WEAV3D’s booth 6P32e in the American Pavilion.

The mLLDPE market saw a sharp increase in spot prices in both Europe and the US in the first half of January 2024
This was due to various factors, such as sellers raising prices, material shortages, geopolitical conflicts, and shipping issues. Red Sea Crisis
The US market also recovered from the holiday slump, with more trading activity and higher prices.
In Europe, mLLDPE spot prices rose significantly, despite the stable feedstock Ethylene prices. This was because sellers announced price hikes, breaking the previous downward trend.
They also lowered their offers to attract buyers, as the market was weak and demand was low.
However, the situation in the Middle East added more uncertainty to the market. The shipping disruptions in the Red Sea led to higher freight rates, as ships had to take a longer and more costly route through the Cape of Good Hope. Red Sea Crisis
This posed many challenges for exporters, such as longer transit times, higher fuel costs, and possible delays.
In the US, mLLDPE prices also went up during the same period. They bounced back from the low levels in mid-December, as the market regained momentum after the New Year holiday.
Spot resin trading picked up gradually, as more participants returned to the market. Some processors bought resin to secure their operations, resulting in a decent volume of business.
The low inventories held by traders also helped to push up the average prices in the US.
ChemAnalyst predicts that mLLDPE prices will remain high in the near future, due to the supply chain problems and freight rate increases in both regions. Red Sea Crisis
Moreover, the anticipated rise in the costs of Ethylene and Naphtha may also drive up the production costs, leading to higher mLLDPE prices.

The US dollar enjoys a special status as the world’s reserve currency, which gives the US a huge advantage in the global economy
However, this status is not guaranteed, and recent events have challenged the dominance of the dollar. Red Sea Crisis
Many countries that are not aligned with the US are looking for ways to reduce their dependence on the dollar.
This was triggered by the US’s decision to impose harsh sanctions on Russia for invading Ukraine in February 2022.
The sanctions aimed to cut off Russia’s access to the dollar and weaken its currency, the rouble.
US treasury secretary Janet Yellen said this was an “unprecedented action” that would “significantly limit Russia’s ability to use assets to finance its destabilising activities”.
But this also had the effect of pushing Russia and other countries to seek alternatives to the dollar.
One of these alternatives is the Chinese renminbi, which is gaining popularity as a currency for international trade and investment. Red Sea Crisis
Russia is now using the renminbi for a quarter of its foreign trade, and most of its trade with China is done in their own currencies.
China has also made deals with the UAE and Saudi Arabia to use the renminbi instead of the dollar for gas and oil transactions.
These moves are undermining the demand for the dollar, which is reflected in the decline of its share in central banks’ foreign exchange reserves. Red Sea Crisis
The dollar’s share has fallen from over 70 per cent in the early 2000s to under 60 per cent today, the lowest level in decades.
This is not a temporary dip, but a long-term trend that reflects the changing balance of power in the world economy.
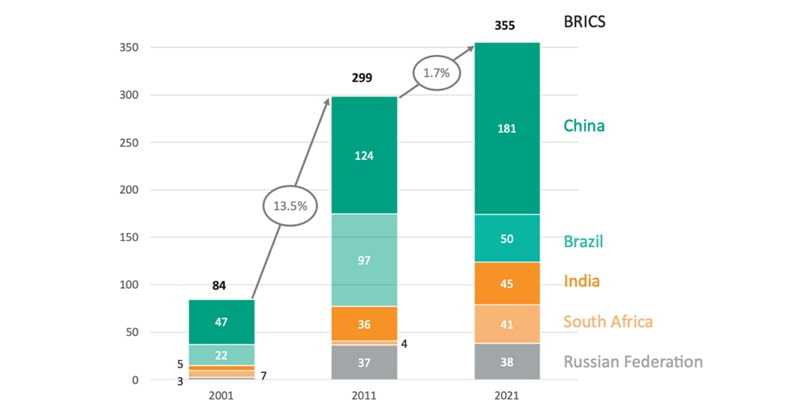
The US is losing ground to emerging economies, especially China, which is now the largest trading partner for more than 120 countries and exports more than US$3.6 trillion (£2.8 billion) worth of goods.
China’s share of the global economy has more than doubled from 8.9 per cent to 18.5 per cent in the last 20 years, while the US’s share has dropped from 20.1 per cent to 15.5 per cent, based on purchasing power parity (which compares the prices of specific goods across countries). Red Sea Crisis
The shift in economic power is also reflected in the rise of the BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa), which have surpassed the G7 countries (US, Canada, UK, Germany, France, Italy, Japan and Germany) in terms of their share of world GDP, based on purchasing power parity.
This means that the dollar is facing more competition from other currencies in the global market.

Red Sea Crisis
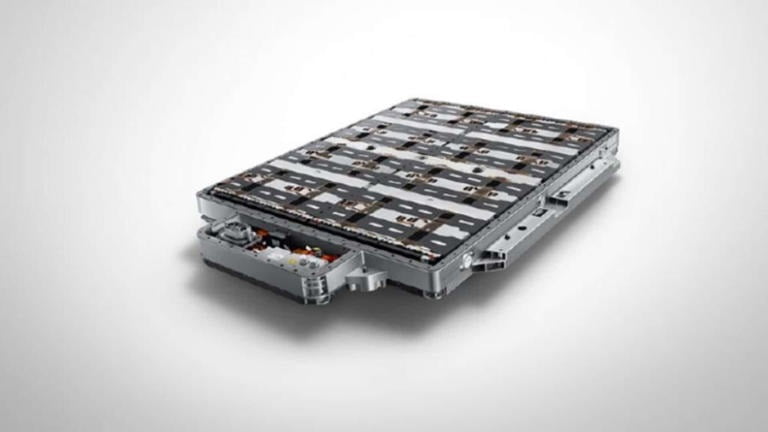
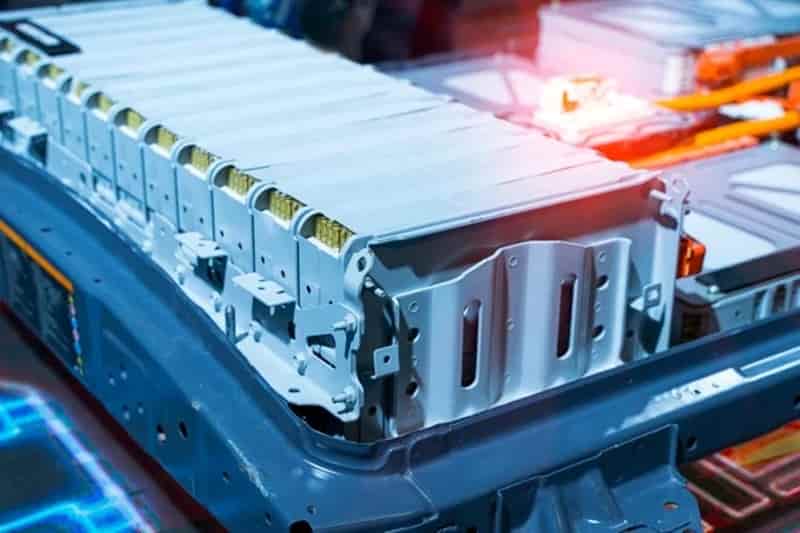
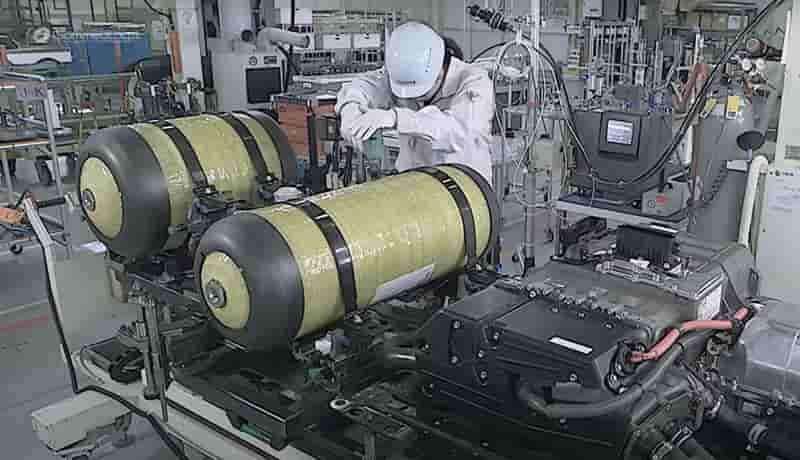
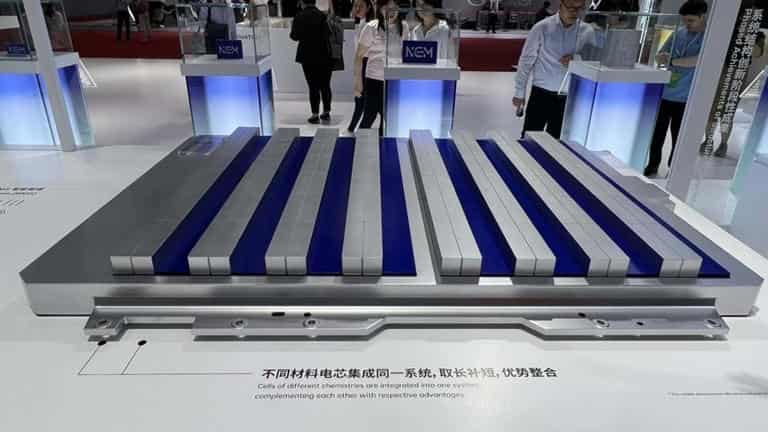
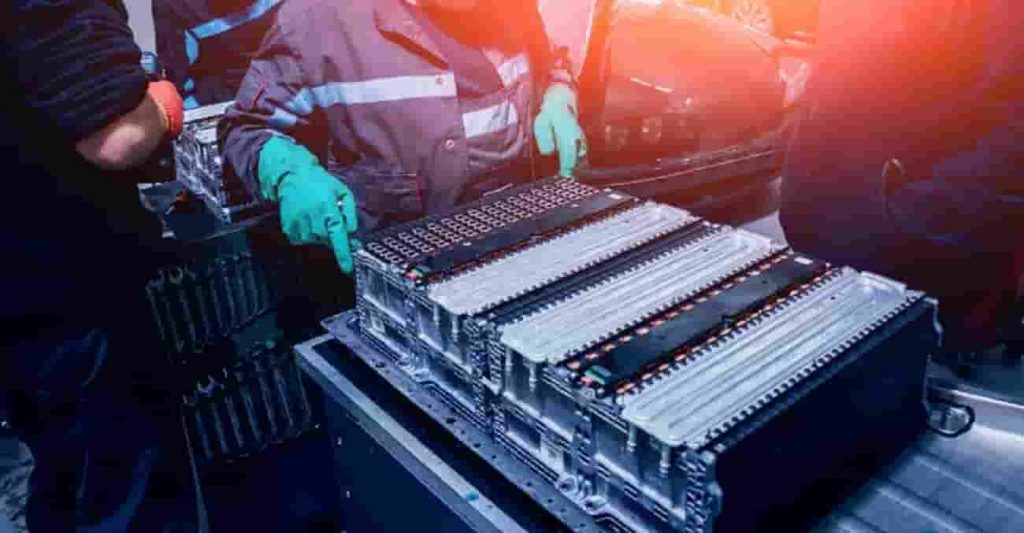
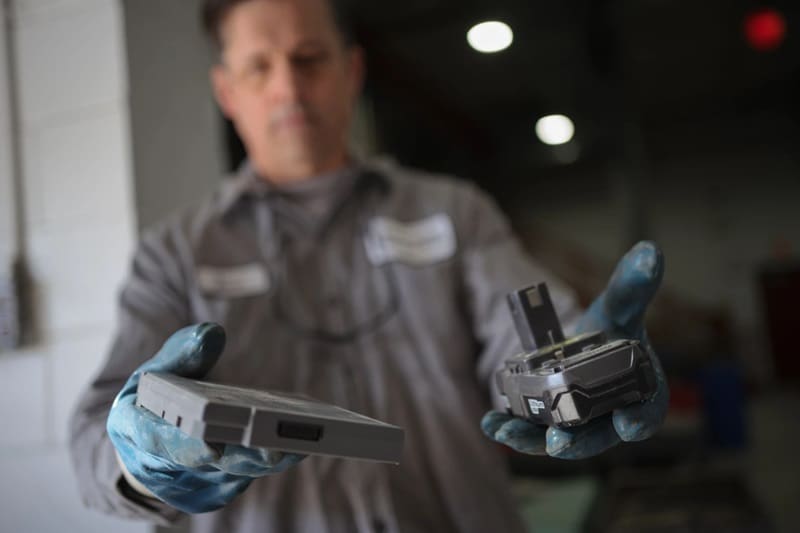
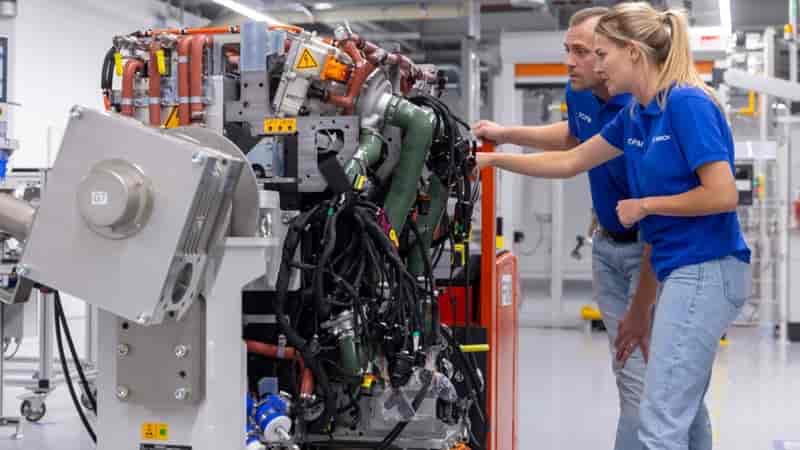
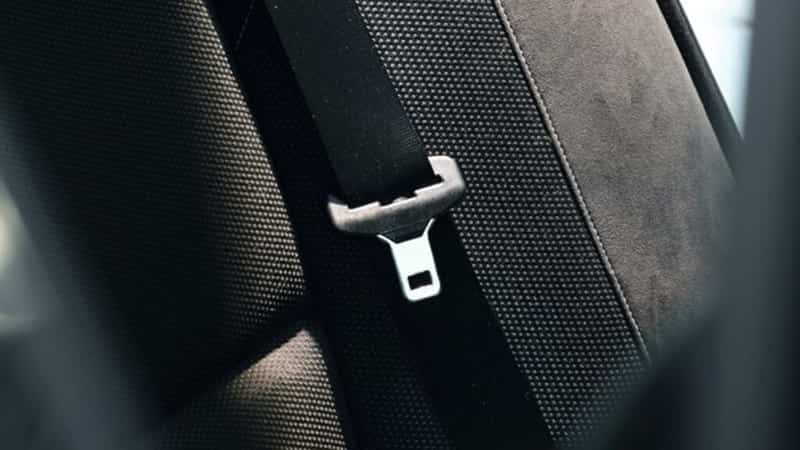
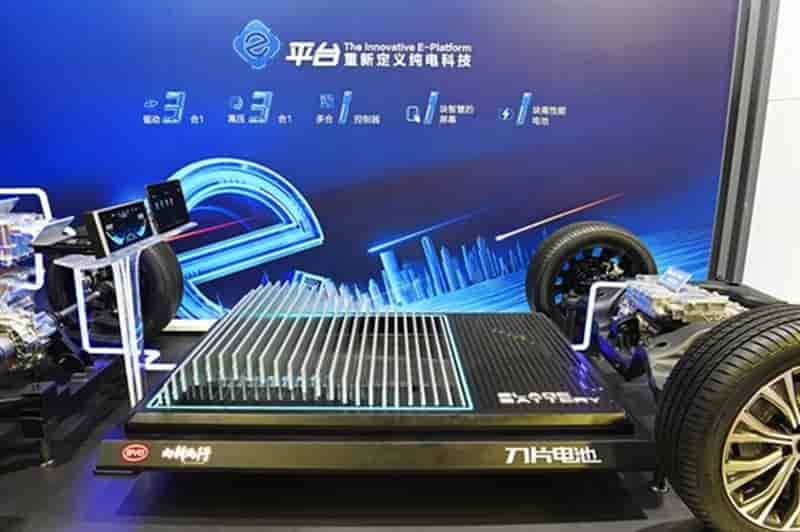
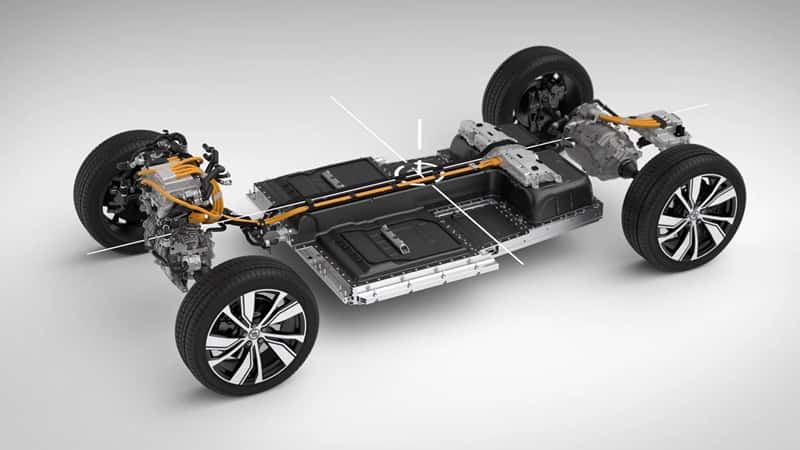
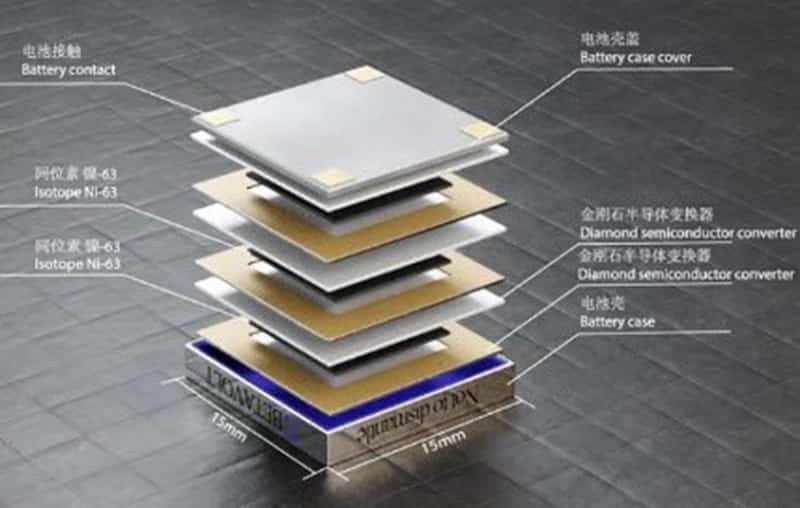
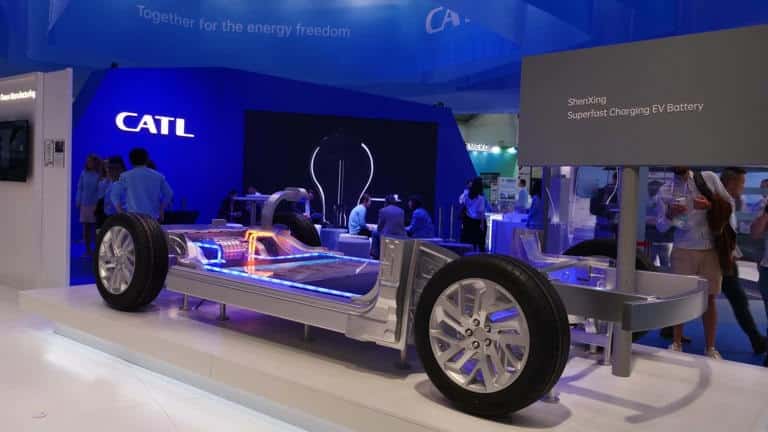
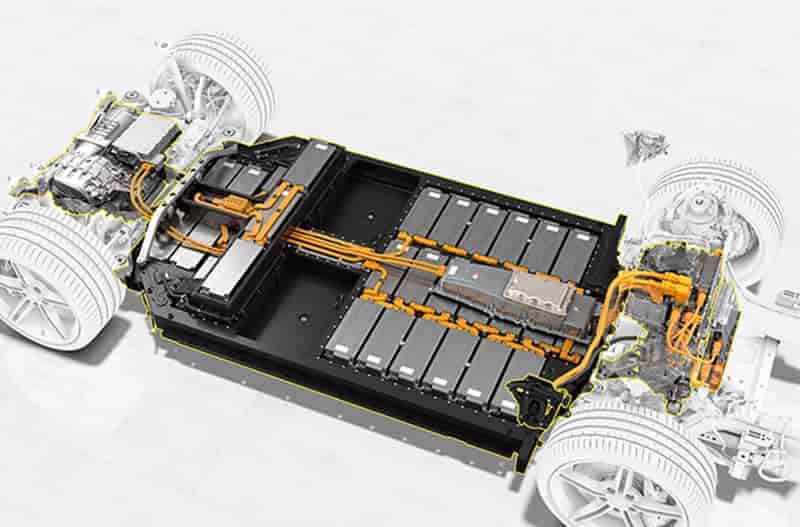
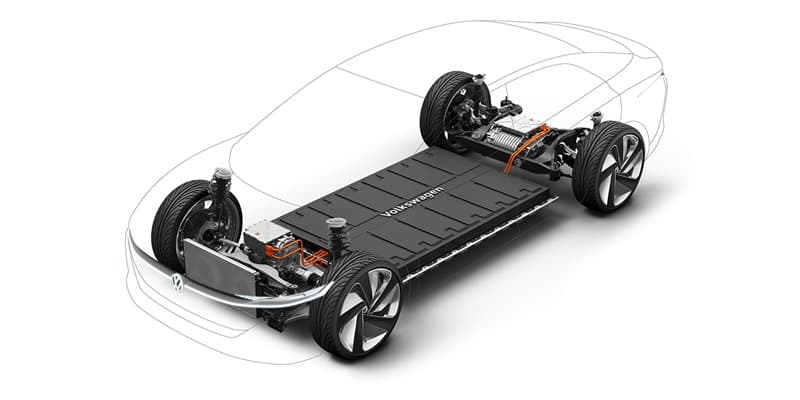
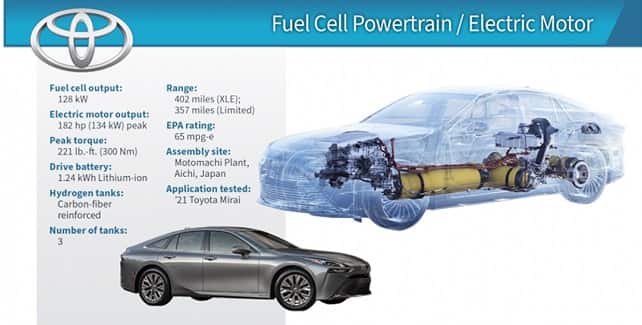
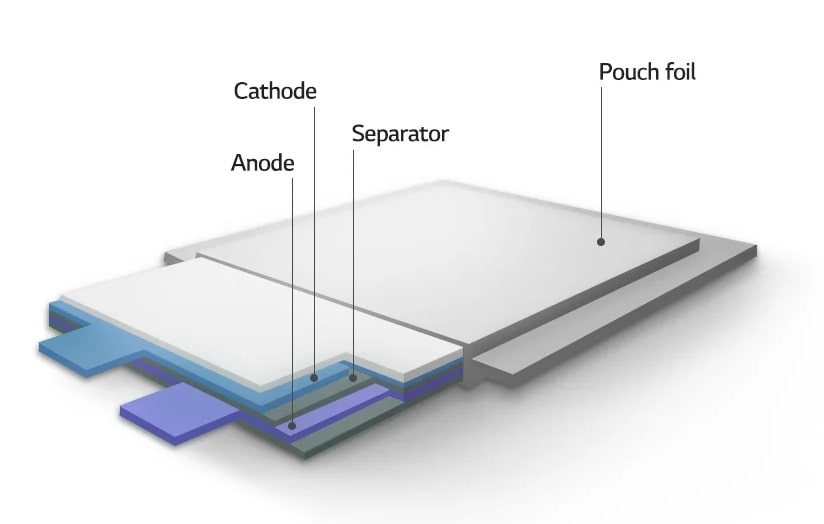
Battery technology – Polyamide 6.6: A Versatile Material in Automotive Applications 18-01-2024