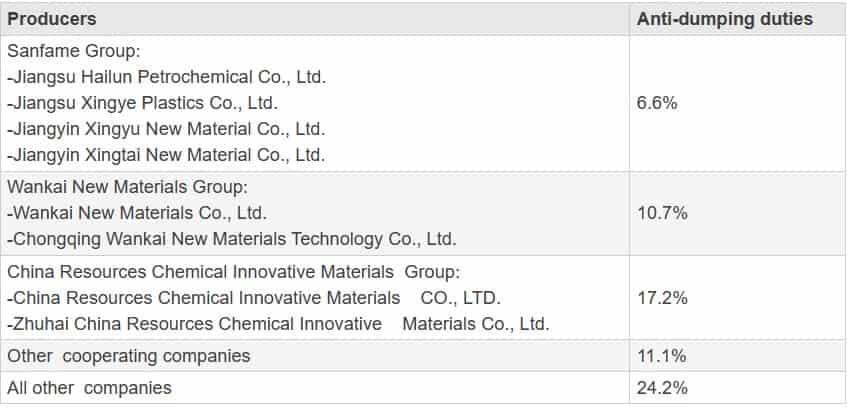
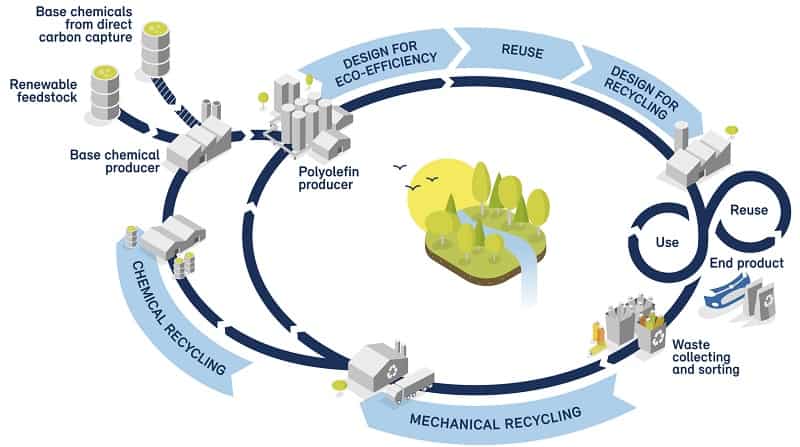
Hydrogen plastic waste
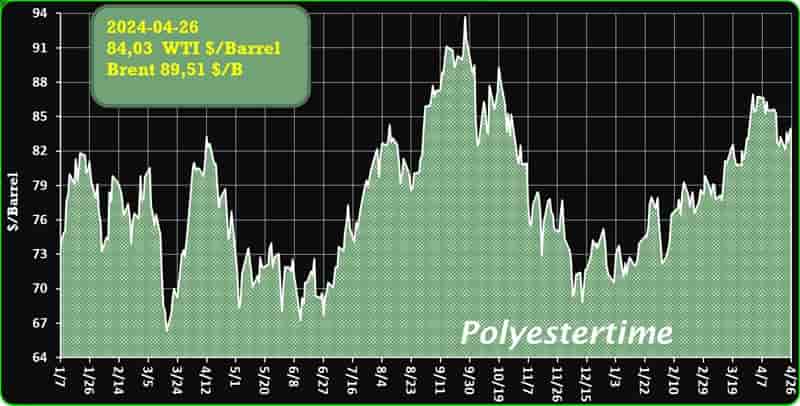
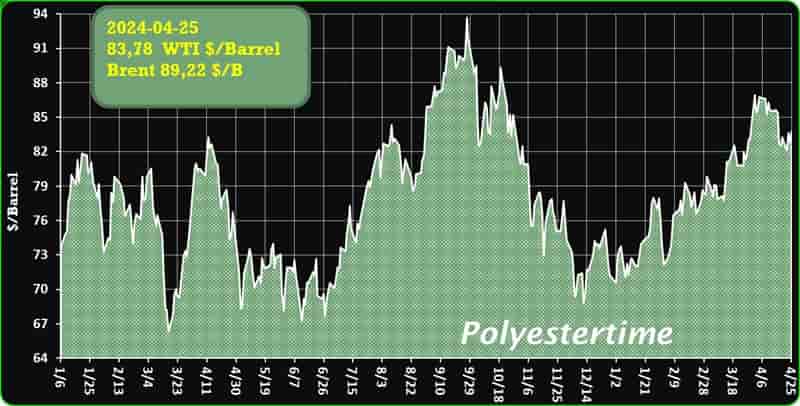
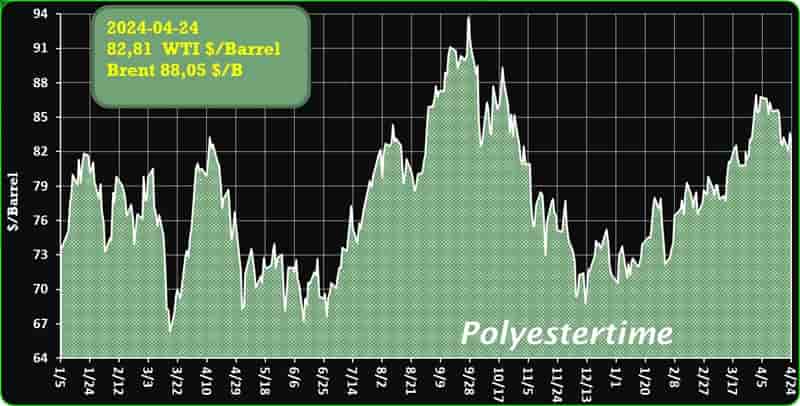
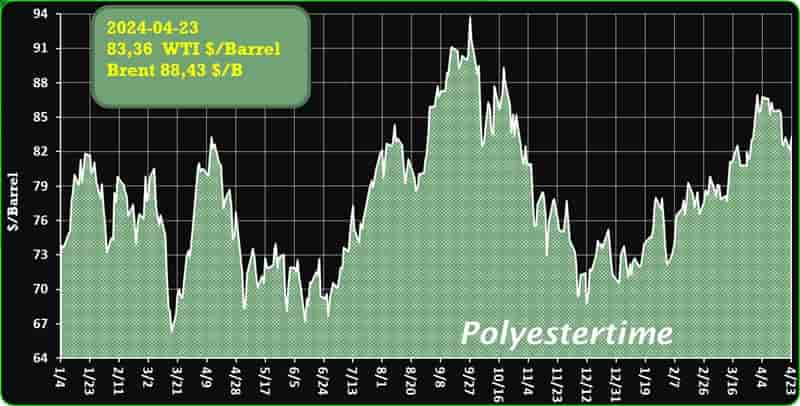
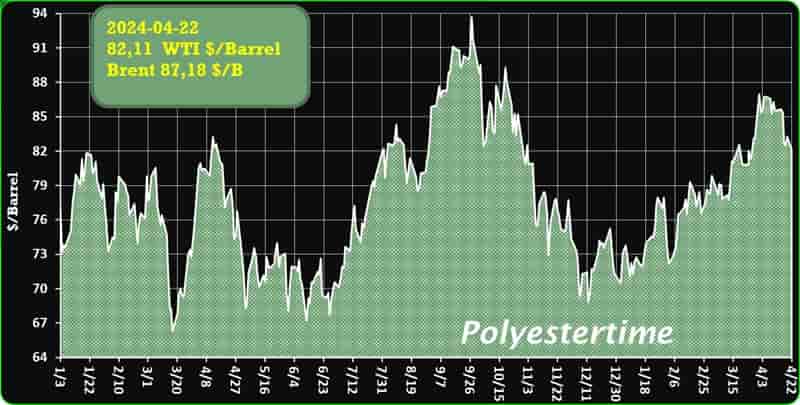
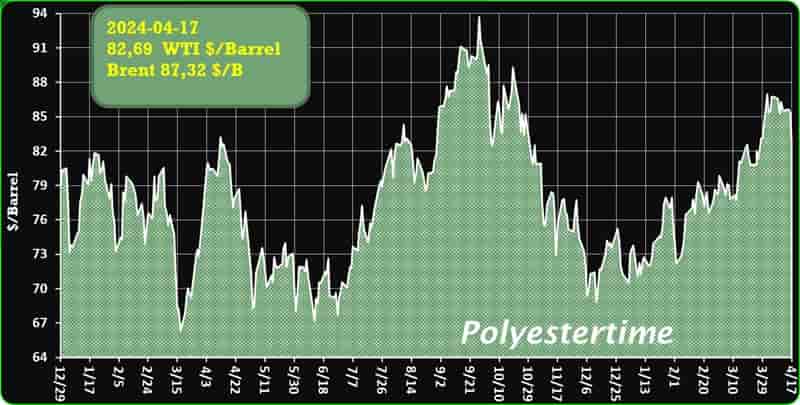
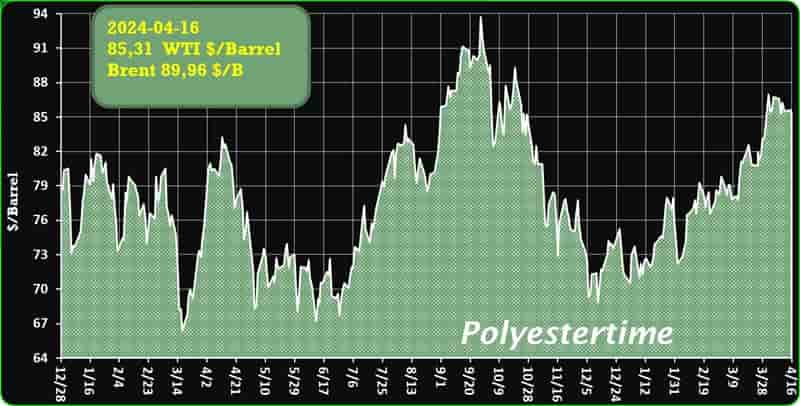
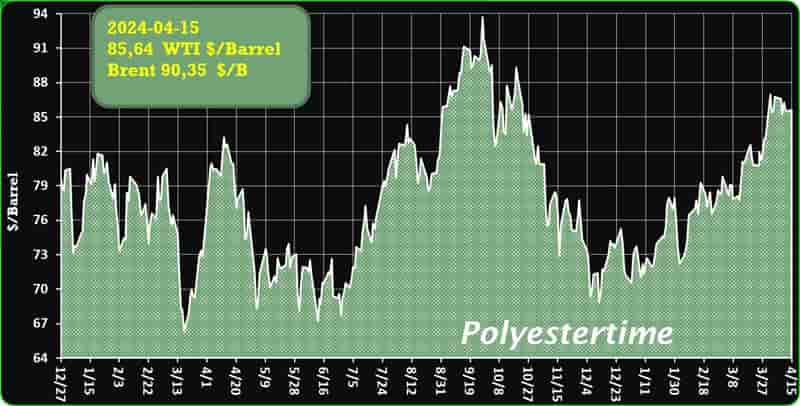
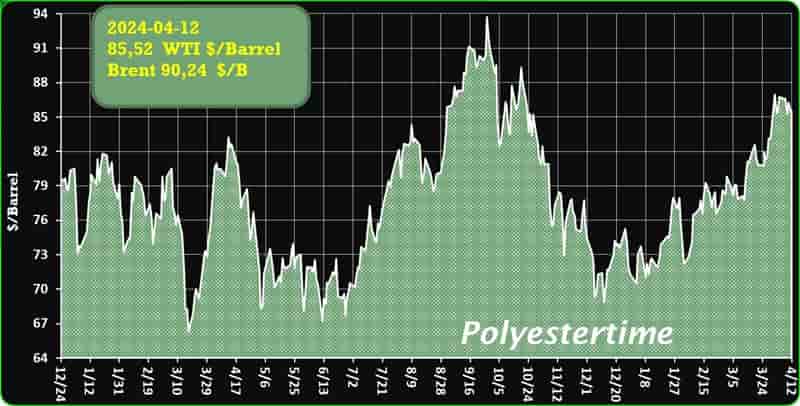
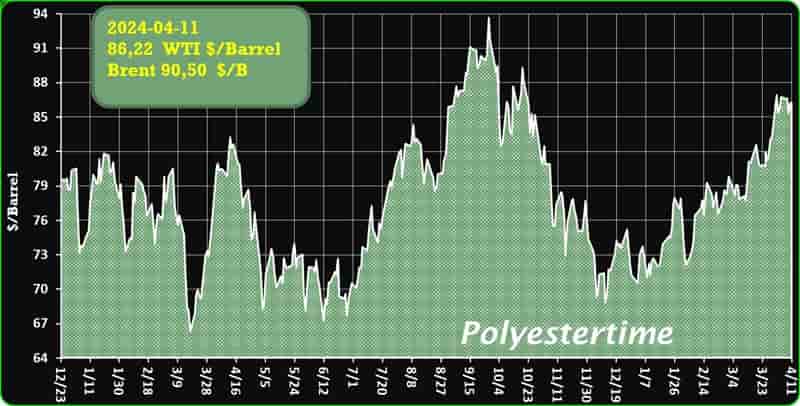
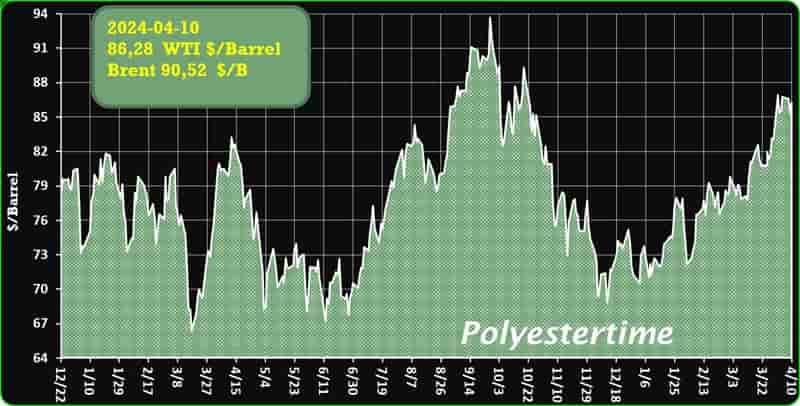
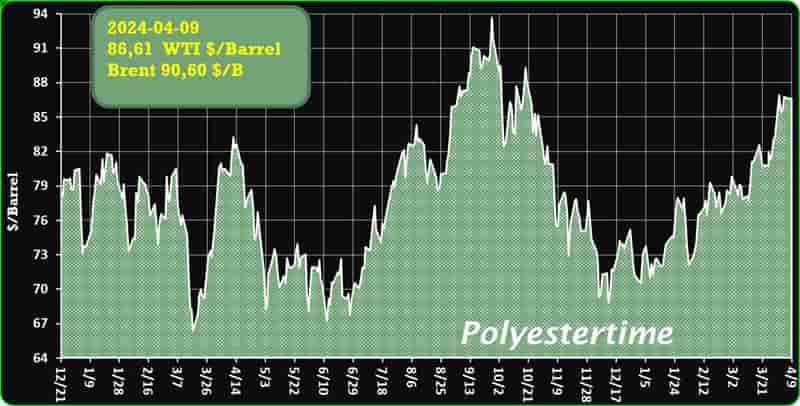
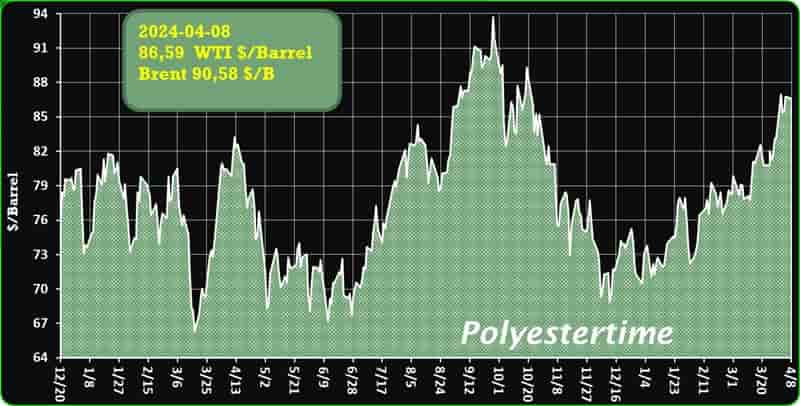
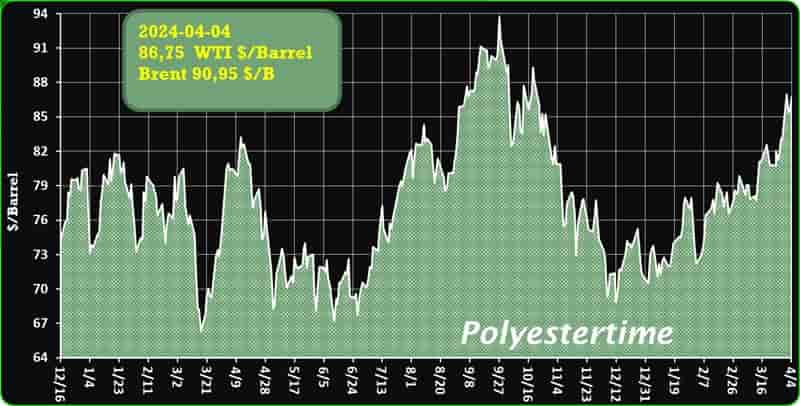
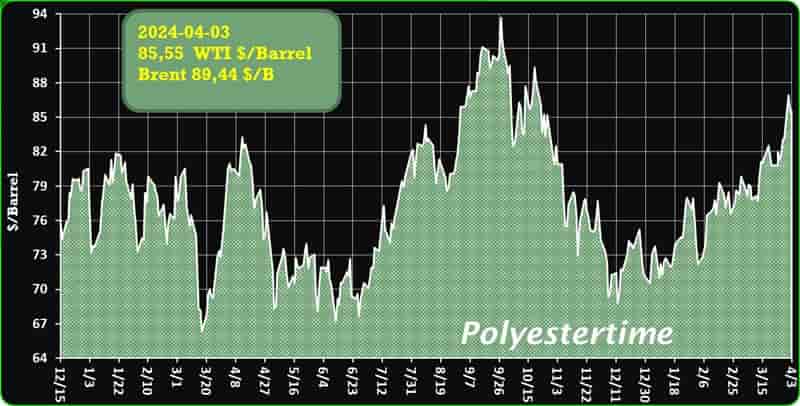
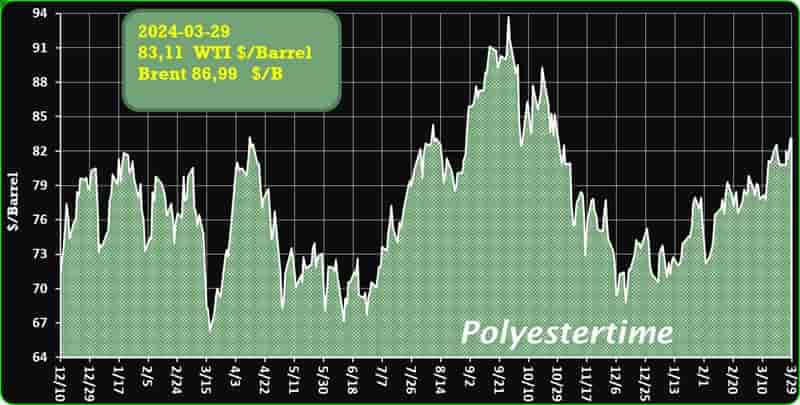
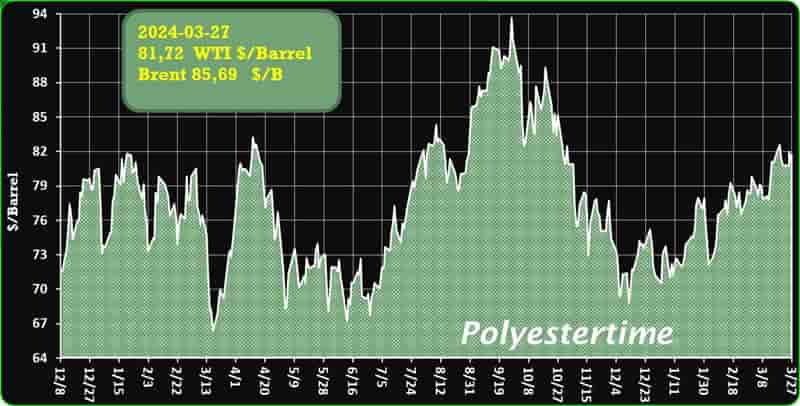
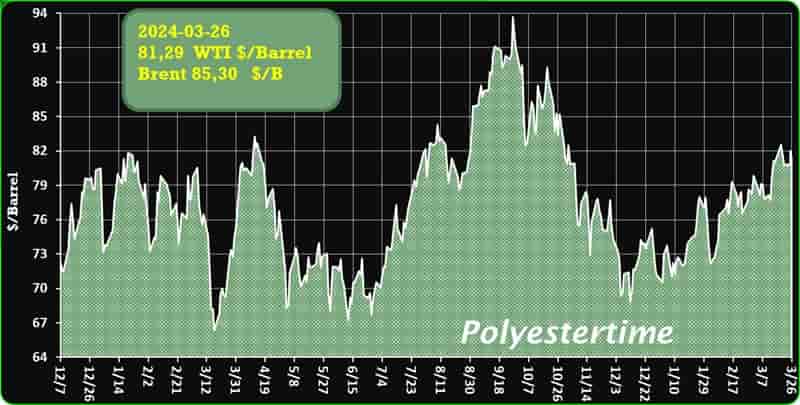
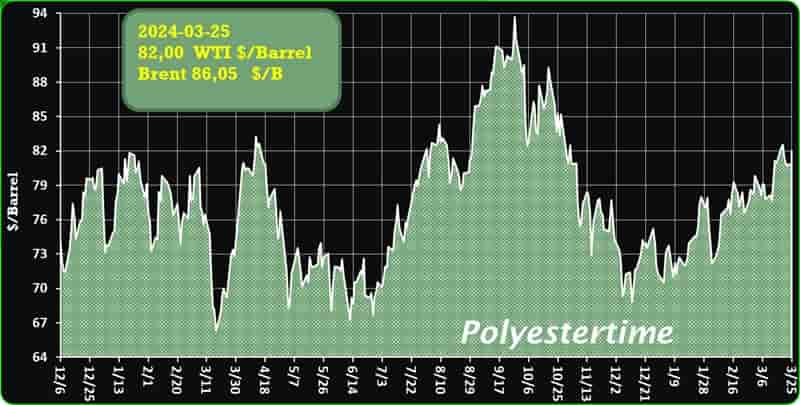
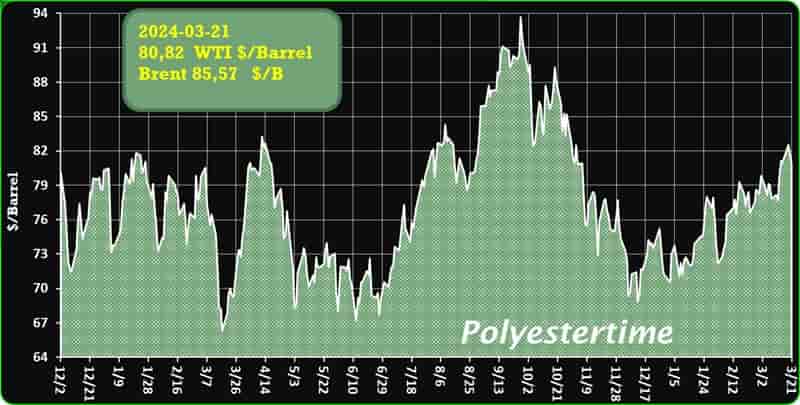
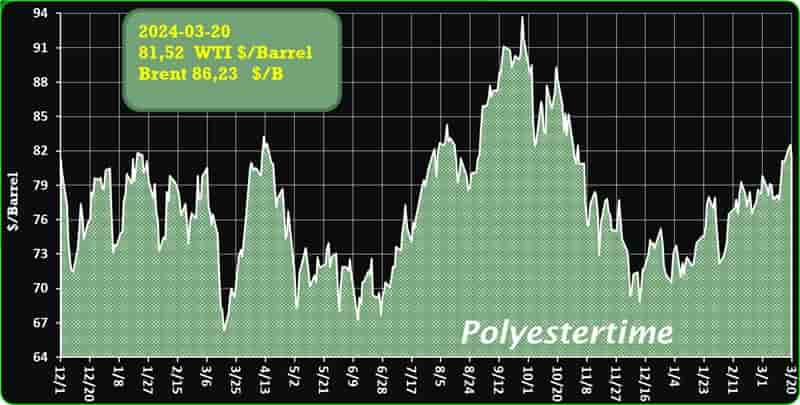
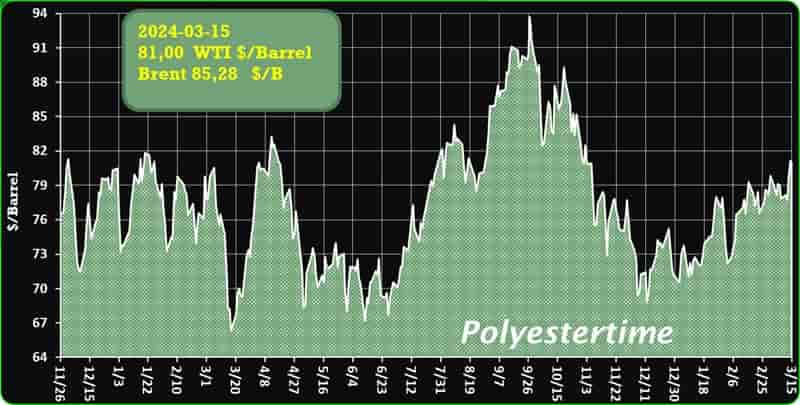
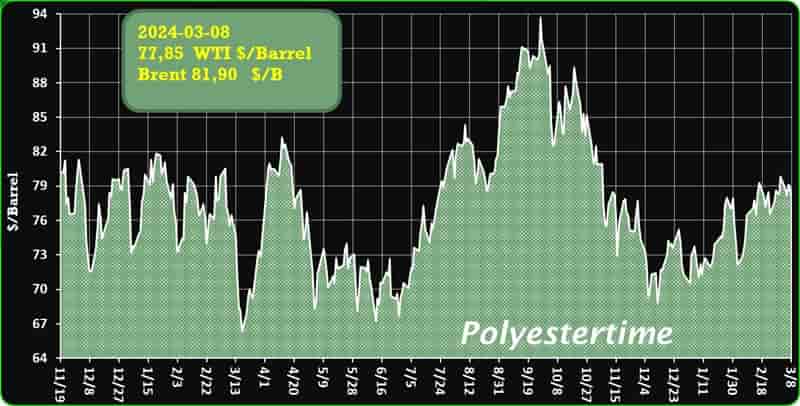
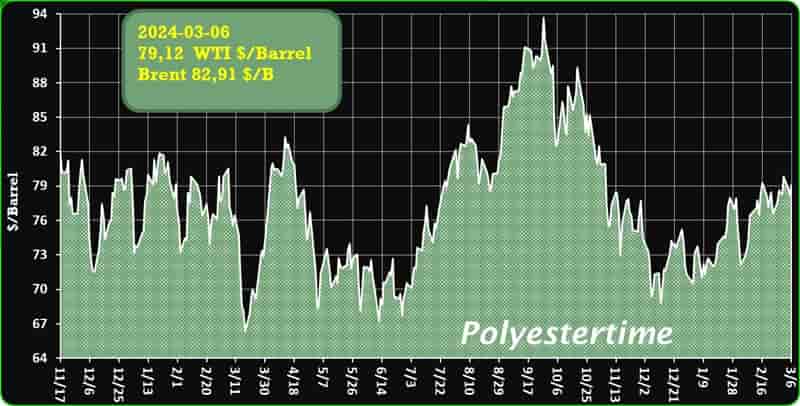
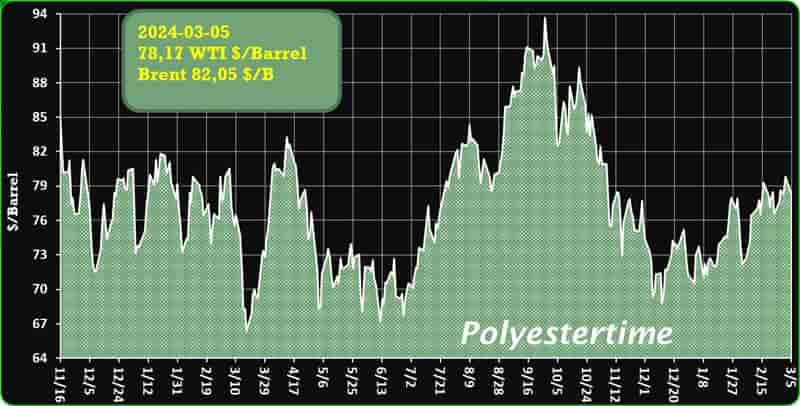
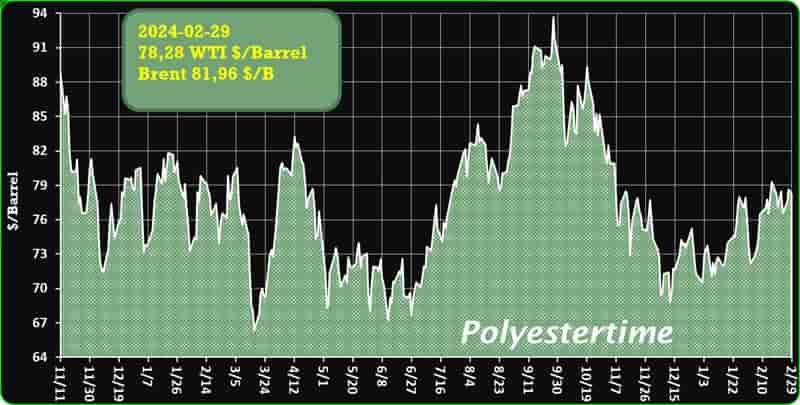
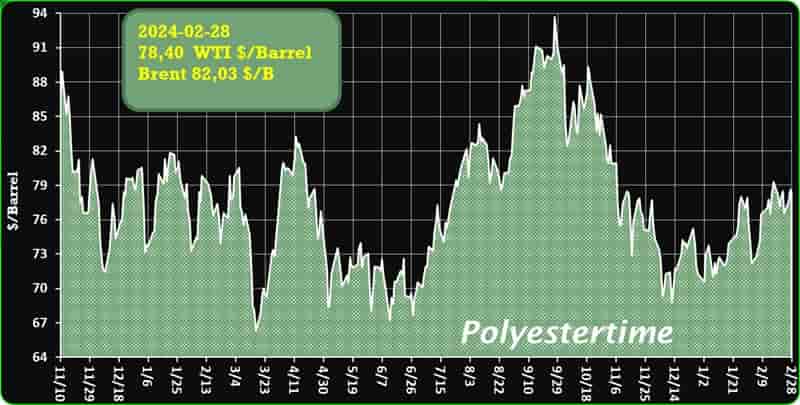
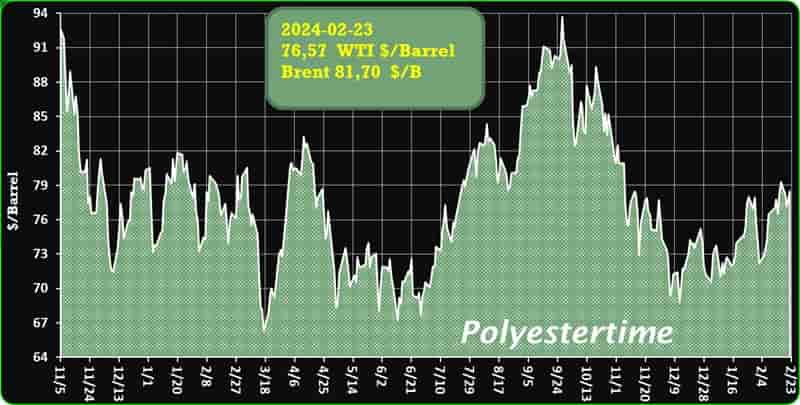
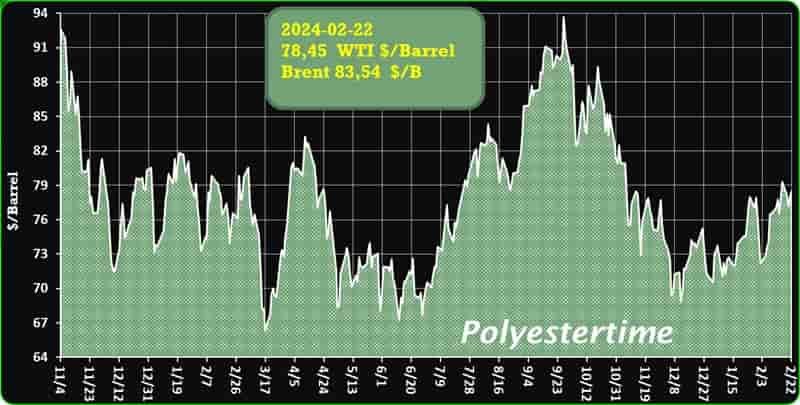
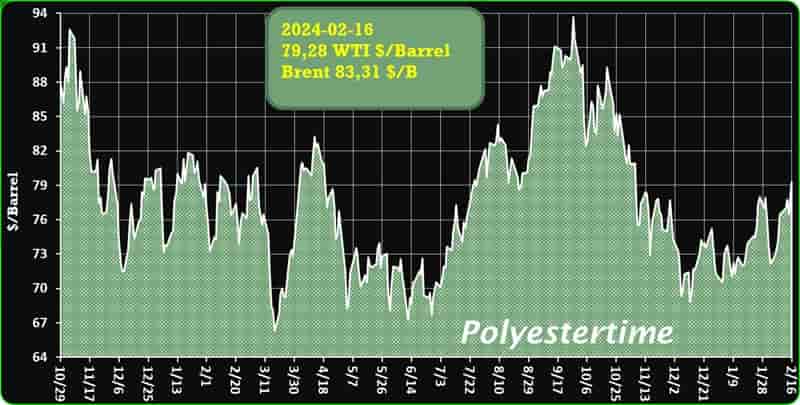
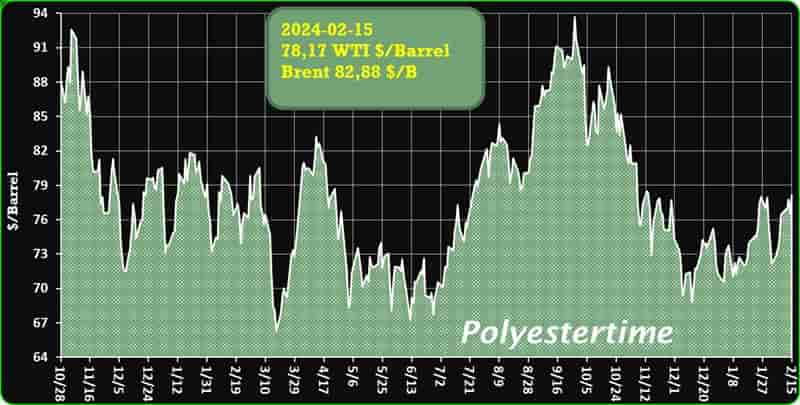
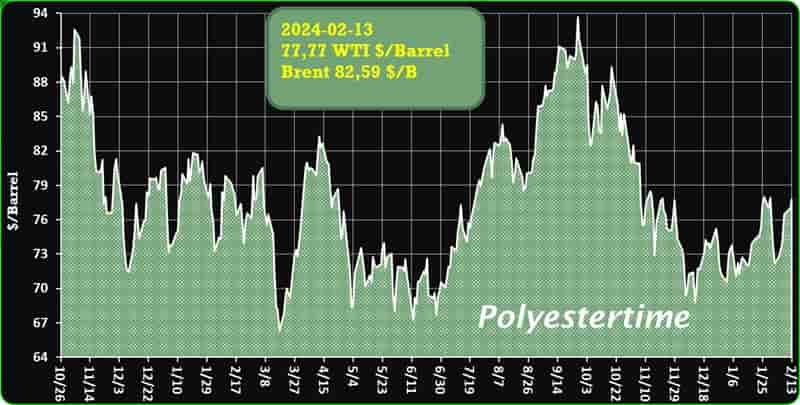
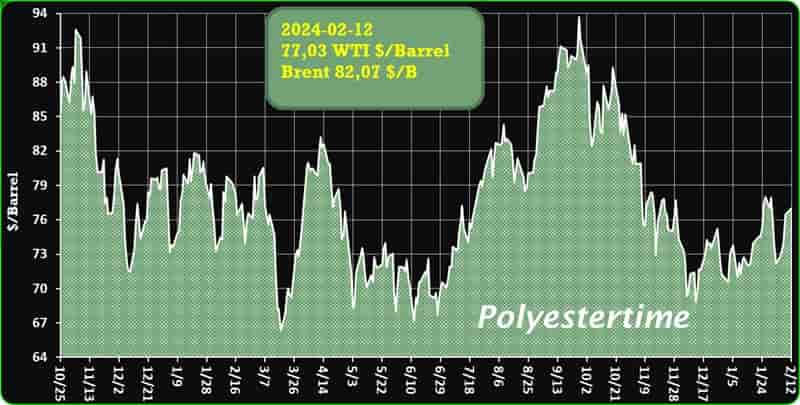
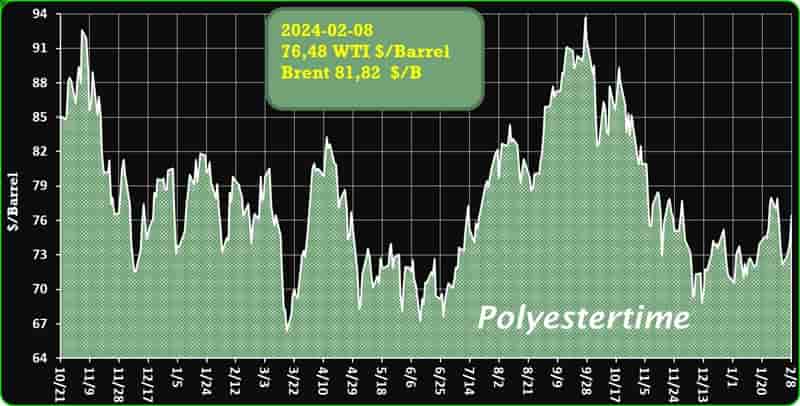
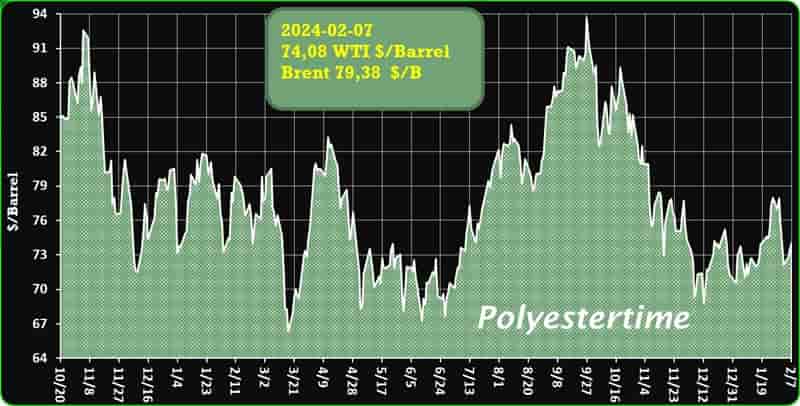
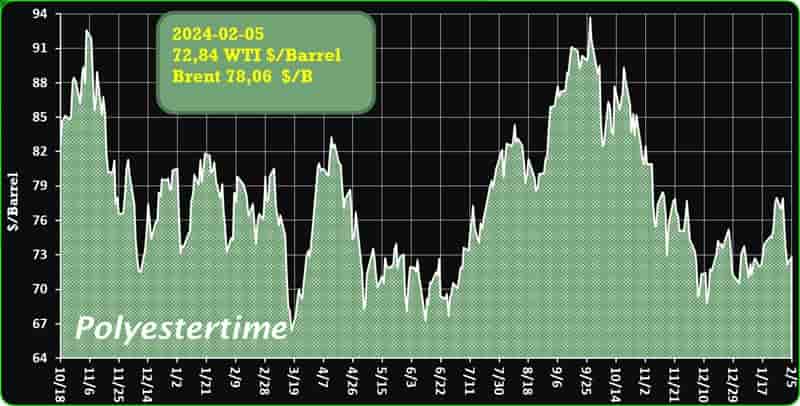
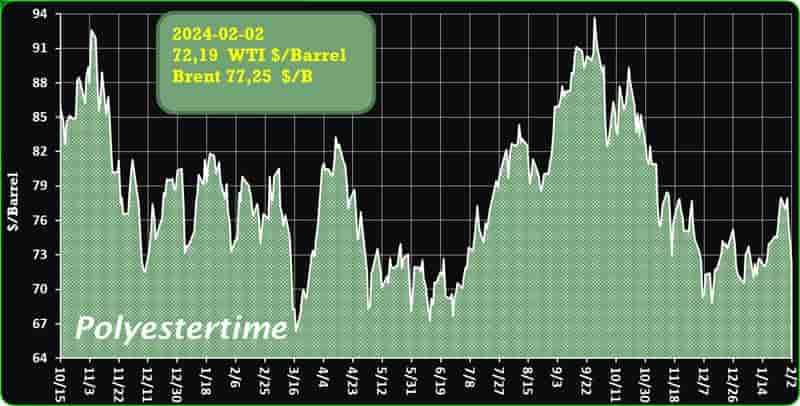
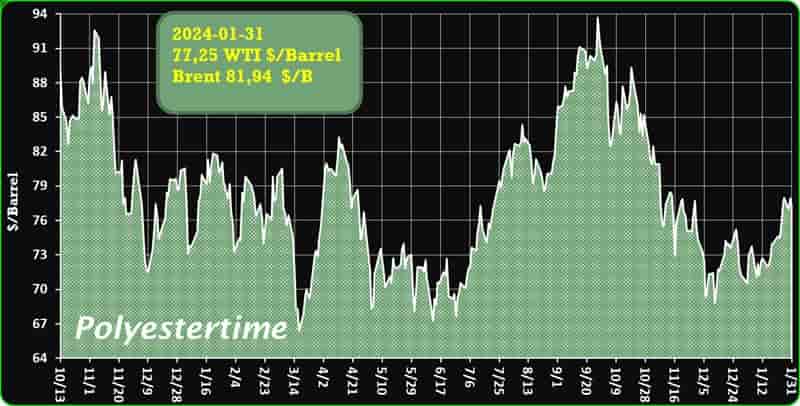
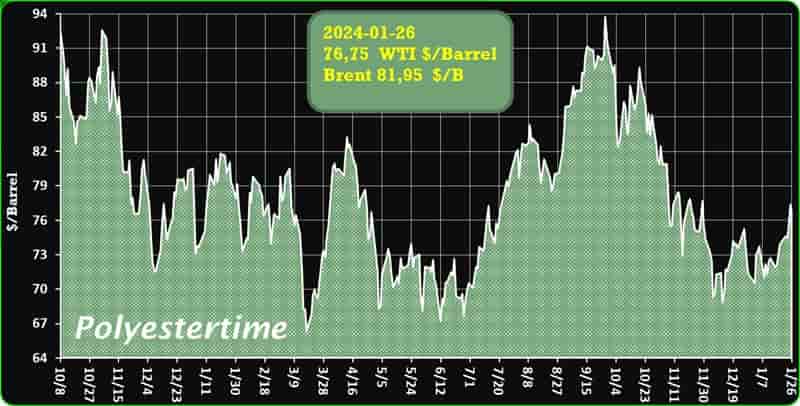
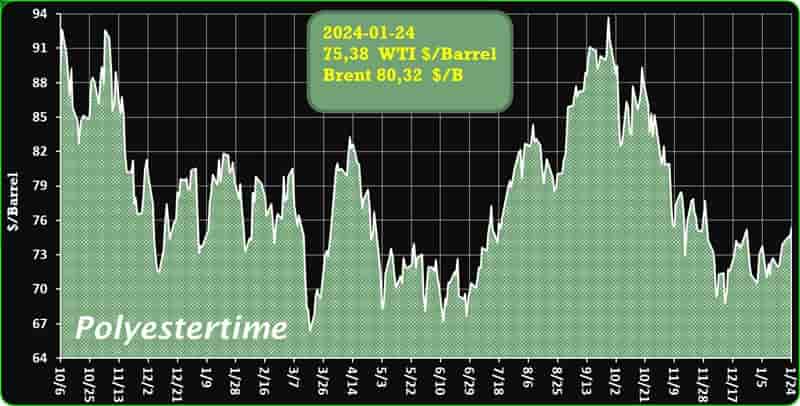
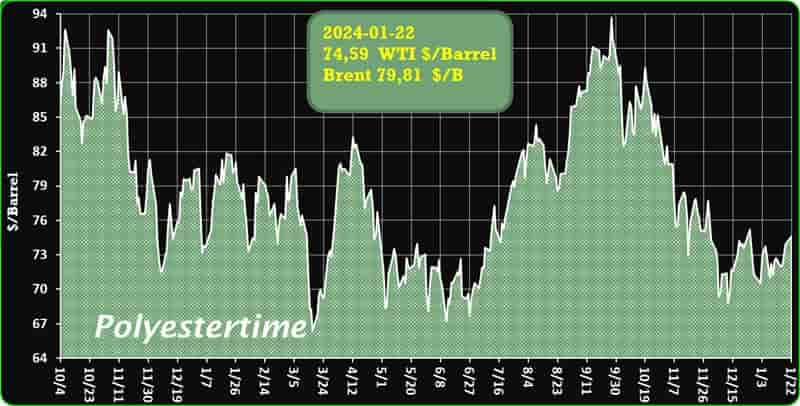
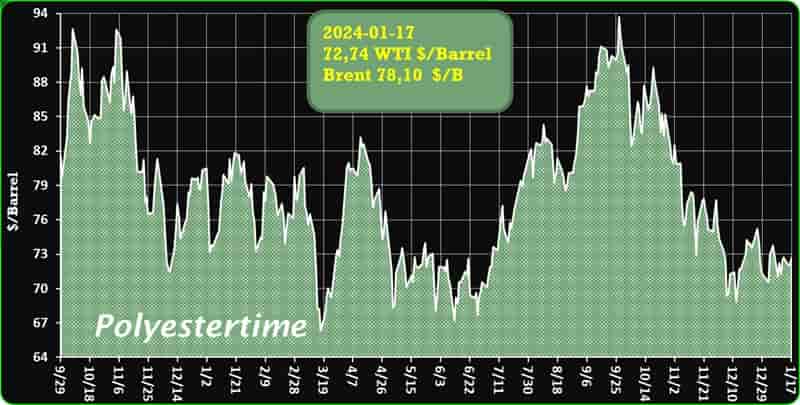
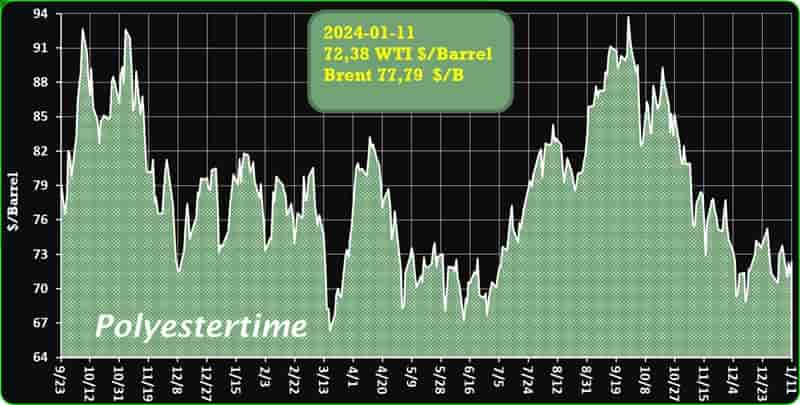
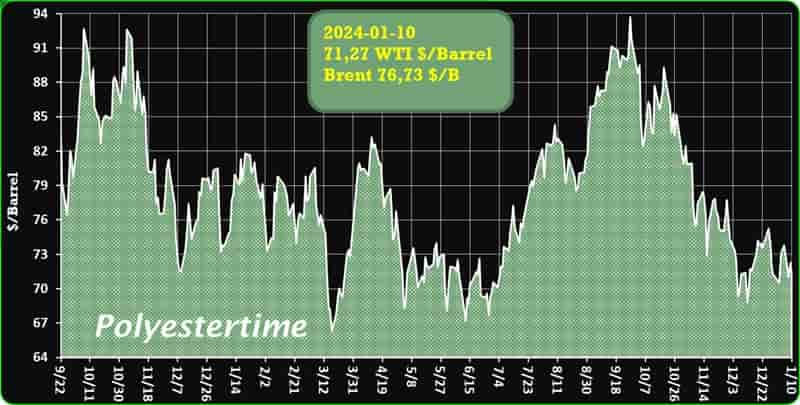
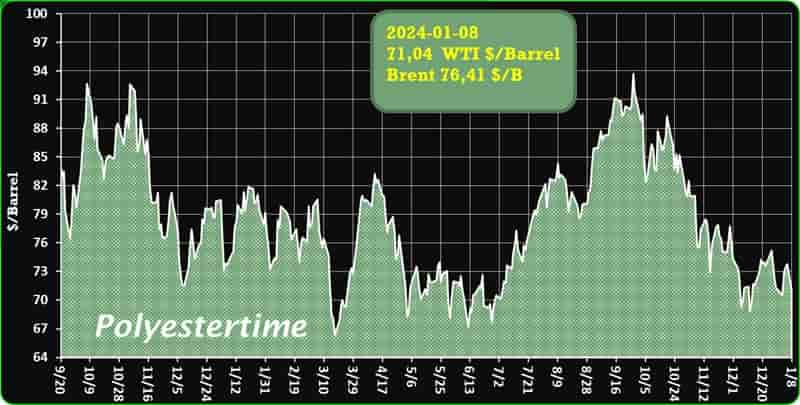
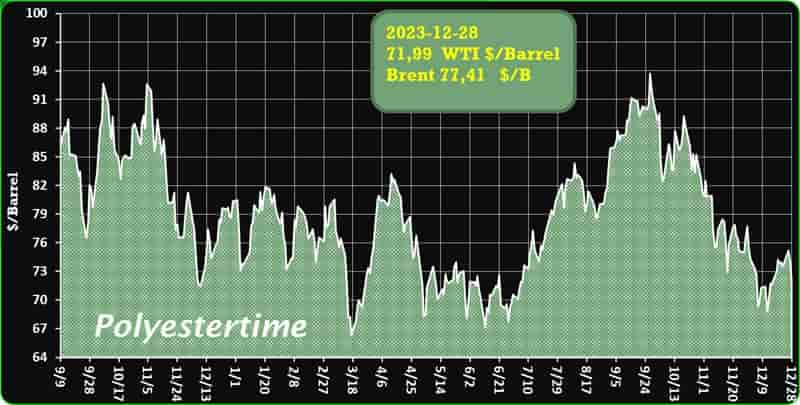
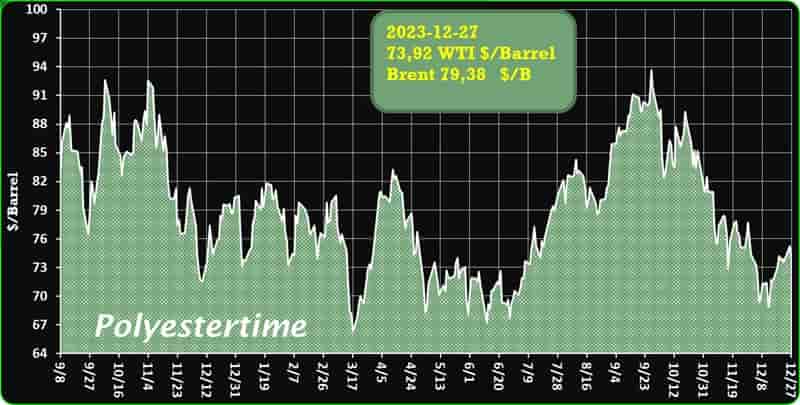
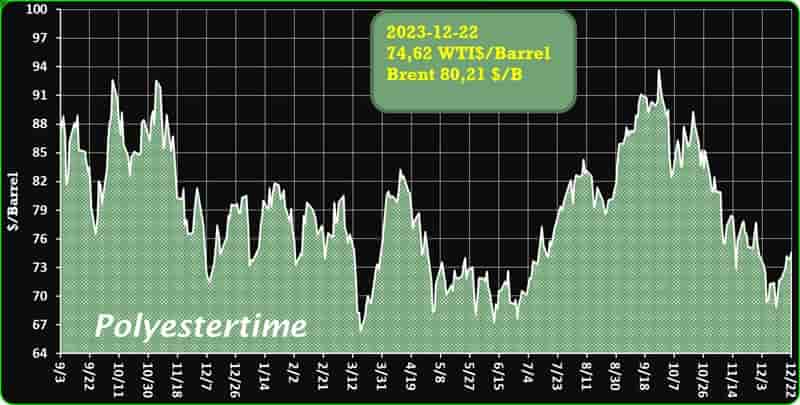
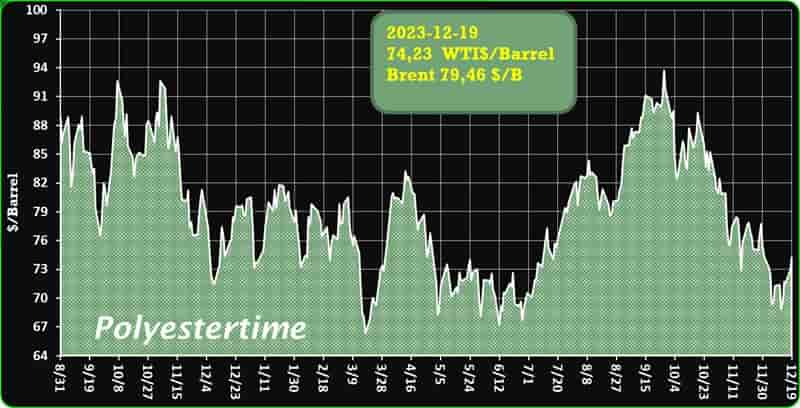
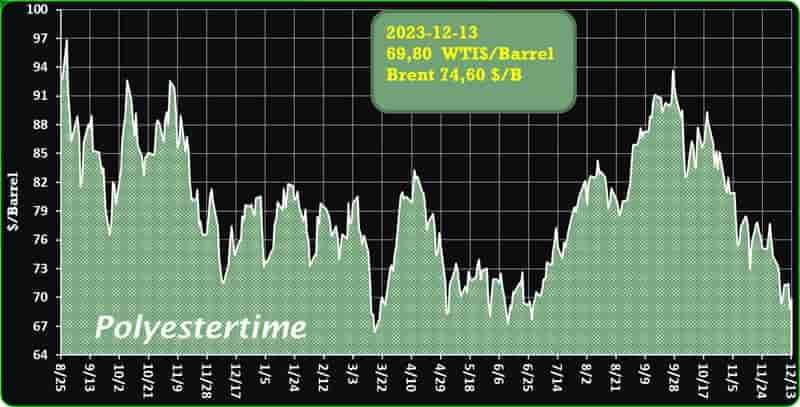
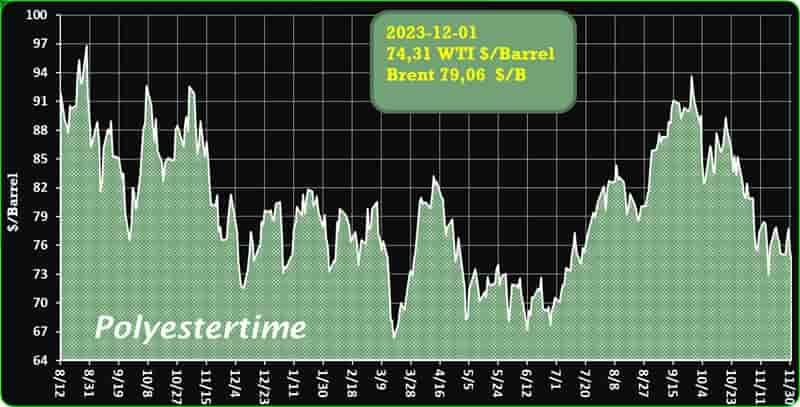
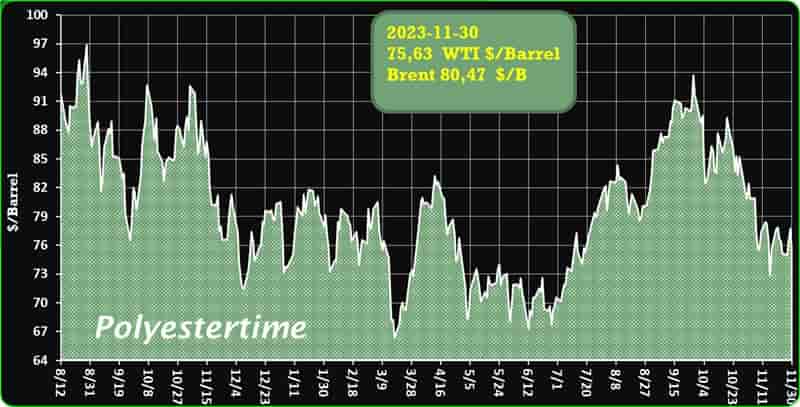
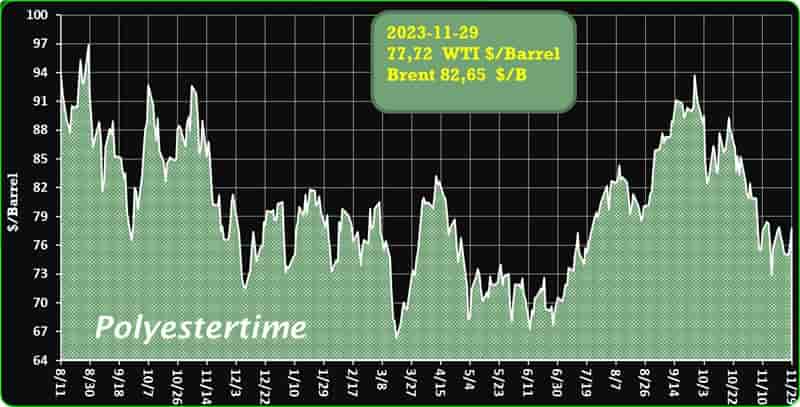
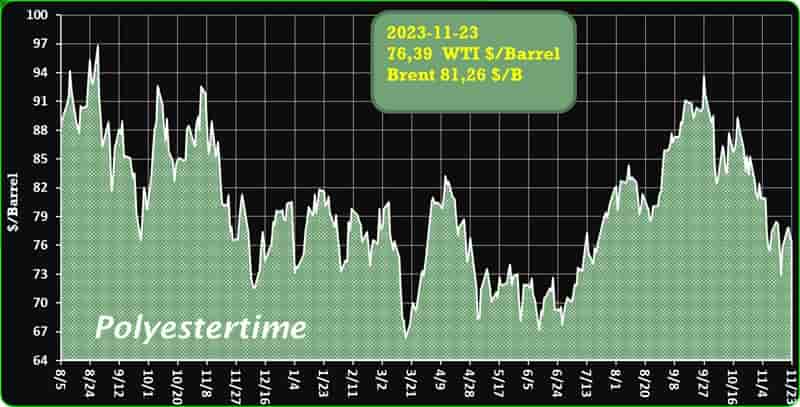
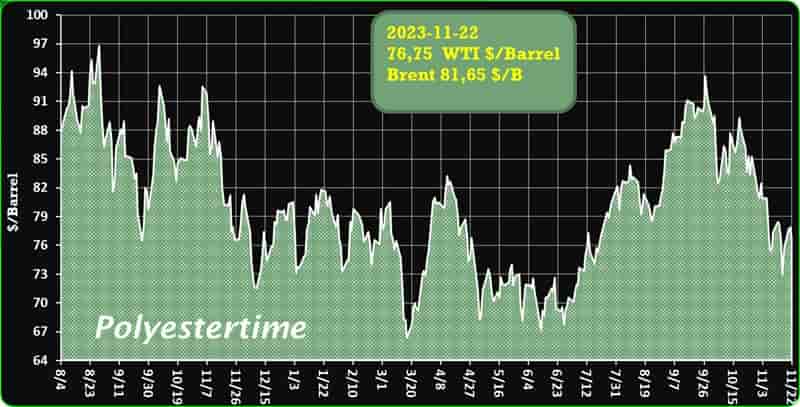
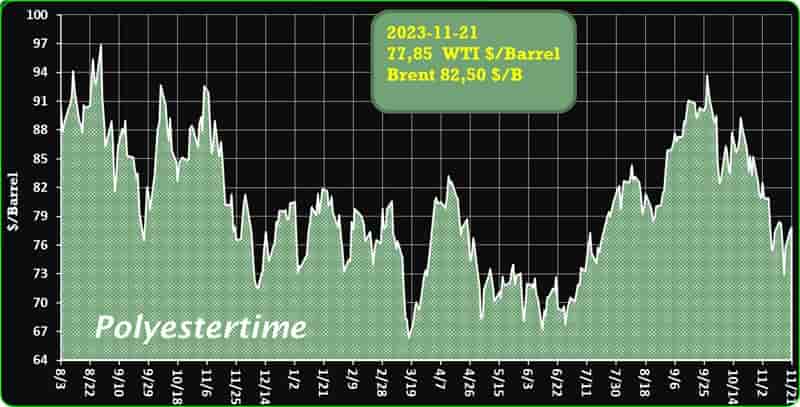
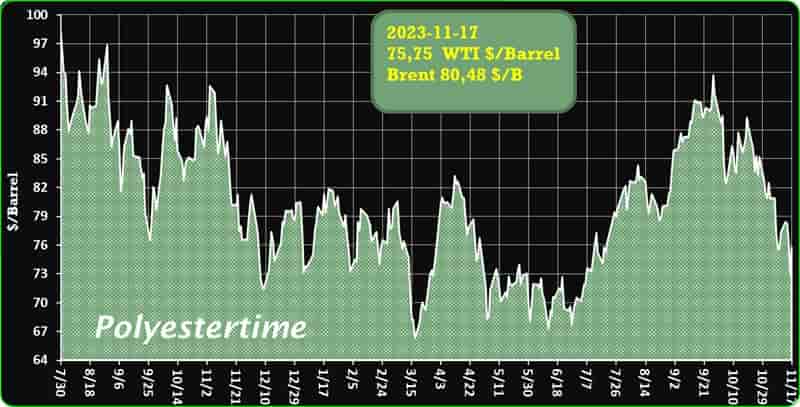
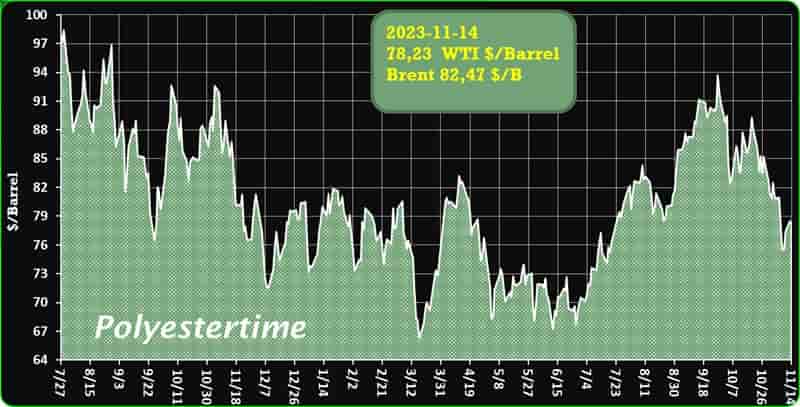
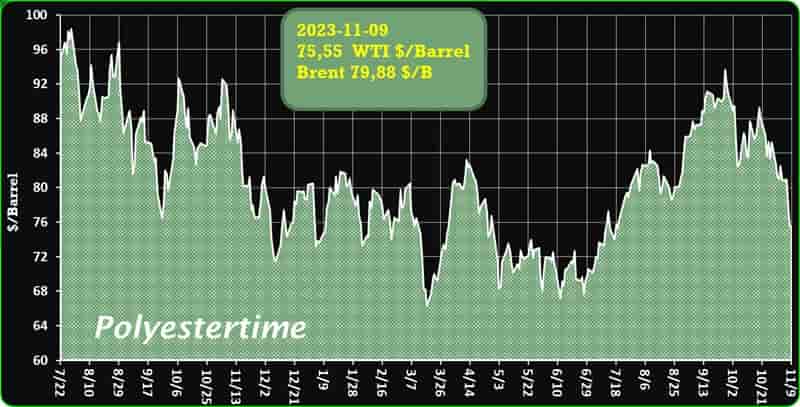
Crude Oil Prices Trend
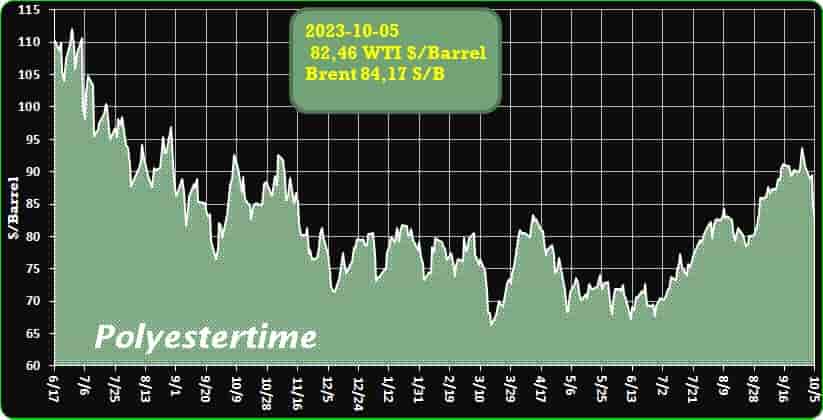
Crude Oil Prices Trend by Polyestertime
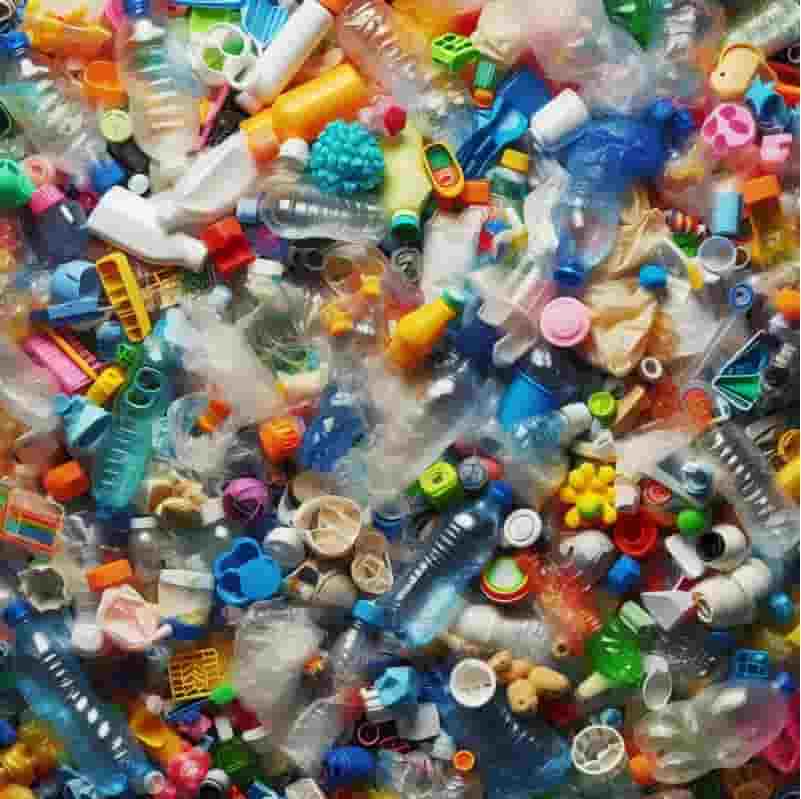
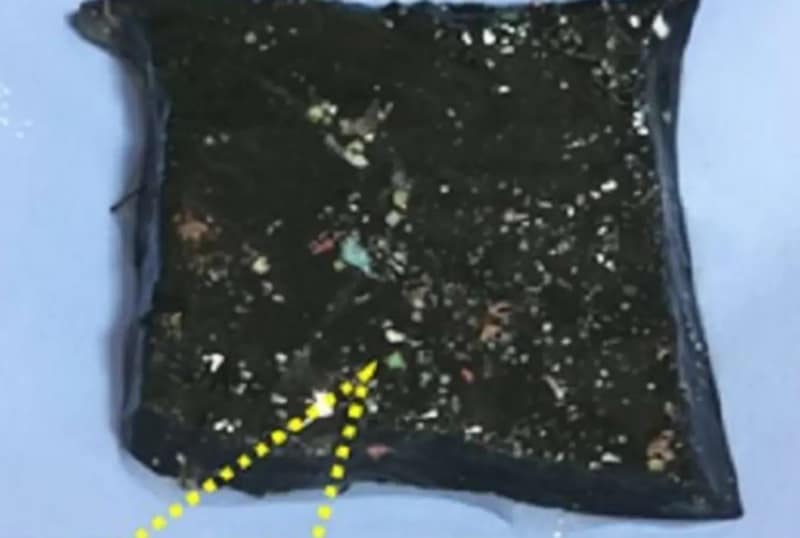
Flash method may be solution for hydrogen, plastic waste
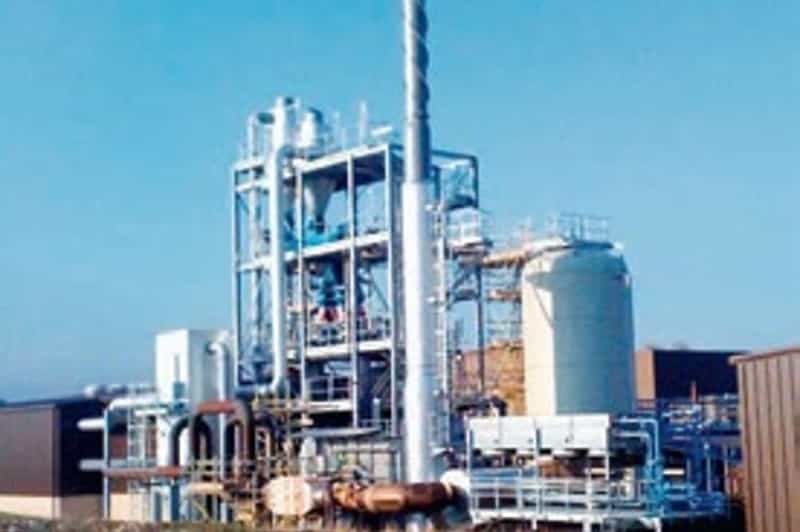
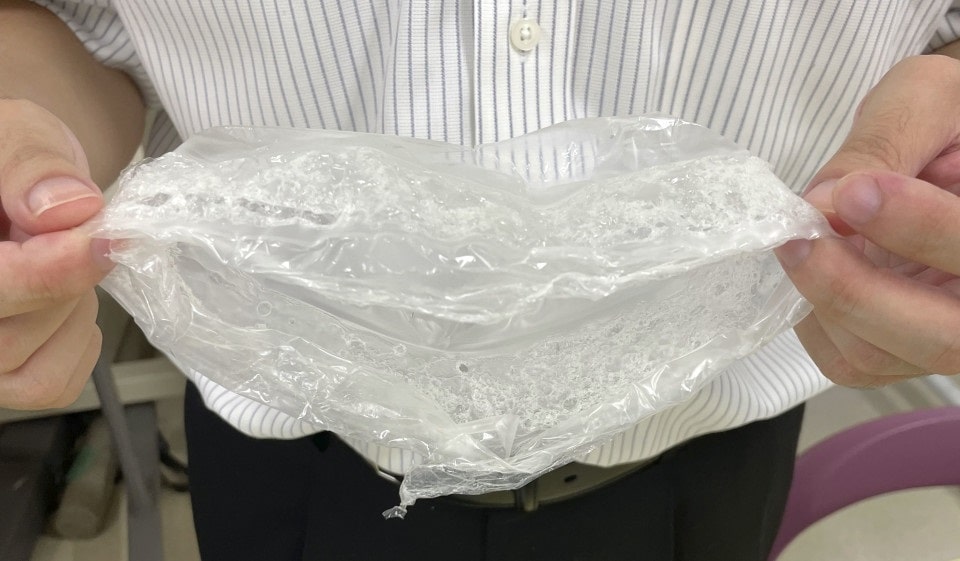
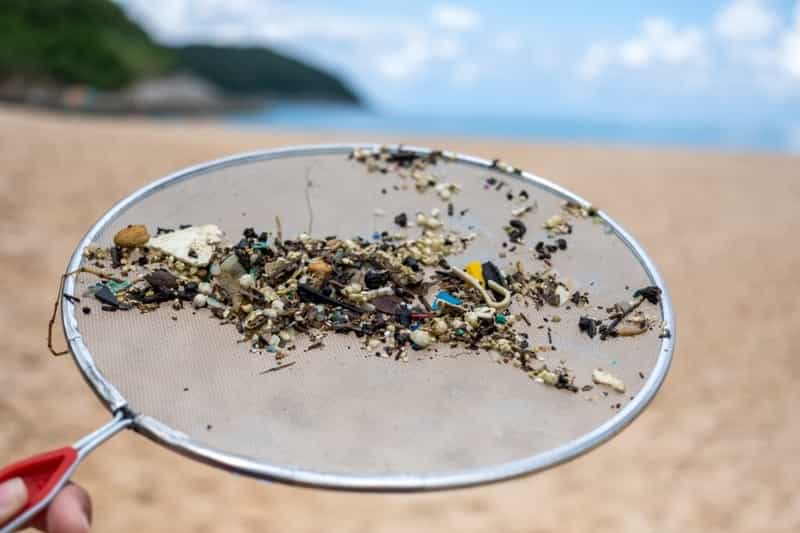
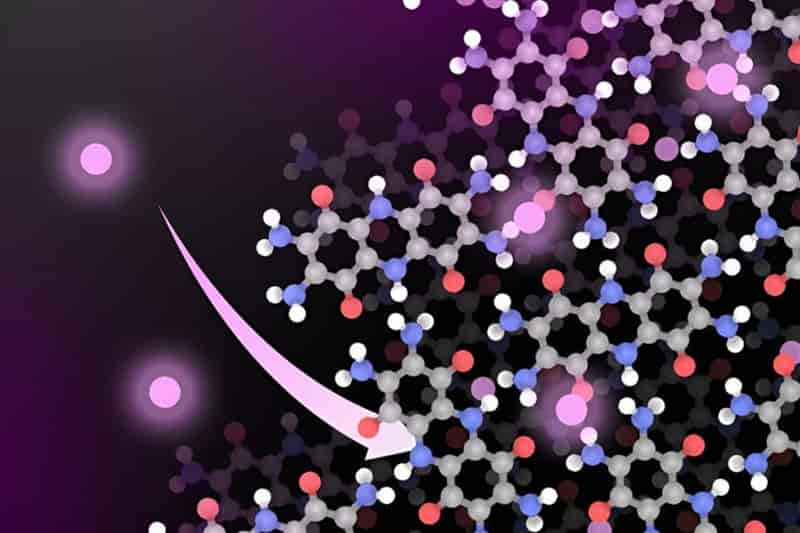
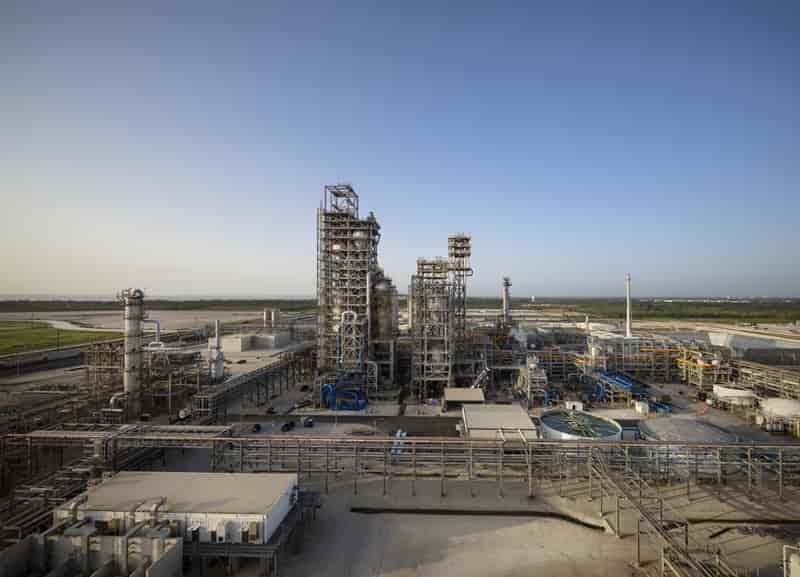
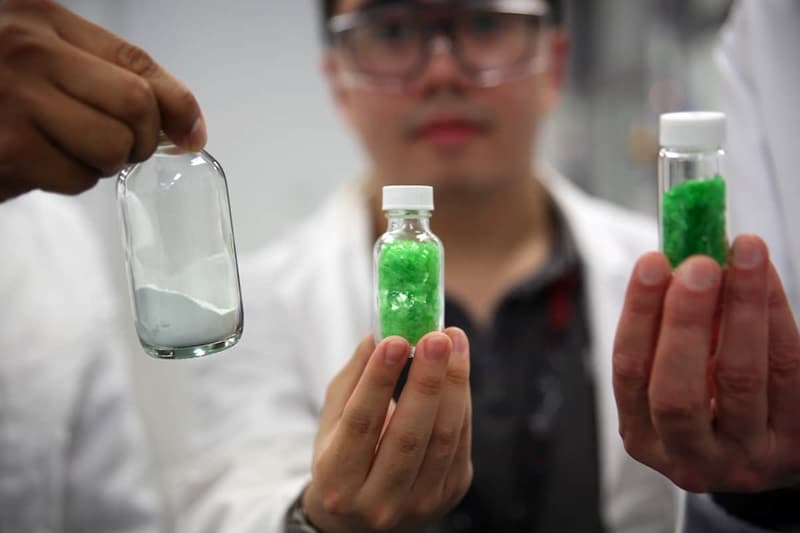
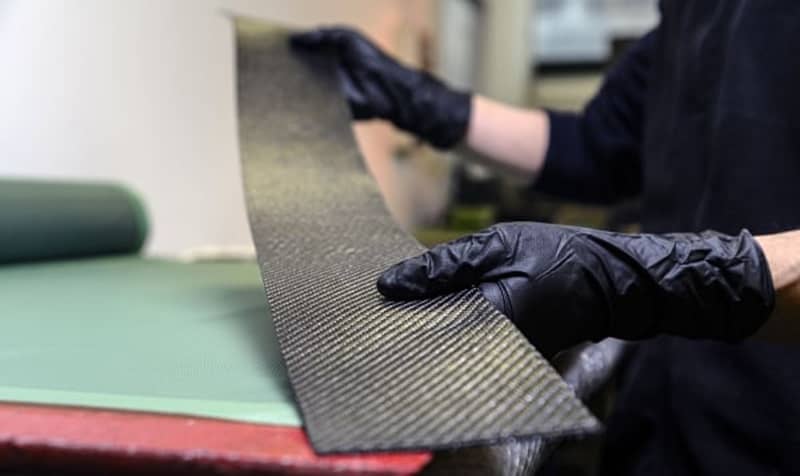
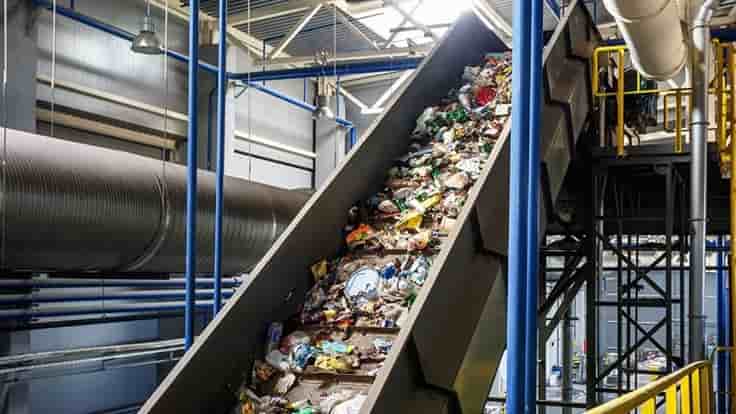
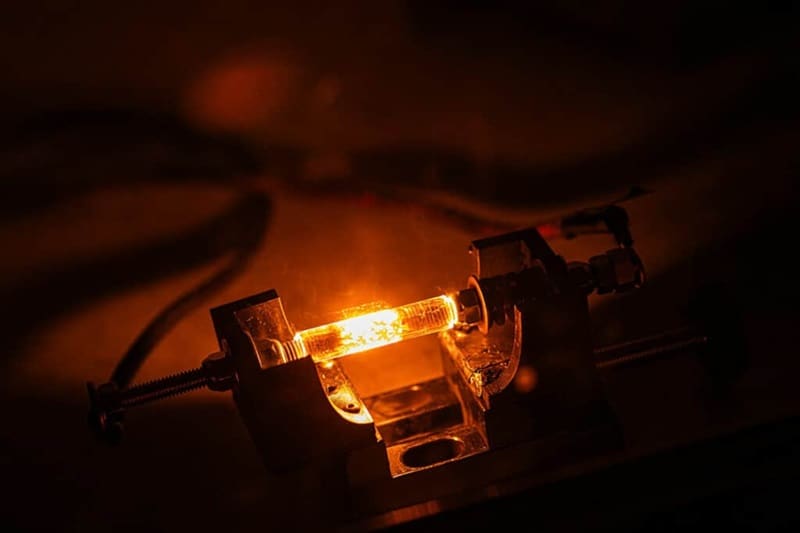
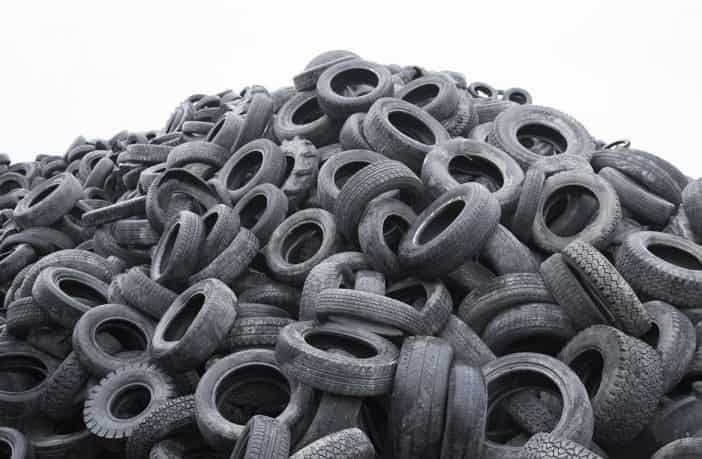
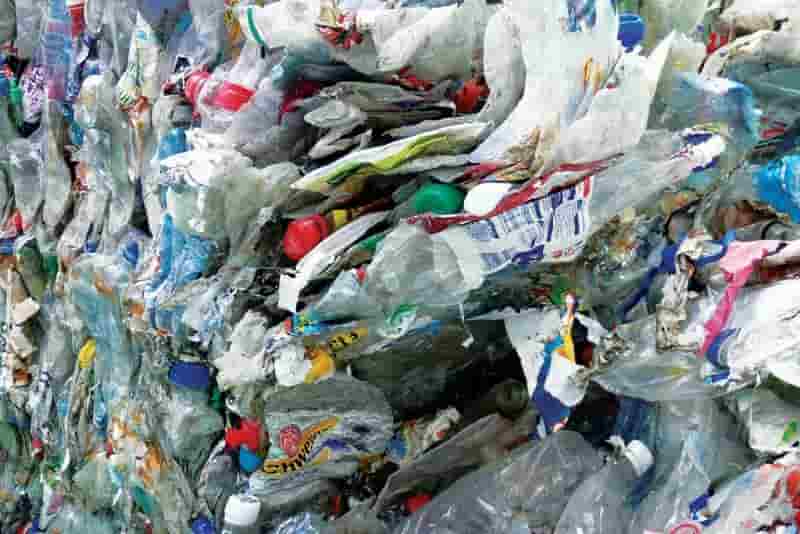
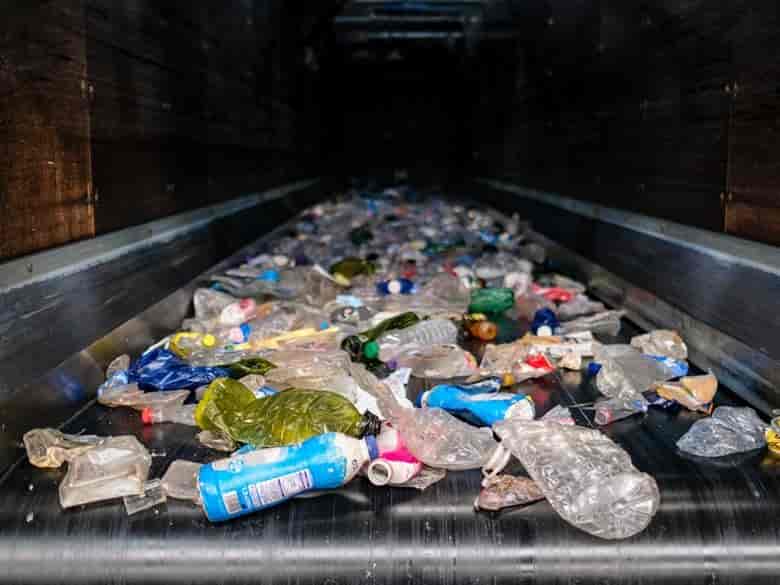
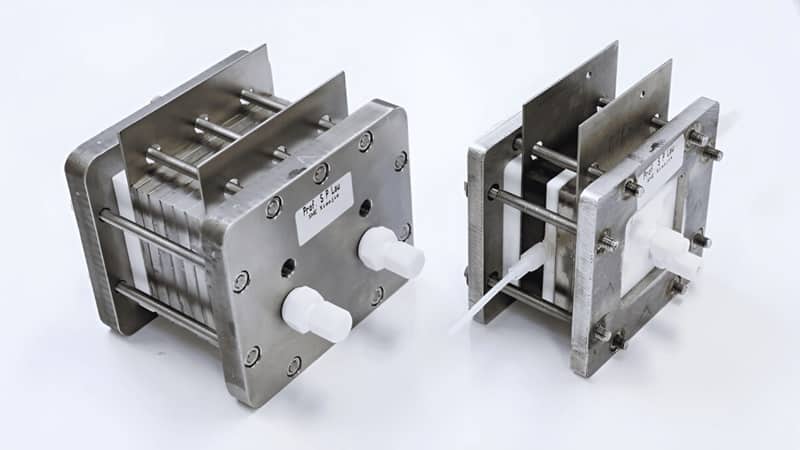
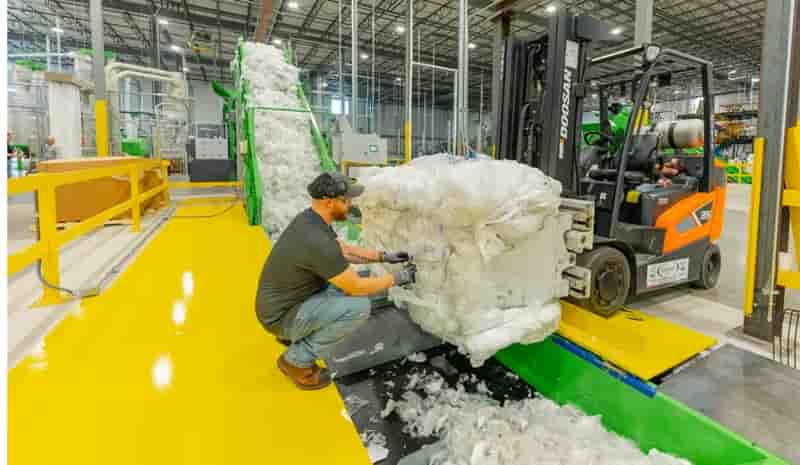
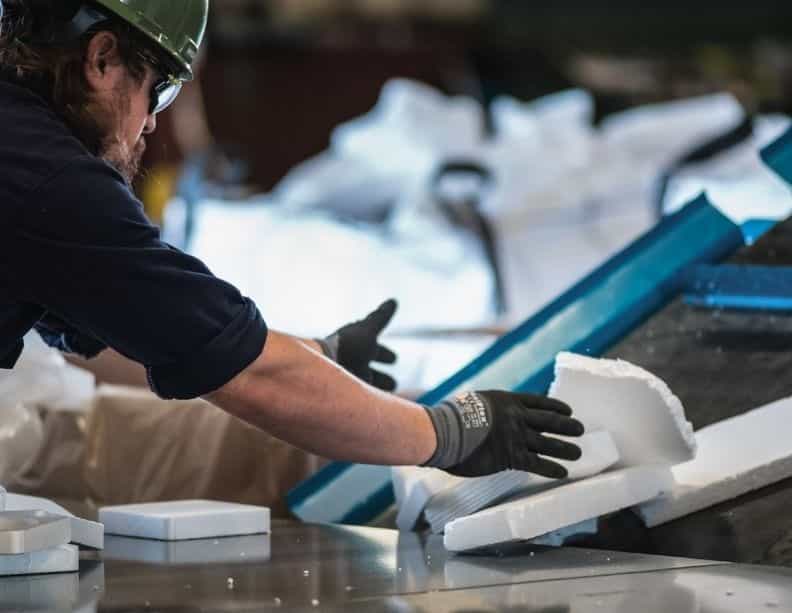
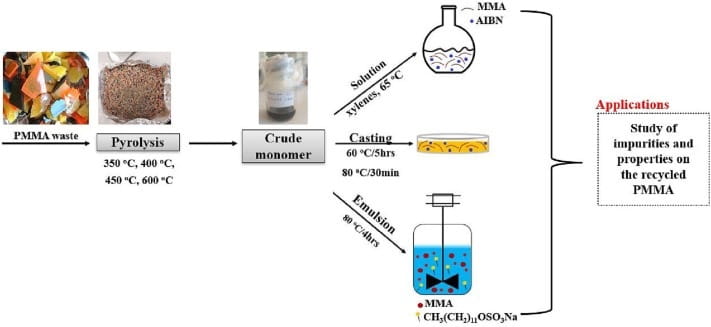
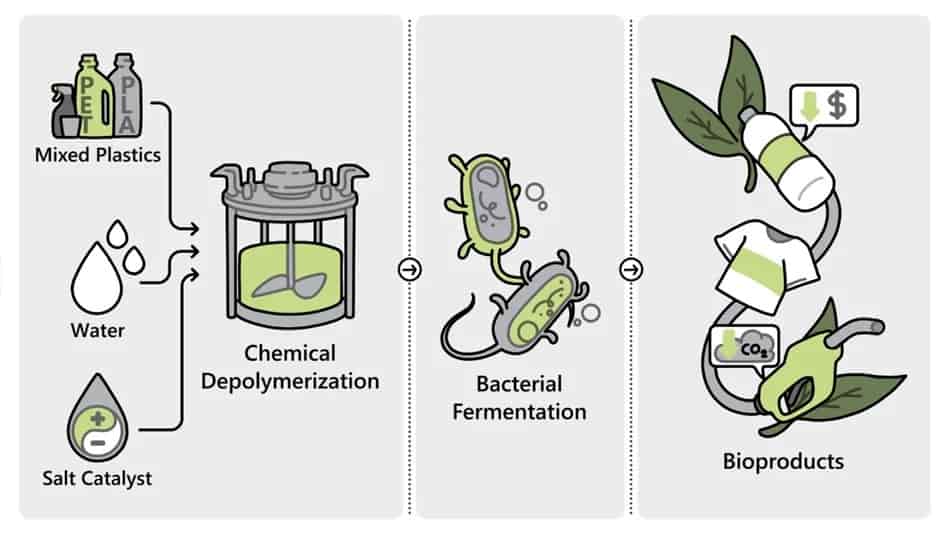
Rapid flash joule heating (FJH) of waste plastics produces large quantities of hydrogen gas and high-purity graphene, researchers at Rice University in Houston, Texas, have found, a method that could turn the nascent hydrogen industry on its head if proved to be scalable.
FJH discharges current through a carbon-based product to increase the temperature up to 3,000C within a tenth of a second. The sudden heating reorganizes the product’s chemical bond, converting the carbon-carbon bonds to graphene and releasing the hydrogen.
“We just bore a hole in one of the electrodes and the hydrogen comes spurting out,” says James Tour, Professor of Chemistry, Computer Science, Materials Science, and NanoEngineering at Rice University, founder of 14 companies, and author of over 785 research publications. Hydrogen plastic waste
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) ‘Earth Shot’ hydrogen strategy aims to create an industry that can make one kilo of hydrogen for $1 within one decade.
“This method solves your 1-1-1 challenge. And we’re at much less than $1,” says Tour.
“You take plastic off the street, you form a material that allows you to use less building material, because you’re strengthening it with the graphene, and you get hydrogen as your byproduct. It’s a tremendous way to go.”
One Tour-founded company, Universal Matter, has headquarters in Canada, the United States, and Britain and is focused on producing graphene from the process.
The company aims to have a demonstration plant in Burlington, Ontario, by the end of 2023. Hydrogen plastic waste
Tough, flexible, and light
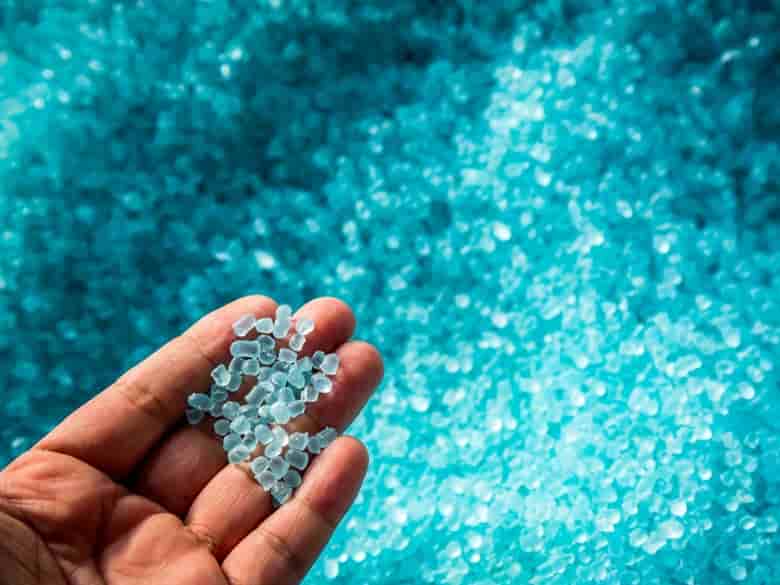
Turbostratic graphene, through the FJH process and without the use of solvents or reactive gases, can be produced from a broad range of carbon-based feedstock material, including recycled plastics, coke, and petroleum, as well as biomass and discarded food waste, Universal Matter says.
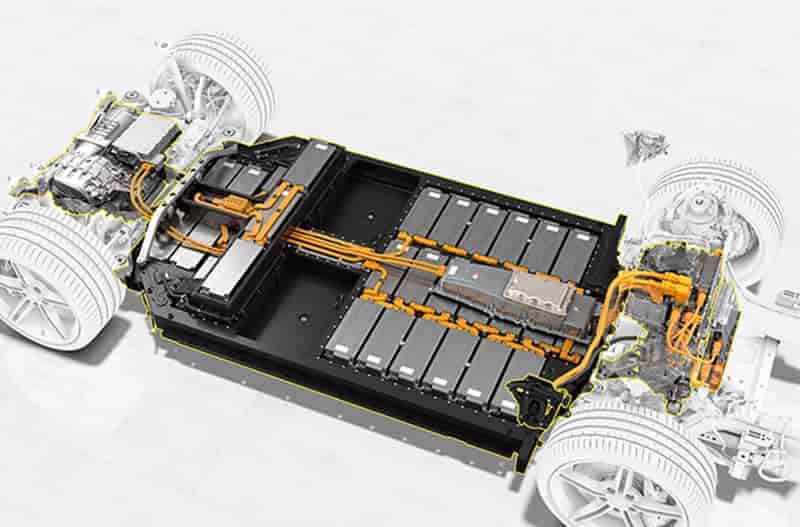
Graphene is a tough, flexible, light, nanomaterial with a high resistance. An individual sheet is 200 times stronger than an equally thin piece of steel, says Ford Motor Co., one of the only companies to use graphene at an industrial scale.
“The graphene is mixed with foam constituents, and tests done by Ford and suppliers have shown about a 17% reduction in noise, a 20% improvement in mechanical properties, and a 30% improvement in heat endurance properties, compared with that of the foam used without graphene,” the company said in a statement.
More…

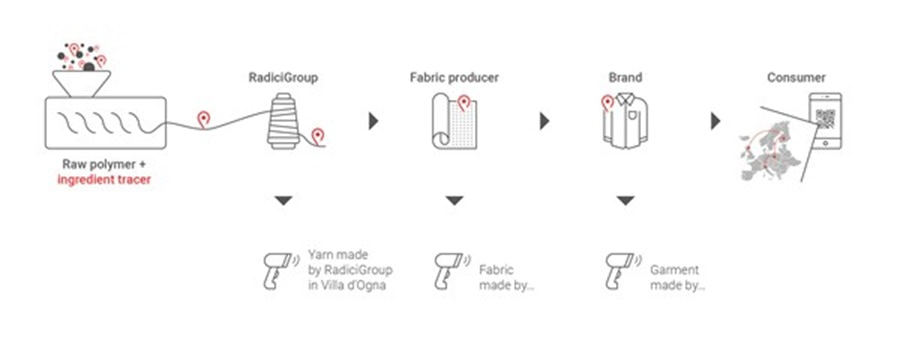
Carbios’ textile preparation line ‘closes loop’ on fibre-to-fibre recycling
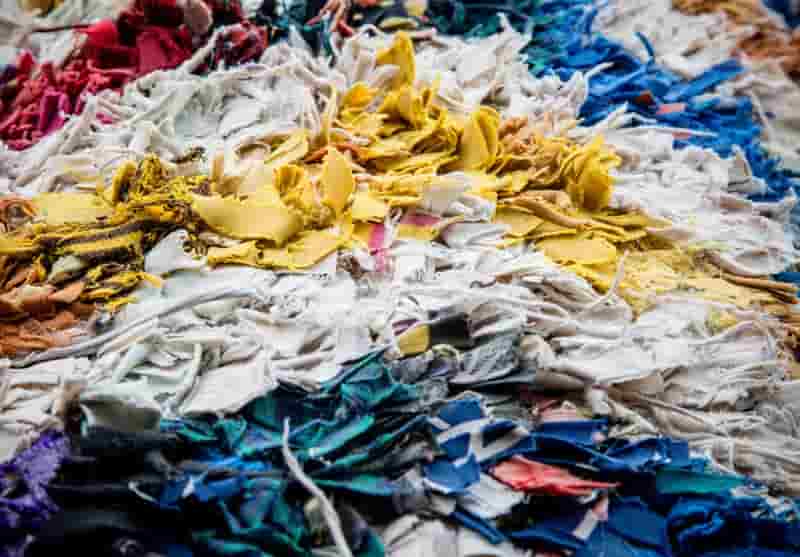
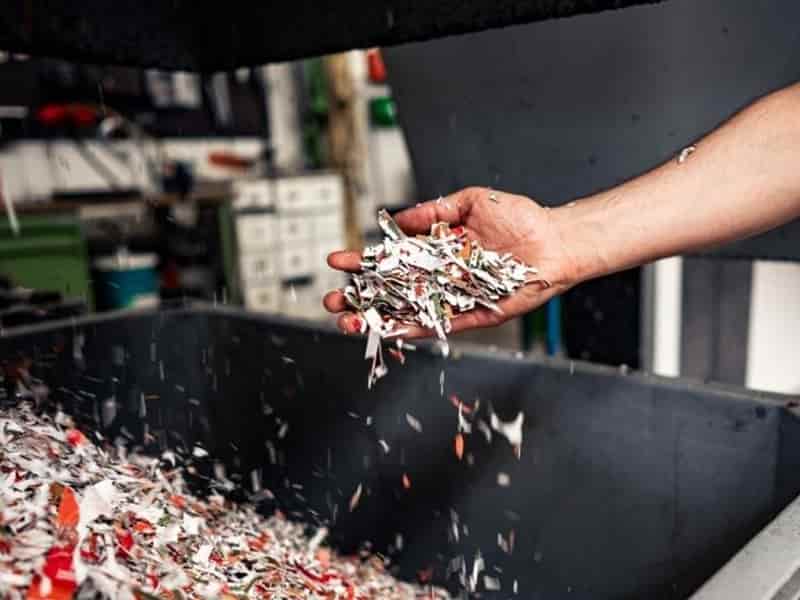
Biochemistry researcher, Carbios inaugurated its textile preparation line at its demonstration plant in France, to turn textile waste from used garments into raw materials suitable for enzymatic recycling.
Carbios’ textile preparation line aims to optimise the sorting and preparation of textiles, especially those with challenging components like zips and buttons, resulting in higher yields and accelerating bio-recycling in the industry. Hydrogen plastic waste
The biochemistry researcher has developed a highly selective enzyme capable of depolymerising polyester in textile material, which is a challenging task due to the complex nature of textiles.
Enzymatic recycling not only contributes to establishing a textile recycling chain but also promotes textile circularity and allows brands to reduce their reliance on virgin materials.
Key information about the textile preparation line:
- Textiles (used clothing or cutting scraps) are loaded onto the line, shredded, and have “hard points” (e.g., buttons, zips) removed, resulting in a material suitable for enzymatic recycling
- 300kg of textiles are processed per hour in a continuous process
- The patent was filed in 2023 Hydrogen plastic waste
According to Carbios, only 13% of textile waste is recycled globally, with a mere 1% undergoing “fibre-to-fibre” recycling. To address this pressing issue, the patented line streamlines the entire preparation process, encompassing shredding and the extraction of hard points such as buttons or fasteners.
This follows the announcement that starting from 1 January 2025, separate collection of textile waste will be mandatory in Europe, with the European Union targeting a minimum content of recycled fibres in textiles by 2030.
At the inauguration of the line, which took place in Clermont-Ferrand, France, Roland Lescure, French Minister for Industry explained that only 13% of textile waste is currently recycled worldwide, with the majority ending up in landfills or incineration.
He said: “Carbios is contributing to the creation of a French recycling industry and providing a solution – cutting-edge and made in France – to what was until now a real obstacle to textile recycling.” Hydrogen plastic waste
More…

Recycling in the car, but in a closed-loop
Beverage producers worried about competition on regenerated materials that could be triggered by the new regulation on end-of-life vehicles.
In July, the European Commission announced measures to encourage the recyclability and end-of-life recycling of motor vehicles, through a new Regulation intended to replace and unify the current Directives 2000/53/EC and 2005/64/EC.
Among the measures proposed by Brussels is the obligation to use recycled plastic in new cars, starting from 2030, for 25% of the total used, of which 25% comes from end-of-life vehicles, therefore in a sort of closed circuit. Hydrogen plastic waste
However, four organizations representing drinks producers, recycling and environmentalism – Natural Mineral Waters Europe (NMWE), The Reloop Platform, Unesda Soft Drinks Europe and Zero Waste Europe – are wondering where 75% of non-recycled material will come from of automotive origin and what impact it will have on the availability of recycled material for other uses, in this case packaging.
“The experience of recent years suggests that part of the recycled content used to achieve the new objective will come from other sources, including quality ones, such as materials approved for contact with food, therefore with an unwanted downcycling – we read in the signed document by the four organizations -. A further negative effect could arise from the automotive industry’s use of recycled material which would have the potential for continuous recycling in applications that are no longer recyclable, breaking the closed-loop in other sectors.” Hydrogen plastic waste
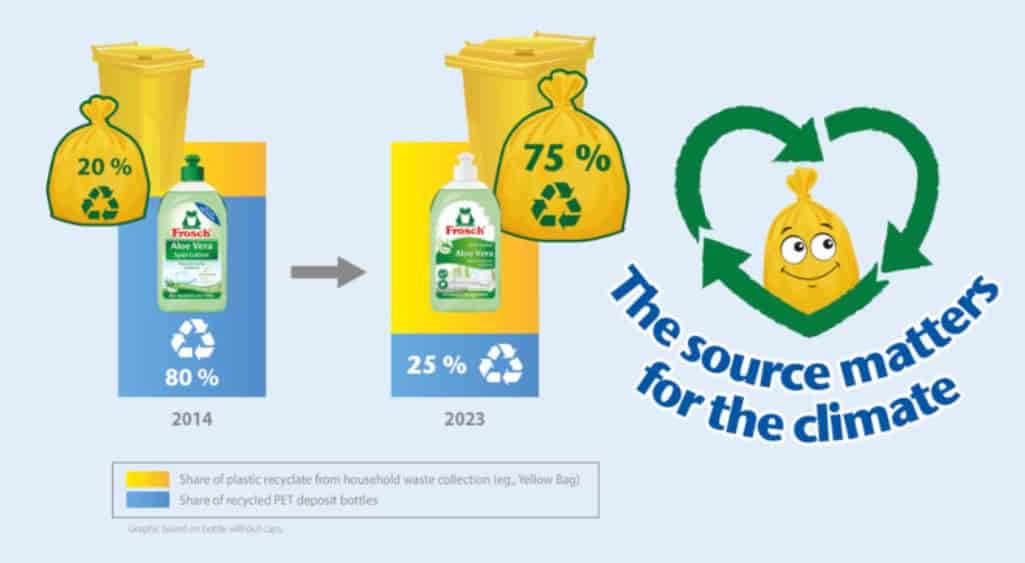
The signatories fear that it could create competition on recycled materials, which could jeopardize the ability of other sectors to meet their recycled content obligations imposed by Brussels, as in the case of PET bottles.
“Thanks to the supply chain’s sustained investments in Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) and Deposit Responsibility (DRS) systems – the note continues -, PET beverage bottles boast a fairly high collection and recycling rate. They provide recycled materials of high quality for food use which can then be reused to produce new beverage bottles in a ‘closed loop’, bottle to bottle.” “However, PET bottle recycling is often diverted from other sectors to lower-quality, no-longer-recyclable applications. A downcycling that jeopardizes the ability of drinks manufacturers to meet their obligations under the Single-Use Plastics Directive ( SUP) – 25% recycling by 2025 and 30% in 2030 – and the ambitions of the upcoming Regulation on Packaging and Packaging Waste”. Hydrogen plastic waste
The signatories suggest, to prevent these problems, to focus, in the formulation of the regulation on end-of-life vehicles, on closed-loop recycled content objectives, taking into account technical feasibility and foreseeing their gradual revision and expansion over time.
Furthermore, the use of recycled material should be discouraged where this material can be recovered in a closed cycle from other sectors. Finally, the EU Commission proposal should support the principle of ensuring priority access to its own raw materials for recycling in every sector subject to mandatory recycled content targets. In other words, Downcycling should only be allowed when closed-loop recycling is not technically feasible or environmentally desirable. Hydrogen plastic waste

Plastic Recycling Inc. is now processing post-consumer curbside PP, with an eye toward obtaining an FDA food-contact letter in the near future.
The Indianapolis-based plastics reclaimer is initially sorting and washing about 25 million pounds of PP per year on the system, said Brandon Shaw, marketing manager for Plastic Recycling Inc. (PRI), but the system is modular and can be scaled up easily.
The line, which processes PP bales from materials recovery facilities (MRFs), includes a trommel, metal removal technology, shredding, optical sorting, wet grinding, washing and rinsing steps, float-sink separation, drying and color sorting.
The company is also looking to add sorting robots to produce a stream of PP scrap consisting entirely of food and drink packaging. Hydrogen plastic waste
PRI has invested millions of dollars in recent years to boost its production capabilities, including by building-out a $3 million lab.
With the investments, including two new extruders that added 60 million pounds of annual capacity, PRI now has the capacity to produce 160 million pounds of recycled plastic, Shaw said.
In terms of post-consumer PP, specifically, the reclaimer can produce about 45 million pounds a year, said Marco Meloni, chief operating officer at PRI.
“We are able now to really respond to all the requests of the market in terms of recycled content, PCR content and virgin plus recycled products,” Meloni said. “So we are able now to give a very wide range of products to the market.” Hydrogen plastic waste
Commercial-scale production starts
Located at PRI’s 550,000-square-foot compounding facility in Indianapolis, the new PP line is currently running. (PRI also has a 120,000-square-foot scrap processing plant in Indianapolis, as well as facilities in Tennessee and South Carolina.)
Shaw estimated the line cost about $2 million, not counting roughly $1 million worth of equipment already owned by PRI.
PRI has been buying bales for the last three months, with commercial production starting in August. “We’re working with all the big MRFs,” he said. Hydrogen plastic waste
So far, PRI hasn’t had any trouble sourcing enough PP feedstock, Shaw said, noting that relatively few reclaimers are recycling curbside PP bales, with the market dominated by KW Plastics.
Prices for PP have been low lately, with post-consumer scrap averaging only about 5 cents per pound nationally, according to RecyclingMarkets.net. Throughout 2022, a year that included some high PCR pricing, bales averaged nearly 20 cents per pound, and during the first half of this year, they averaged 7.5 cents per pound.
Virgin pricing has also been low. Citing marketing conditions, plastics producer Braskem recently decided to reduce PP production levels at a plant in Pennsylvania, according to Plastics News. Hydrogen plastic waste
Shaw acknowledged that there is a “tough market right now economically, but we are playing the long game and using the lab upgrade to create real compounds with the ability to create colors.”
PRI has invested substantially in its lab, which is expected to employ a staff of 17 people conducting testing on raw materials and finished goods, as well as R&D, Meloni said.
More…

Avient India’s specialty material solutions
Polymer materials for sustainability in packaging and tech verticals
Avient Corporation, a global manufacturer of specialized polymer materials, addresses the demand of the rapidly changing market with the development of new specialty materials. The company produces thermoplastic compounds, plastic colorants and additives, thermoplastic resins, vinyl resins, thermoplastic composites, and specialty thermoset composite materials. Hydrogen plastic waste
As mentioned in Dominique Huret’s article on beverage developments shown at Interpack in this issue, Avient has also been part of the newly developed, Cerac Milky Monsters, a playful small format bottle suitable for children shown in Dusseldorf. She writes, “The preforms come from SGT and were developed in partnership with Avient – a coloring specialist. They are a single-layer dairy preform with a very low mineral content (less than 4%).
“Intended especially for the dairy products market, these preforms incorporate a new Avient additive technology called ColorMatrix Lactra Four One Zero which offers superior whiteness to the bottle and high protection for photosensitive liquids, blocking light up to 99.9%, even with a low wall thickness of 200 microns.” Hydrogen plastic waste
Speaking about the company’s activity in India, Vikas Vij, managing director of Avient India, said, “We are born of the collective power of two leading innovators — PolyOne and Clariant Masterbatch. The Avient name was derived from the combination of l’avenir – which means the future, vie – which means life, and -ent – a suffix that means to perform, and which can also be heard in the words environment and invent. Our corporate brand position is Challenge Accepted, and we work every day to live and fulfill that promise to all of our stakeholders.”
In September 2022, Avient welcomed more than 1,000 new associates to its new Avient Protective Materials business, further expanding its growing composites portfolio with the globally admired brand of Dyneema, claimed to be the ‘world’s strongest fiber.’
“We have created a next-level specialty material solutions company that addresses the demands of the rapidly changing world that lies before us. We are cutting a new path in the development of specialty materials, one where our distinctive problem-solving passion can have the deepest impact and enable us to conquer the challenges of the future we all share.” Hydrogen plastic waste
Industrial and tech verticals
Apart from polymer materials, Avient provides technologies that improve the recyclability of products, thus enabling a more circular economy. There are lightweight solutions that replace heavier traditional materials such as metal, glass, and wood, which can improve fuel efficiency in all modes of transportation and reduce carbon footprint. Then come sustainable infrastructure solutions that increase energy efficiency, renewable energy, natural resource conservation, and fiber optic / 5G network accessibility.
In the last quarter of 2023, Avient will launch new technologies in the automotive, E&E, and packaging sectors. These will be showcased at the Fakuma show in Germany from 17-21 October 2023 in Hall B5, Stand 5316. Hydrogen plastic waste
The impact, resilience, and growth of responsible packaging in a wide region are daily chronicled by Packaging South Asia.
A multi-channel B2B publication and digital platform such as Packaging South Asia is always aware of the prospect of new beginnings and renewal. Its 16-year-old print monthly, based in New Delhi, India has demonstrated its commitment to progress and growth. The Indian and Asian packaging industries have shown resilience in the face of ongoing challenges over the past three years. Hydrogen plastic waste
As we present our publishing plan for 2023, India’s real GDP growth for the financial year ending 31 March 2023 will reach 6.3%. Packaging industry growth has exceeded GDP growth even when allowing for inflation in the past three years.
The capacity for flexible film manufacturing in India increased by 33% over the past three years. With orders in place, we expect another 33% capacity addition from 2023 to 2025. Capacities in monocartons, corrugation, aseptic liquid packaging, and labels have grown similarly. The numbers are positive for most of the economies in the region – our platform increasingly reaches and influences these.
Even given the disruptions of supply chains, raw material prices, and the challenge of responsible and sustainable packaging, packaging in all its creative forms and purposes has significant headroom to grow in India and Asia. Our context and coverage engulf the entire packaging supply chain – from concept to shelf and further – to waste collection and recycling. We target brand owners, product managers, raw material suppliers, packaging designers and converters, and recyclers. Hydrogen plastic waste
More…

Taiwan encourages companies to invest in Lithuania to deepen bilateral cooperation
Lithuania has solid research capabilities and innovation while Taiwan has commercialisation capabilities and experiences in developing international markets, a Taiwanese official told Euractiv, adding that they would be glad to provide various kinds of facilitation to deepen this cooperation.
The comment comes after Taiwan’s Naonal Science and Technology Council and the Lithuanian Research Council signed a memorandum of understanding on September 22 to strengthen research and development cooperation in lasers, biotechnology, semiconductors, and other areas. Hydrogen plastic waste
“Lithuania has solid research capabilities and innovation, while Taiwan has commercialisation capabilities and experiences in developing international markets, which will be an essential model for broadening Taiwan-Lithuania economic cooperation,” Alex Liao, director of the Economic Division on behalf of the Taiwanese Representative Office in Lithuania, told Euractiv.
According to Liao, both countries share the same development direction, as Lithuania has chosen biotechnology and laser as its strategic industries, while Taiwan’s strategic industries include biotechnology precision machinery and semiconductors.
“We encourage enterprises and research institutes between Taiwan and Lithuania to expand contacts and deepen exchanges, and we will be glad to provide various kinds of facilitation,” he said. Hydrogen plastic waste
Relations between both countries increased after Lithuania allowed Taiwan to open its de facto embassy under its own name, The Taiwanese Representative Office in Lithuania, rather than after its capital city – Taipei.
China heavily criticised the move, which accused Lithuania of violating the one-China principle, according to which Taiwan is an inalienable part of the country. This resulted in China removing Lithuania from its customs registry, blocking shipments, and pressuring international businesses to leave the Baltic country. Hydrogen plastic waste
More…

Accelerating Circularity working group to tackle textile chemical recycling ambiguity
Non-profit Accelerating Circularity, which focuses on textile-to-textile recycling has created the Alliance of Textile Chemical Recycling (ACTR) working group to give the textile industry a common voice and facilitate accurate information on textile chemical recycling.
The mission of Accelerating Circularity is to create new supply chains and business models to turn textile waste into mainstream raw materials and its new working group aims to share the benefits of chemical textile recycling. Hydrogen plastic waste
“We formed this collective to move chemical recycling technology forward, share common definitions, and address policies in a collaborative way to maximise the elimination of textile waste to landfills and incineration,” explained Karla Magruder, Founder and President of Accelerating Circularity. “Chemical recycling technology has many benefits, including quality more similar to virgin fibre and the ability to recycle multiple times.”
ACTR plans to provide the industry with information on how textile chemical recycling can:
- Offer solutions for diverting textile waste to landfill
- Enable textile to textile recycling versus incineration/landfill
- Provide sustainably sourced/circular materials
- Support brand/retailers/producers in achieving their CO2 reduction targets
- Provide long term price stability and consistent supply of raw materials versus virgin. Hydrogen plastic waste
More…

Graphene plastic recycling -Is graphene the silver bullet for plastic recycling woes? 04-10-2023
Hydrogen plastic waste